你好!
在本文中,我将简要讨论SQL(DML)语句的批处理:INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE,这是实现提高性能的一种方法。
好处
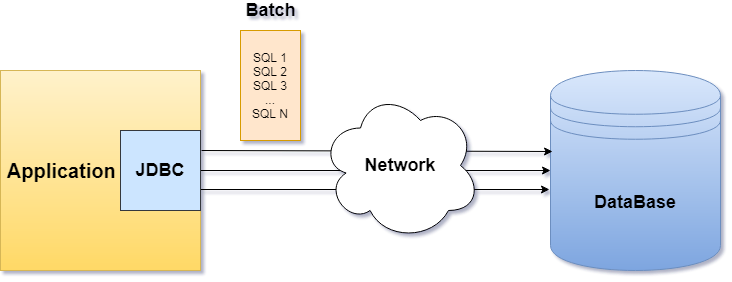
与每个SQL查询的顺序执行不同,批处理使在一个调用中发送整套查询(数据包)成为可能,从而减少了所需的网络连接数量,并允许数据库并行执行一定数量的查询,这可以显着提高执行速度。立即进行保留,以便在向数据库表中插入,更新或删除大量数据时可以看到明显的效果。
数据库表
例如,我们将使用带有id和title字段的book表。
1. JDBC-批处理
在继续执行示例之前,有必要重点强调以下几点:
- JDBC , supportsBatchUpdates() DatabaseMetaData, , . true, .
- , setAutoCommit(false). , commit() rollback(). rollback() SQL .
- — , JDBC Statement, PreparedStatement CallableStatement, .
, Statement, PreparedStatement CallableStatement . , BATCH_SIZE. , . , , Hibernate 10 50.
, SQL INSERT. UPDATE, DELETE .
1.1. Statement
Statement book.
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
try (Statement stmt = connection.createStatement()) {
for (int i = 1; i <= SIZE; i++) {
stmt.addBatch("INSERT INTO book (title) VALUES ('" + "JDBC Insert Example: " + i + "')");
if (i % BATCH_SIZE == 0 || i == SIZE) {
try {
int[] result = stmt.executeBatch();
connection.commit();
} catch (BatchUpdateException ex) {
Log(ex);
connection.rollback();
}
}
}
}
:- C Statement;
- C void addBatch( String SQL );
- executeBatch(). executeBatch() .
Statement SQL INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE.
SQL , .
1.2. PreparedStatement
PreparedStatement book.
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
try (PreparedStatement pstmt = connection.prepareStatement("INSERT INTO book (title) VALUES (?)")) {
for (int i = 1; i <= SIZE; i++) {
pstmt.setString(1, "JDBC Insert Example: " + i);
pstmt.addBatch();
if (i % BATCH_SIZE == 0 || i == SIZE) {
try {
int[] result = pstmt.executeBatch();
connection.commit();
} catch (BatchUpdateException ex) {
Log(ex);
connection.rollback();
}
}
}
}
:- C PreparedStatement SQL ;
- , ;
- void addBatch();
- executeBatch().
3) 4) , Statement, — addBatch() .
SQL , , . , .
PreparedStatement SQL (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE) Statement, - .
1.3. CallableStatement
CallableStatement .
, OUT INOUT.
CallableStatement book.
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
try (CallableStatement cstmt = connection.prepareCall("call insert_book(?)")) {
for (int i = 1; i <= SIZE; i++) {
cstmt.setString(1, "JDBC Insert Example: " + i);
cstmt.addBatch();
if (i % BATCH_SIZE == 0 || i == SIZE) {
try {
int[] result = cstmt.executeBatch();
connection.commit();
} catch (BatchUpdateException ex) {
Log(ex);
connection.rollback();
}
}
}
}
:- C CallableStatement ;
- , ;
- void addBatch();
- executeBatch().
, PreparedStatement.
, , .
- , .
CallableStatement , - .
1.4. BatchUpdateException
BatchUpdateException, . BatchUpdateException , SQL , - , ResultSet. BatchUpdateException ( getUpdateCounts()), , executeBatch. , SQL . , c (Statement.EXECUTE_FAILED) .
:
...
} catch (BatchUpdateException ex) {
int[] updateCount = ex.getUpdateCounts();
int count = 1;
for (int i : updateCount) {
if (i == Statement.EXECUTE_FAILED) {
System.out.println("Request " + count + ": Execute failed");
} else {
System.out.println("Request " + count + ": OK");
}
count++;
}
}
...
. , , , , . BatchUpdateException SQL , . .
2. Hibernate —
2.1.
, , hibernate.jdbc.batch_size Hibernate.cfg.xml . Hibernate SQL INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE JDBC . SQL JDBC hibernate.order_inserts, hibernate.order_updates true, Hibernate SQL . SQL , JDBC Hibernate addBatch() PreparedStatement, SQL .
Hibernate.cfg.xml
...
<property name="hibernate.jdbc.batch_size">50</property>
<property name="hibernate.order_inserts">true</property>
<property name="hibernate.order_updates">true</property>
...
2.2.
. , . , Hibernate , OutOfMemoryException. 2 :
- flush() clear() .
:
try (Session session = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory().getCurrentSession()) {
Transaction transaction = session.getTransaction();
transaction.begin();
for (int i = 1; i <= SIZE; i++) {
session.persist(new Book("Hibernate Insert Example: " + i));
if (i % BATCH_SIZE == 0) {
session.flush();
session.clear();
}
}
transaction.commit();
}
- StatelessSession. StatelessSession . , , , (aliasing) . , Hibernate. Hibernate.
:
try (StatelessSession session = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory().openStatelessSession()) {
Transaction transaction = session.getTransaction();
transaction.begin();
for (int i = 1; i <= SIZE; i++) {
session.persist(new Book("Hibernate Insert Example: " + i));
}
transaction.commit();
}
SQL查询的批处理是提高性能的众所周知的方法之一,您应该注意这一点。减少与数据库的网络连接数量并提高查询执行速度是使用批处理的重要优势。
可以在GitHub上找到代码示例。