在本文中,我们不会解析MVP,MVVM,MVI或类似的东西。今天,我们将讨论的不仅仅是展示级别的体系结构,更全球化的事情。如何设计一个大型应用程序,使数十或数百名开发人员可以舒适地工作?无论我们编写了多少代码,都易于扩展的应用程序。
大型项目的要求:
- 弱代码连接。任何更改都应影响尽可能少的代码。
- 重用代码。相同的东西应该易于重用而无需复制粘贴。
- 易于扩展。开发人员向现有代码添加新功能应该很容易。
- 稳定性。使用功能切换可以轻松禁用任何新代码,尤其是在使用基于主干的开发时。
- 代码所有权。该项目应分为多个模块,以便为每个模块轻松分配所有者。这将有助于我们进行代码审查。这里不仅涉及诸如Gradle / Pods模块之类的大型事物,还涉及可能具有不同所有者的普通功能。
零件

. - (MV*) Presenter/ViewModel/Interactor/- . , - - . , , , // . , -, .
, . .

- . - .
- . .
- . .
- . , , .
- UI. .
- Unidirectional data flow . .
- . feature toggles.
, , , . , - .
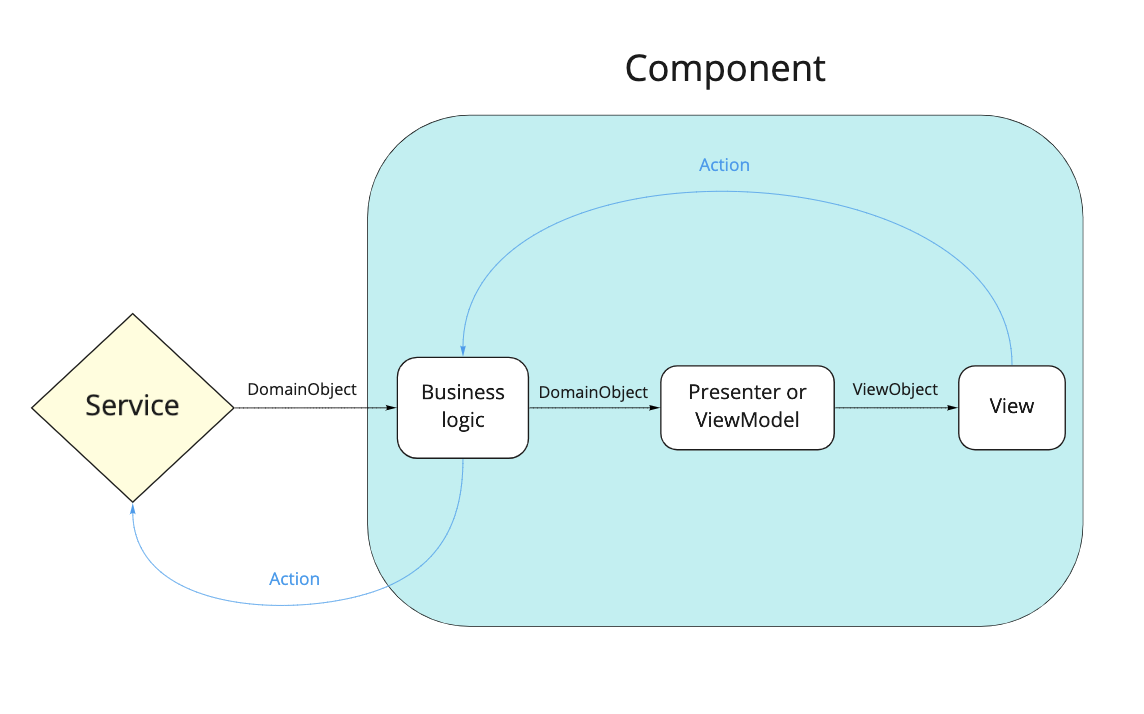
- (DomainObject).
- (UI State).
- .
- - ( , ), (Action) , . UI State, (Action) , Service. Service (. 1).
, , (Actions) (Service). Service (DomainObjects) . Service - : UserService, PaymentsService, CartService, : ProductDetailsService, OrderService.

, , MVP/MVC/MVVM/MVI , ().
— , , , , .
:
- Middleware — (Actions). , Middleware . .
- Reducer — Middleware. .
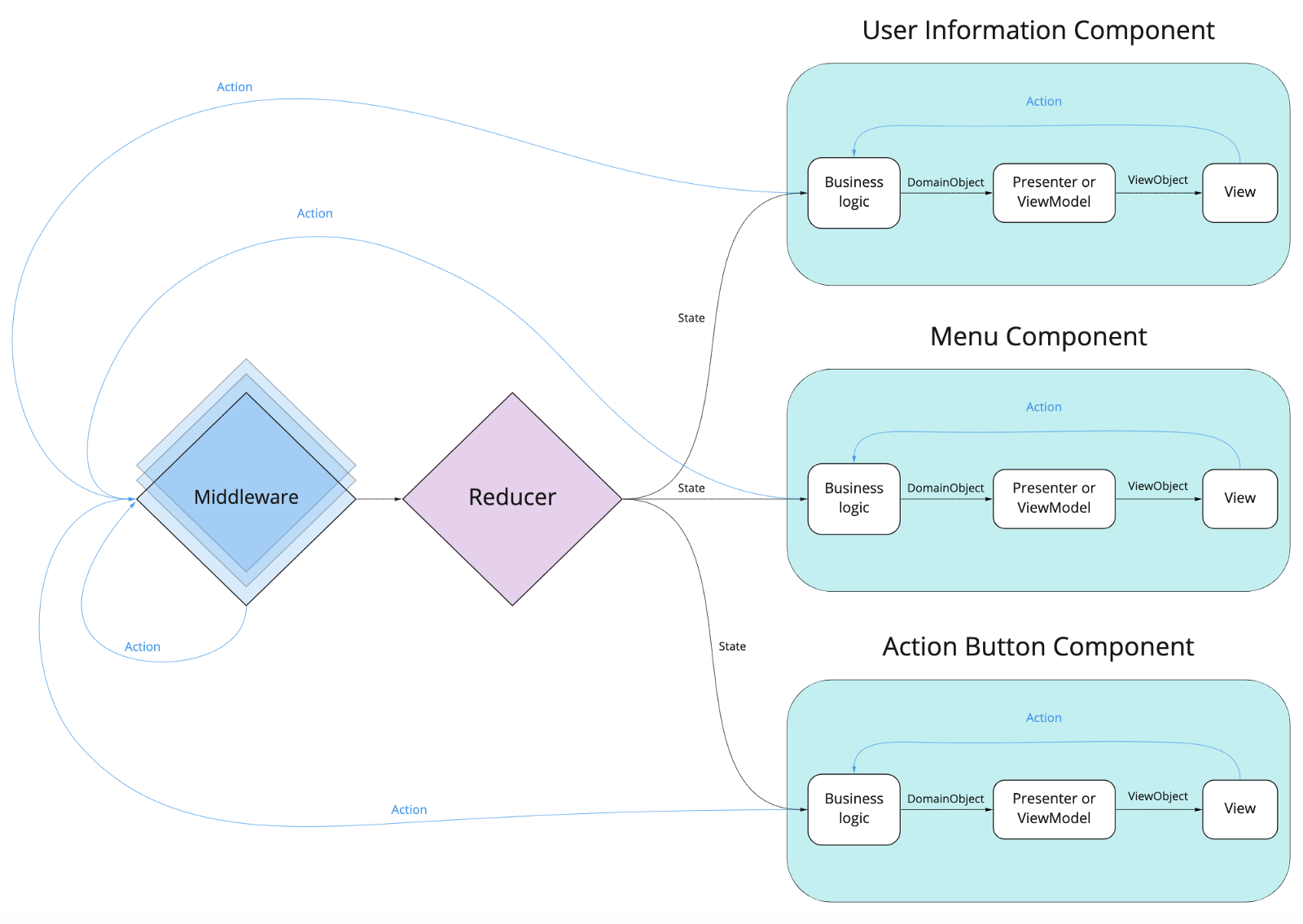
, Middleware Reducer , Middleware Reducer.
: Flux, Redux, MVI
Server Drive UI
, (DomainObject), . Play Store/App Store. , !
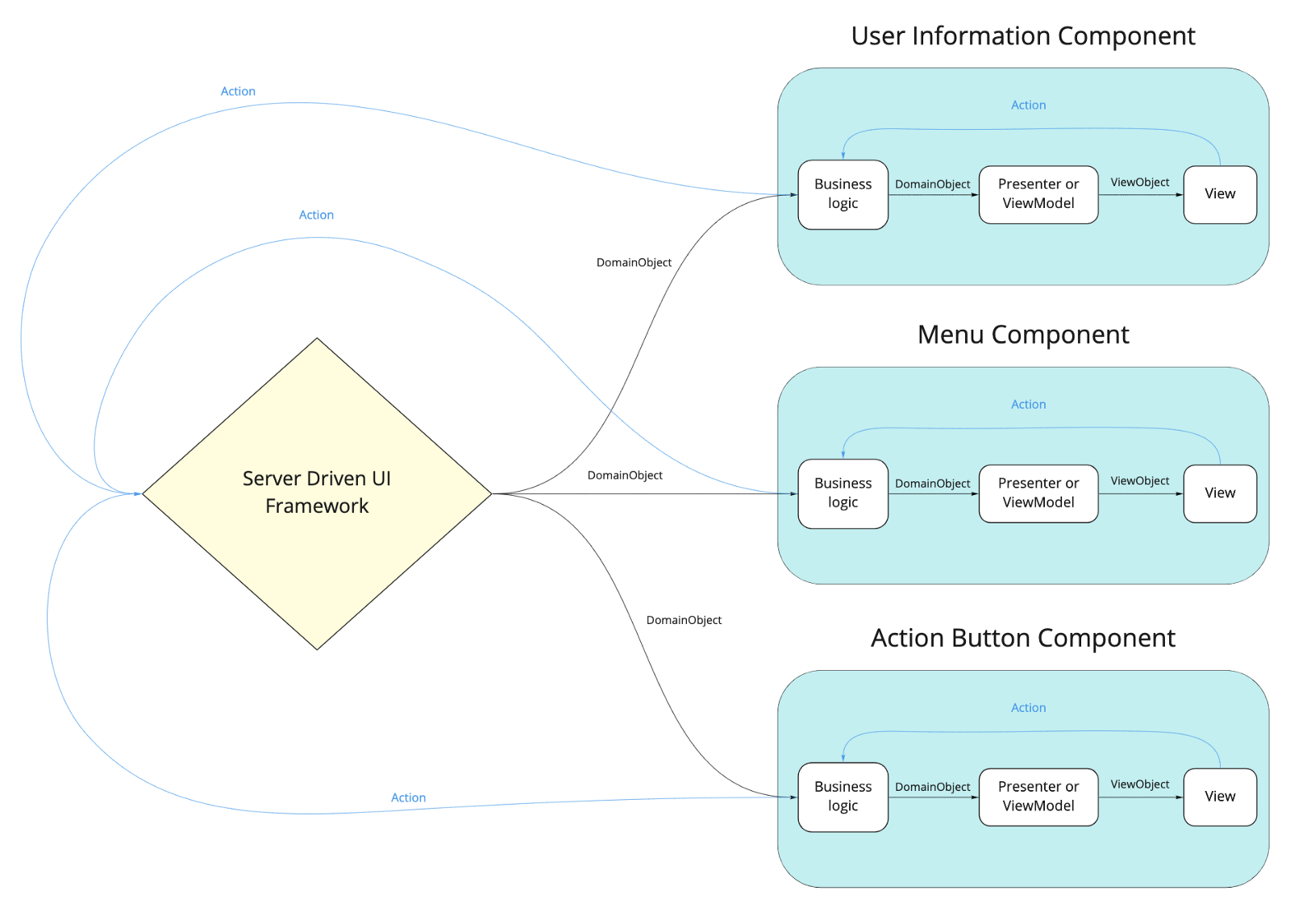
从服务器,我们可以在屏幕上接收组件列表,指示它们的类型,在屏幕上的位置,版本以及操作和显示所需的数据。
{
"components": [
{
"type": "toolbar",
"version": 3,
"position": "header",
"data": {
"title": "Profile",
"showUpArrow": true
}
},
{
"type": "user_info",
"version": 1,
"position": "header",
"data": {
"id": 1234,
"first_name": "Alexey",
"last_name": "Glukharev"
}
},
{
"type": "user_photo",
"position": "header",
"version": 2,
"data": {
"user_photo": "https://image_url.png"
}
},
{
"type": "menu_item",
"version": 1,
"position": "content",
"data": {
"text": "open user details",
"deeplink": "app://user/detail/1234"
}
},
{
"type": "menu_item",
"version": 1,
"position": "content",
"data": {
"text": "contact us",
"deeplink": "app://contact_us"
}
},
{
"type": "button",
"version": 1,
"position": "bottom",
"data": {
"text": "log out",
"action": "log_out"
}
}
]
}
有什么问题吗
我参与了使用该架构的多个大型项目的开发,并且对一般架构问题和Android实现的技术细节都很开放。