预期课程的开始“开发人员算法”已为您准备了另一本有用的材料的翻译。
霍夫曼编码是一种数据压缩算法,表达了文件压缩的基本思想。在本文中,我们将讨论固定长度和可变长度编码,唯一解码的代码,前缀规则以及霍夫曼树的构造。我们知道每个字符都存储为0和1的序列,占用8位。之所以称为固定长度编码,是因为每个字符使用相同的固定位数进行存储。假设给出了文本。我们如何减少存储一个字符所需的空间?基本思想是可变长度编码。我们可以使用以下事实:文本中的某些字符比其他字符更常见(请参见此处)来开发一种算法,该算法将用更少的位表示相同的字符序列。在编码可变长度时,我们根据字符在文本中出现的频率为字符分配可变数量的位。最终,某些字符可能只占1位,而其他字符则占2位,3个或更多。可变长度编码的问题仅在于序列的后续解码。知道位序列如何进行唯一解码?考虑字符串“ aabacdab”。它具有8个字符,并且在编码固定长度时,将需要64位存储它。注意,字符“ a”,“ b”,“ c”和“ d”的频率分别为4、2、1、1。让我们试着想象“aabacdab”用更少的比特,使用的事实,“一”是不是更常见的“B”和“B”是不是更常见的“C”和“d”。首先,我们使用等于0的一位对“ a”进行编码,“ b”分配两位的编码11,并使用100和011这三位对“ c”进行编码,“ D”。结果,我们将成功:因此,我们使用上述代码将字符串“ aabacdab”编码为00110100011011(0 | 0 | 11 | 0 | 100 | 011 | 0 | 11)。但是,主要问题将是解码。当我们尝试对00110100011011行进行解码时,我们会得到一个模棱两可的结果,因为它可以表示为:0|011|0|100|011|0|11 adacdab
0|0|11|0|100|0|11|011 aabacabd
0|011|0|100|0|11|0|11 adacabab
...等为了避免这种歧义,我们必须确保我们的编码满足前缀规则的概念,这反过来意味着可以用一种唯一的方式对代码进行解码。前缀规则可确保没有代码是另一个的前缀。所谓代码,是指用来表示特定字符的位。在上面的示例中,0是前缀011,这违反了前缀规则。因此,如果我们的代码满足前缀规则,那么我们可以进行唯一解码(反之亦然)。让我们回顾一下上面的例子。这次我们将分配字符“ a”,“ b”,“ c”和“ d” 满足前缀规则的代码。使用此编码,字符串“ aabacdab”将被编码为00100100011010(0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 100 | 011 | 0 | 10)。在这里00100100011010,我们可以唯一地解码并返回到原始行“ aabacdab”。霍夫曼编码
现在我们已经弄清楚了变长编码和前缀规则,让我们谈谈霍夫曼编码。该方法基于二叉树的创建。在其中,节点可以是有限的或内部的。最初,所有节点都被视为树叶(叶子),代表符号本身及其权重(即出现的频率)。内部节点包含字符的权重,并引用两个后代节点。根据一般约定,位“ 0”代表左分支的跟随,而位“ 1”代表右分支。在完整的树中,有N个叶子和N-1个内部节点。建议在构建霍夫曼树时,将未使用的字符丢弃以获取最佳长度的代码。我们将使用优先级队列来构建霍夫曼树,其中频率最低的节点将被赋予最高优先级。构造步骤如下所述:- 为每个字符创建一个叶节点,并将它们添加到优先级队列。
- 排队一张以上时,请执行以下操作:
- 从队列中删除优先级最高(频率最低)的两个节点;
- 创建一个新的内部节点,其中这两个节点将成为继承人,并且出现的频率将等于这两个节点的频率之和。
- 将新节点添加到优先级队列。
- 唯一剩余的节点将是根,这将完成树的构建。
想象一下,我们有一些仅由字符“ a”,“ b”,“ c”,“ d”和“ e”组成的文本,其出现频率分别为15、7、6、6和5。下面的插图反映了该算法的步骤。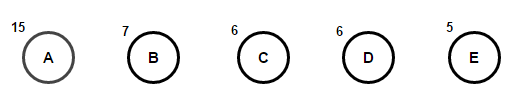
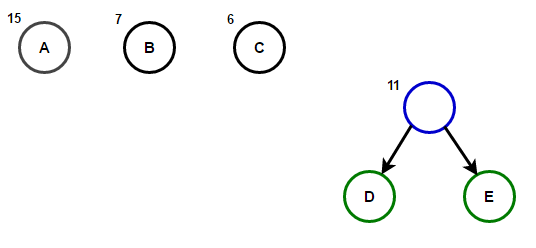
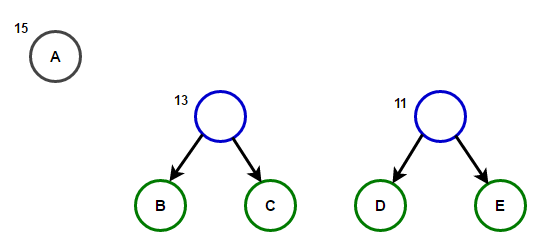
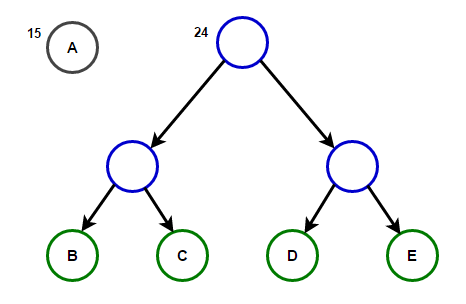
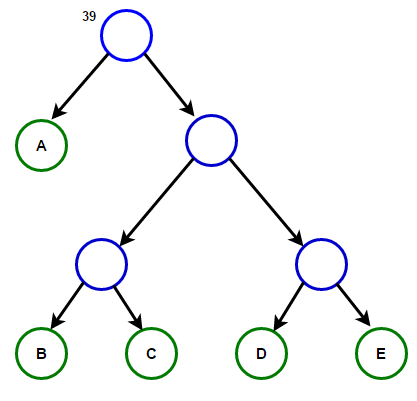 从根到任何终端节点的路径将存储与该终端节点关联的字符相对应的最佳前缀代码(也称为霍夫曼代码)。
从根到任何终端节点的路径将存储与该终端节点关联的字符相对应的最佳前缀代码(也称为霍夫曼代码)。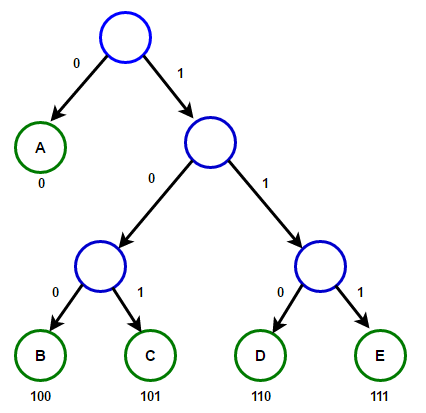 霍夫曼树下面,您将找到C ++和Java中霍夫曼压缩算法的实现:
霍夫曼树下面,您将找到C ++和Java中霍夫曼压缩算法的实现:#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
char ch;
int freq;
Node *left, *right;
};
Node* getNode(char ch, int freq, Node* left, Node* right)
{
Node* node = new Node();
node->ch = ch;
node->freq = freq;
node->left = left;
node->right = right;
return node;
}
struct comp
{
bool operator()(Node* l, Node* r)
{
return l->freq > r->freq;
}
};
void encode(Node* root, string str,
unordered_map<char, string> &huffmanCode)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
if (!root->left && !root->right) {
huffmanCode[root->ch] = str;
}
encode(root->left, str + "0", huffmanCode);
encode(root->right, str + "1", huffmanCode);
}
void decode(Node* root, int &index, string str)
{
if (root == nullptr) {
return;
}
if (!root->left && !root->right)
{
cout << root->ch;
return;
}
index++;
if (str[index] =='0')
decode(root->left, index, str);
else
decode(root->right, index, str);
}
void buildHuffmanTree(string text)
{
unordered_map<char, int> freq;
for (char ch: text) {
freq[ch]++;
}
priority_queue<Node*, vector<Node*>, comp> pq;
for (auto pair: freq) {
pq.push(getNode(pair.first, pair.second, nullptr, nullptr));
}
while (pq.size() != 1)
{
Node *left = pq.top(); pq.pop();
Node *right = pq.top(); pq.pop();
int sum = left->freq + right->freq;
pq.push(getNode('\0', sum, left, right));
}
Node* root = pq.top();
unordered_map<char, string> huffmanCode;
encode(root, "", huffmanCode);
cout << "Huffman Codes are :\n" << '\n';
for (auto pair: huffmanCode) {
cout << pair.first << " " << pair.second << '\n';
}
cout << "\nOriginal string was :\n" << text << '\n';
string str = "";
for (char ch: text) {
str += huffmanCode[ch];
}
cout << "\nEncoded string is :\n" << str << '\n';
int index = -1;
cout << "\nDecoded string is: \n";
while (index < (int)str.size() - 2) {
decode(root, index, str);
}
}
int main()
{
string text = "Huffman coding is a data compression algorithm.";
buildHuffmanTree(text);
return 0;
}
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
class Node
{
char ch;
int freq;
Node left = null, right = null;
Node(char ch, int freq)
{
this.ch = ch;
this.freq = freq;
}
public Node(char ch, int freq, Node left, Node right) {
this.ch = ch;
this.freq = freq;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
};
class Huffman
{
public static void encode(Node root, String str,
Map<Character, String> huffmanCode)
{
if (root == null)
return;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
huffmanCode.put(root.ch, str);
}
encode(root.left, str + "0", huffmanCode);
encode(root.right, str + "1", huffmanCode);
}
public static int decode(Node root, int index, StringBuilder sb)
{
if (root == null)
return index;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
{
System.out.print(root.ch);
return index;
}
index++;
if (sb.charAt(index) == '0')
index = decode(root.left, index, sb);
else
index = decode(root.right, index, sb);
return index;
}
public static void buildHuffmanTree(String text)
{
Map<Character, Integer> freq = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0 ; i < text.length(); i++) {
if (!freq.containsKey(text.charAt(i))) {
freq.put(text.charAt(i), 0);
}
freq.put(text.charAt(i), freq.get(text.charAt(i)) + 1);
}
PriorityQueue<Node> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(
(l, r) -> l.freq - r.freq);
for (Map.Entry<Character, Integer> entry : freq.entrySet()) {
pq.add(new Node(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()));
}
while (pq.size() != 1)
{
Node left = pq.poll();
Node right = pq.poll();
int sum = left.freq + right.freq;
pq.add(new Node('\0', sum, left, right));
}
Node root = pq.peek();
Map<Character, String> huffmanCode = new HashMap<>();
encode(root, "", huffmanCode);
System.out.println("Huffman Codes are :\n");
for (Map.Entry<Character, String> entry : huffmanCode.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " " + entry.getValue());
}
System.out.println("\nOriginal string was :\n" + text);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0 ; i < text.length(); i++) {
sb.append(huffmanCode.get(text.charAt(i)));
}
System.out.println("\nEncoded string is :\n" + sb);
int index = -1;
System.out.println("\nDecoded string is: \n");
while (index < sb.length() - 2) {
index = decode(root, index, sb);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String text = "Huffman coding is a data compression algorithm.";
buildHuffmanTree(text);
}
}
注意:输入字符串使用的内存为47 * 8 = 376位,而编码字符串仅占用194位,即 数据压缩约48%。在上面的C ++程序中,我们使用字符串类存储编码的字符串以使程序可读。由于优先级队列的有效数据结构需要插入O(log(N))时间,并且在具有N个叶子的完整二叉树中有2N-1个节点,而Huffman树是一个完整的二叉树,因此该算法适用于O(Nlog(N ))时间,其中N是字符数。资料来源:
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Huffman_codingen.wikipedia.org/wiki/Variable-length_codewww.youtube.com/watch?v=5wRPin4oxCo
.