
在过去的几年中,用于自然语言处理的机器学习取得了显着的进步。模型离开了研究实验室,并成为领先的数字产品的基础。一个很好的例证就是最近宣布BERT模型已经成为Google搜索背后的主要组成部分。 Google认为,这一步骤(即在搜索引擎中引入一种理解自然语言的高级模型)代表着“过去五年中最大的突破,也是搜索引擎历史上最重要的突破之一”。
本文是使用BERT版本之一对句子进行分类的简单指南。我们研究的示例既简单又足以初次了解该模型,又足够先进以演示关键概念。
除了本文之外,还准备了可以在存储库中查看或在Colab中运行的笔记本电脑。
数据:SST2
在我们的示例中,我们将使用SST2数据集,其中包含来自电影评论的建议,每个建议都有正标签(值1)或负标签(值0):

型号:句子分类
– , ( , ) 1 ( ), 0 ( ). :

:
, , 768. , .
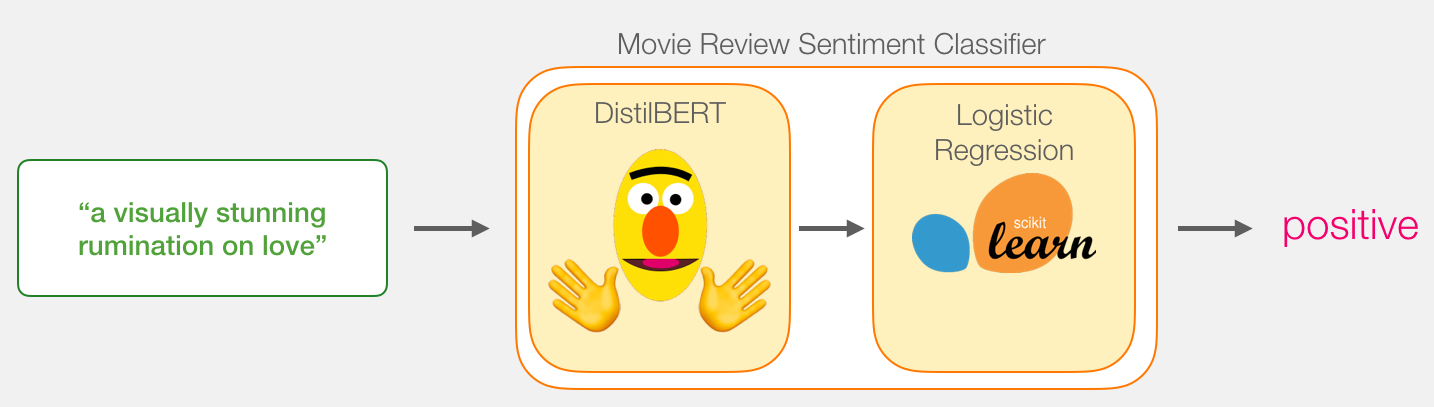
, BERT, ELMO ( NLP ): ( [CLS]).
, , . DistilBERT', . , , «» BERT', . , , BERT , [CLS] . , , . , , BERT .
transformers DistilBERT', .
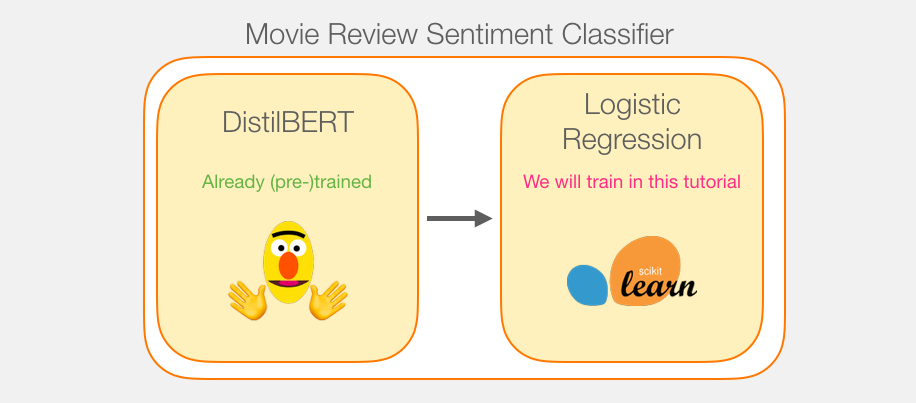
, . DistilBERT' 2 .

DistilBERT'. Scikit Learn. , , :
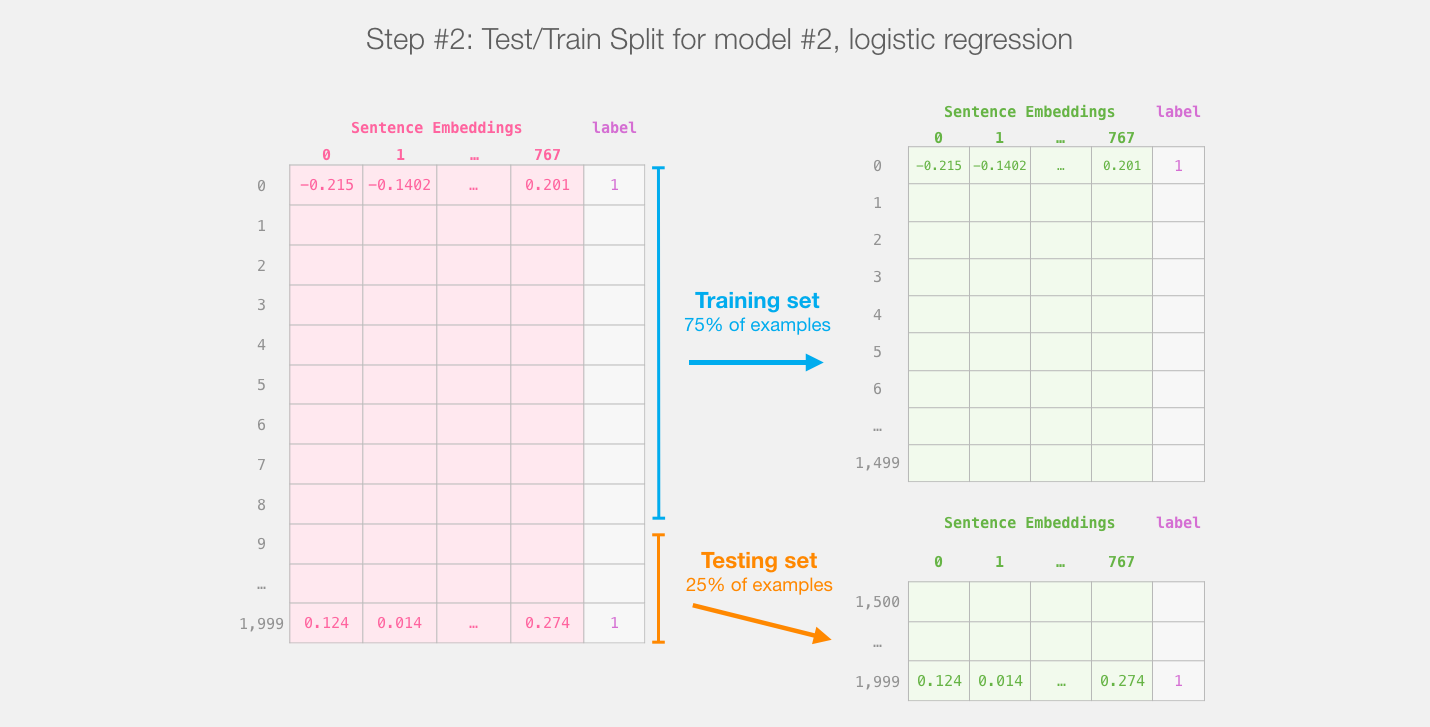
distilBERT' ( #1) , ( #2). , sklearn , , 75% ,
:

, , , .
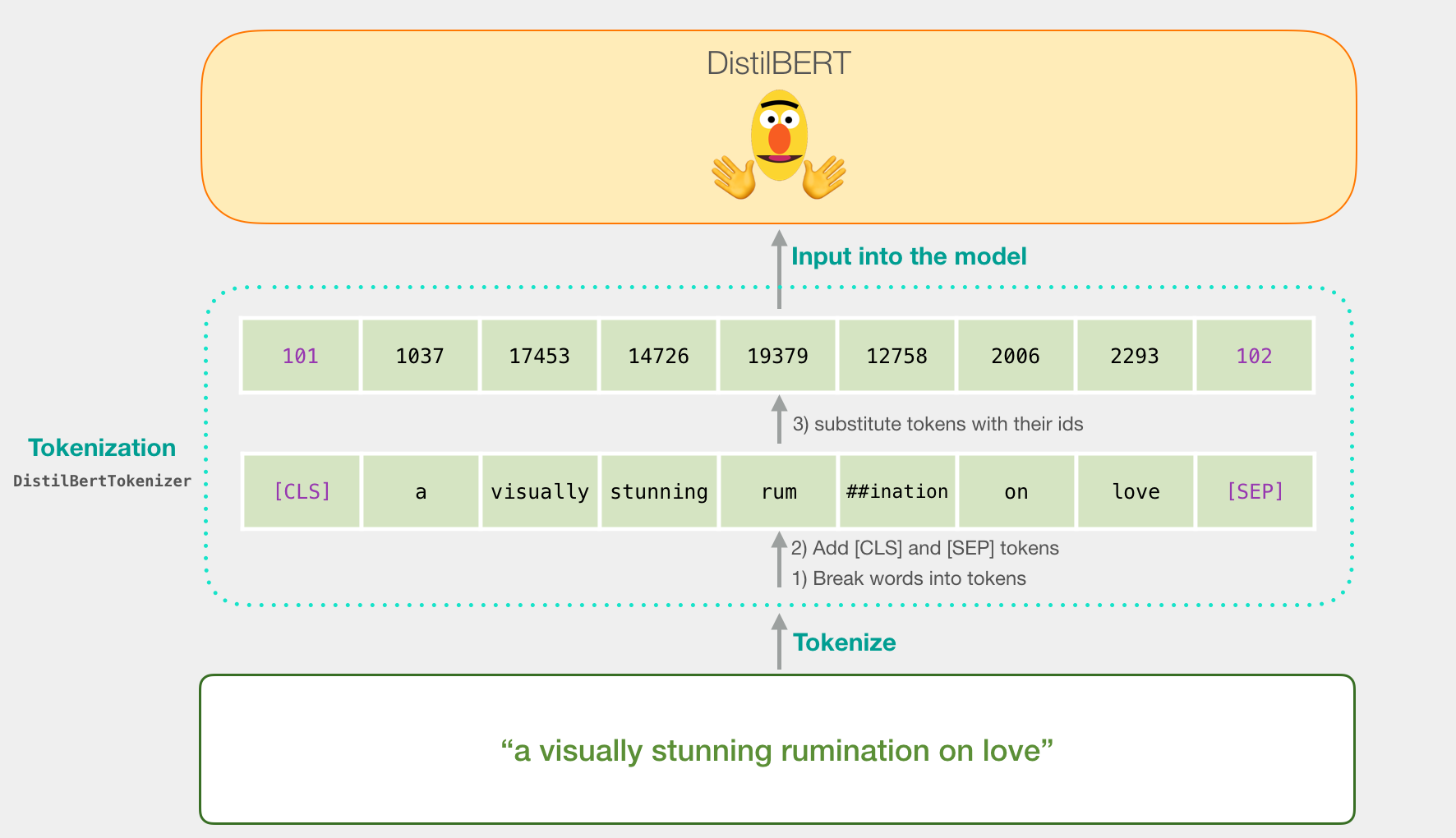
«a visually stunning rumination on love». BERT' , . , ( [CLS] [SEP] ).
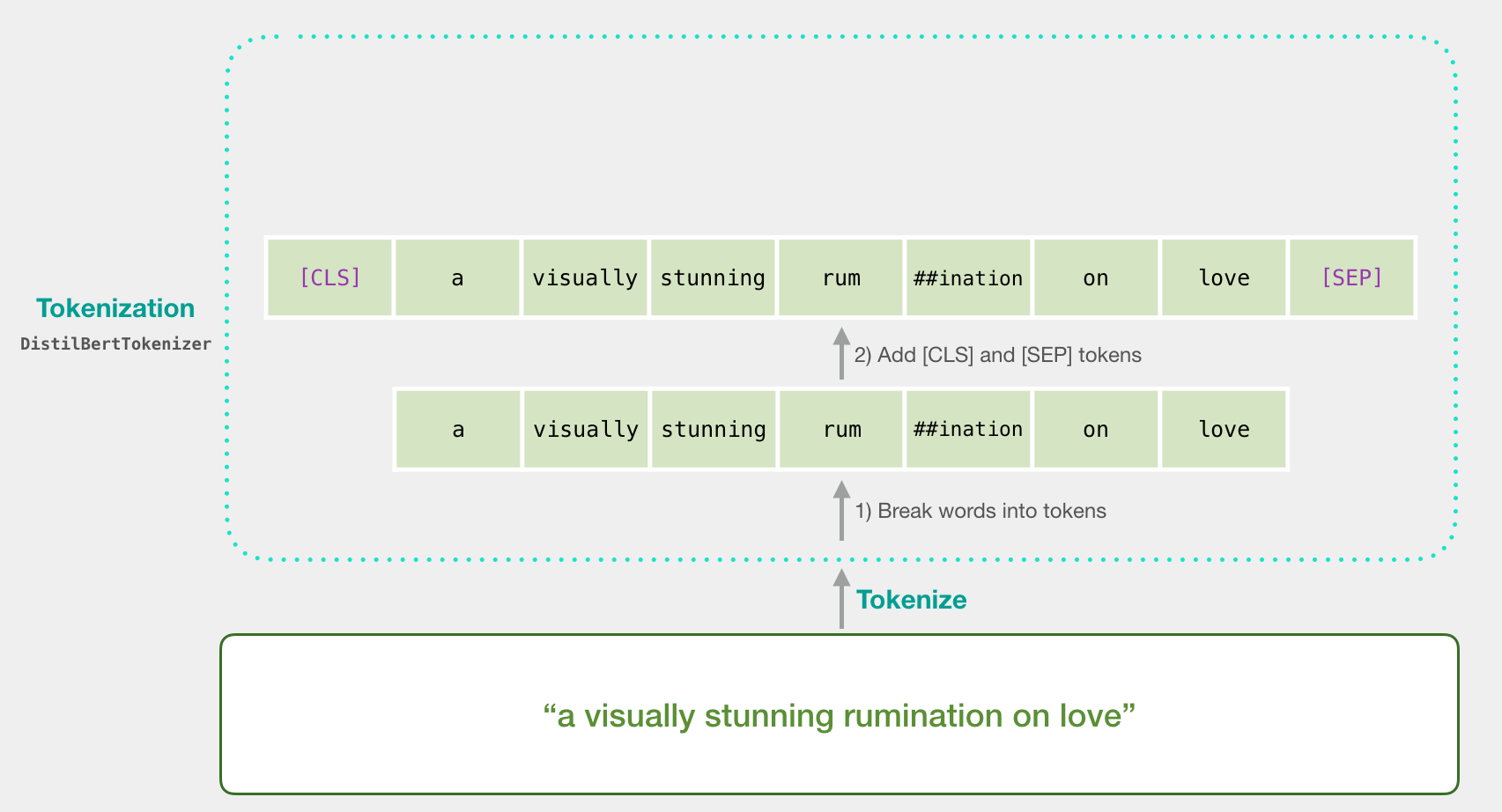
, . Word2vec .

:
tokenizer.encode("a visually stunning rumination on love", add_special_tokens=True)
DistilBERT'.
BERT, ELMO ( NLP ), :
DistilBERT
DistilBERT' , BERT'. , 768 .
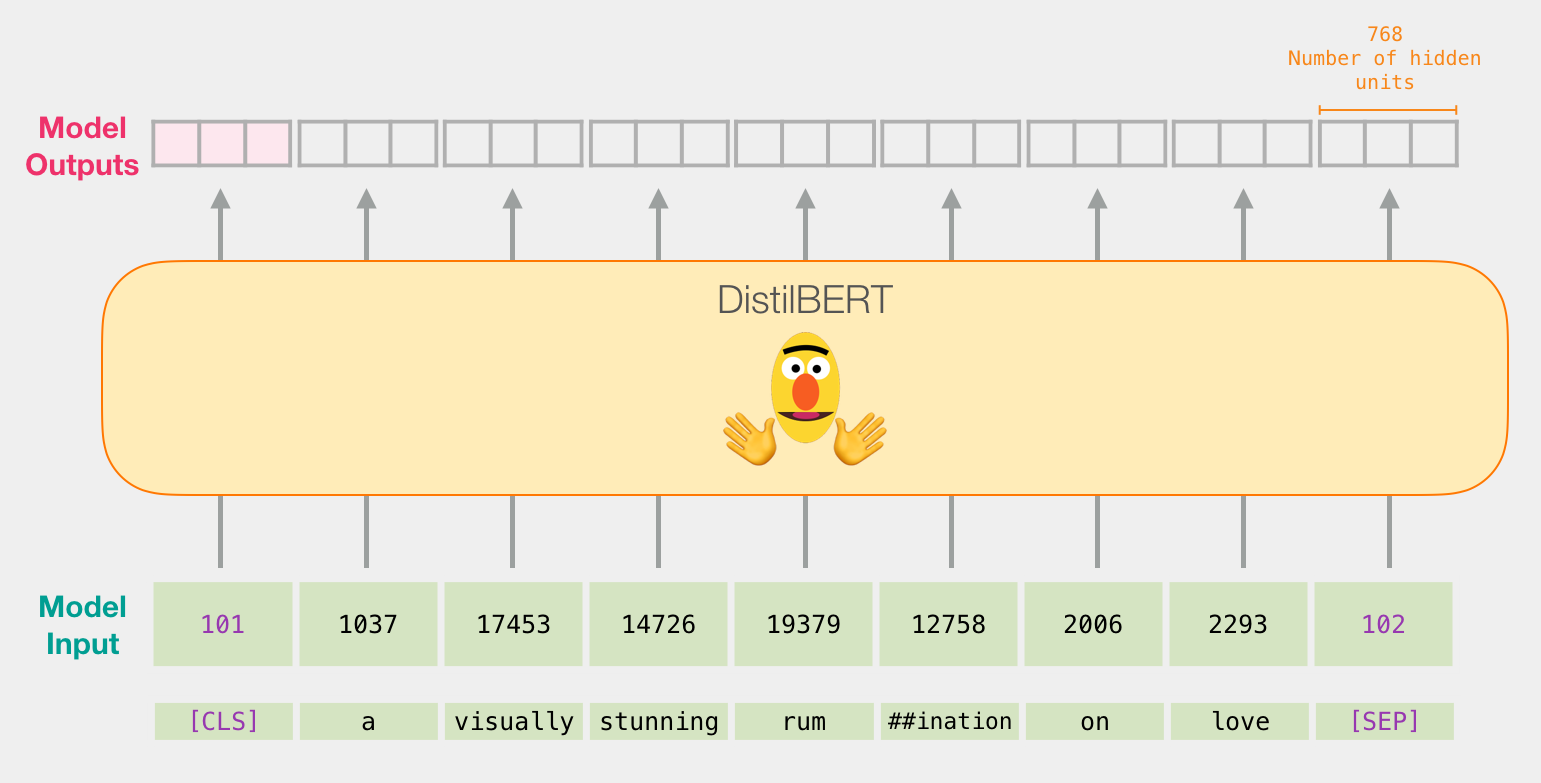
, , ( [CLS] ). .
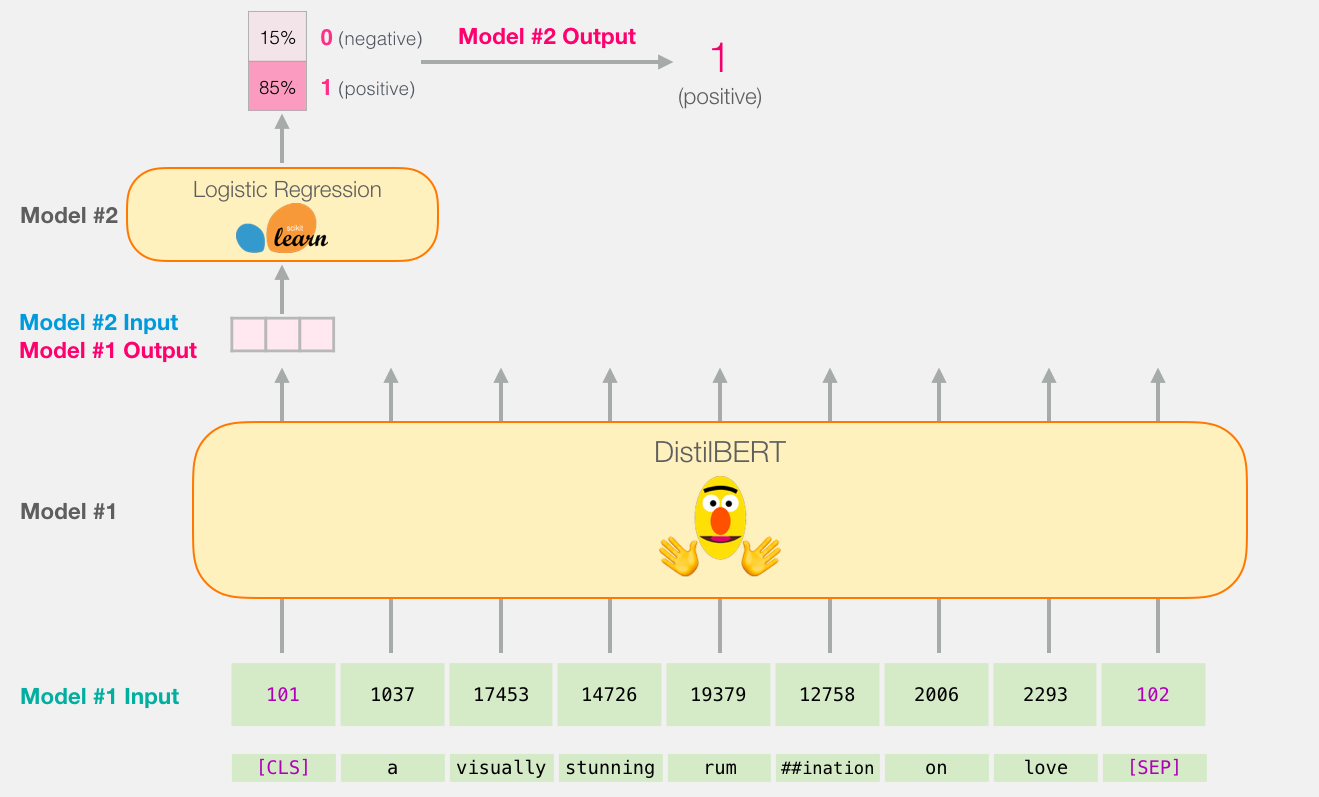
, , . :
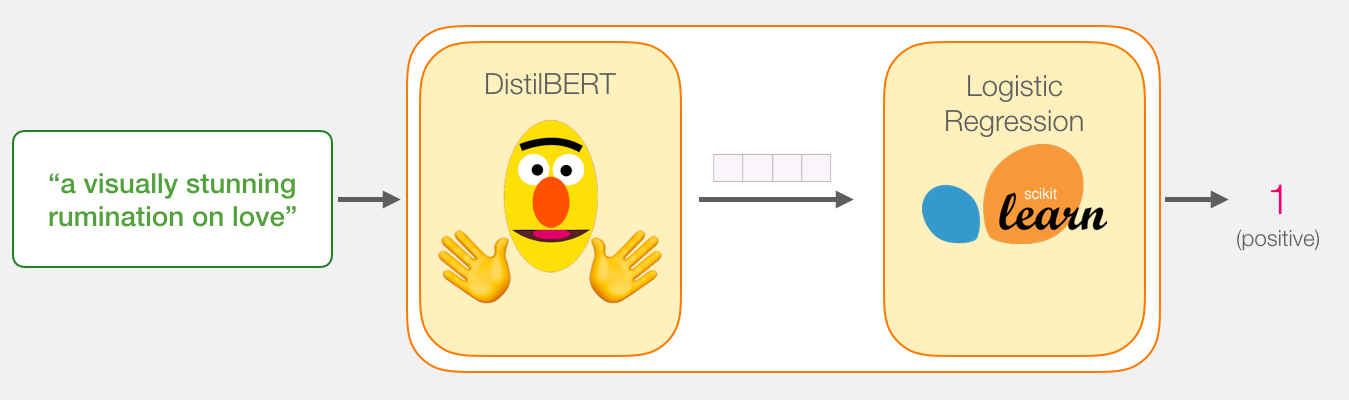
, .
. Colab github.
:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import torch
import transformers as ppb
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
github, pandas:
df = pd.read_csv('https://github.com/clairett/pytorch-sentiment-classification/raw/master/data/SST2/train.tsv', delimiter='\t', header=None)
df.head() , 5 , :
df.head()

DistilBERT
model_class, tokenizer_class, pretrained_weights = (ppb.DistilBertModel, ppb.DistilBertTokenizer, 'distilbert-base-uncased')
tokenizer = tokenizer_class.from_pretrained(pretrained_weights)
model = model_class.from_pretrained(pretrained_weights)
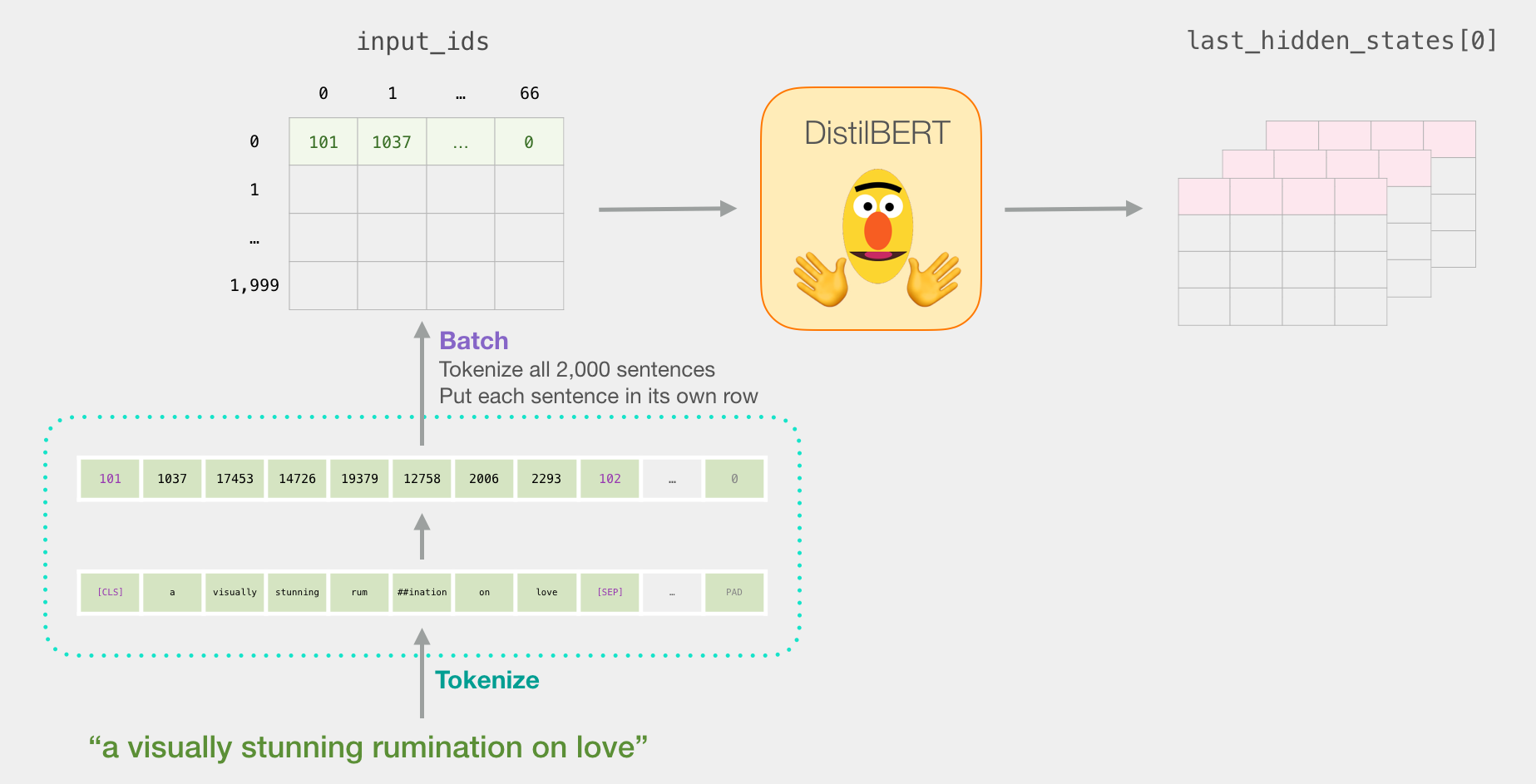
. , , . . ( , 2000).
tokenized = df[0].apply((lambda x: tokenizer.encode(x, add_special_tokens=True)))
.

( Series/DataFrame pandas) . DistilBERT , 0 (padding). , ( , Python).
, /, BERT':
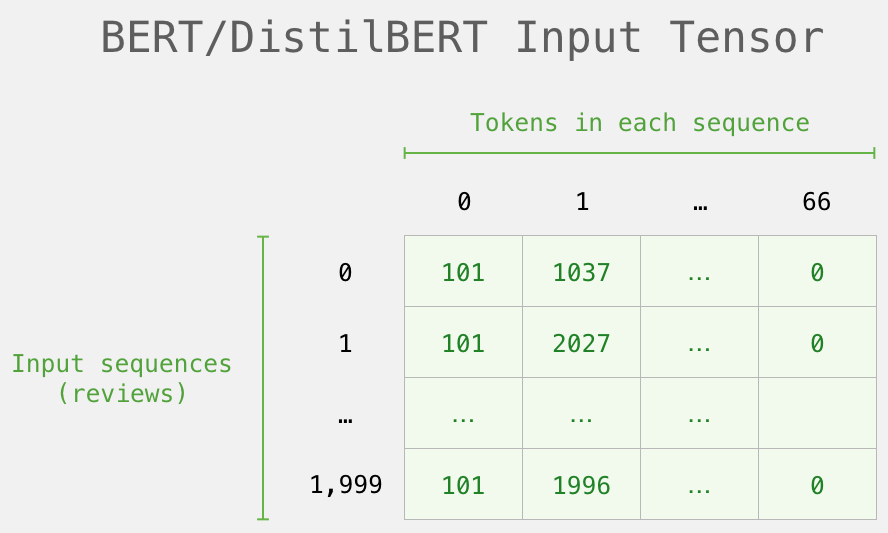
DistilBERT'
DistilBERT.
input_ids = torch.tensor(np.array(padded))
with torch.no_grad():
last_hidden_states = model(input_ids)
last_hidden_states DistilBERT', ( , , DistilBERT). , 2000 (.. 2000 ), 66 ( 2000 ), 278 ( DistilBERT).

BERT'
3-d . :
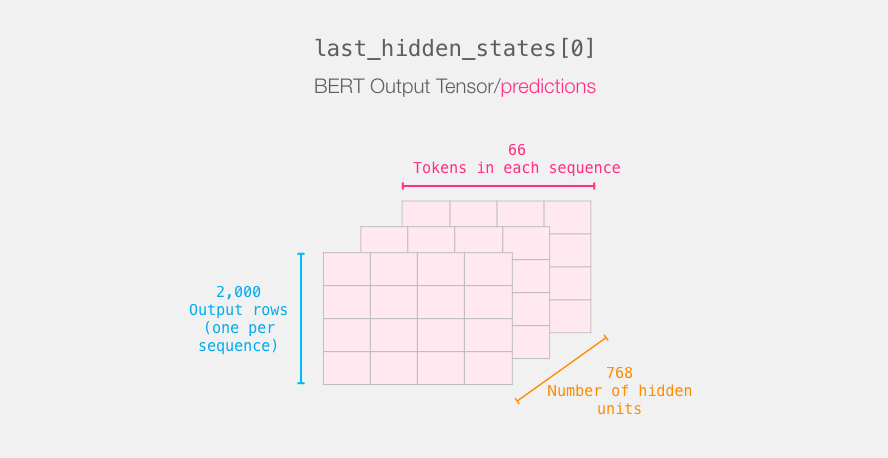
. :
BERT' [CLS]. .

, 3d , 2d :
features = last_hidden_states[0][:,0,:].numpy()
features 2d numpy, .

, BERT'
, BERT', , . 768 , .

, . BERT' [CLS] ( #0), (. ). , – , BERT/DistilBERT
, , .
labels = df[1]
train_features, test_features, train_labels, test_labels = train_test_split(features, labels)
:

.
lr_clf = LogisticRegression()
lr_clf.fit(train_features, train_labels)
, .
lr_clf.score(test_features, test_labels)
, (accuracy) – 81%.
: – 96.8. DistilBERT , – , . BERT , ( downstream task). DistilBERT' 90.7. BERT' 94.9.
Colab.
就这样!第一次相识很好。下一步是转到文档,然后尝试自己动手。您还可以返回一点,从distilBERT转到BERT,看看它是如何工作的。
感谢ClémentDelangue,Victor Sanh和Huggingface团队,他们对本指南的早期版本提供了反馈。
s