“为什么不重新点燃流行病呢?”这个想法突然来了。与合适的组织一起在家工作可能比办公室工作更有效,因此,有充足的额外时间来“思考”其他事情。
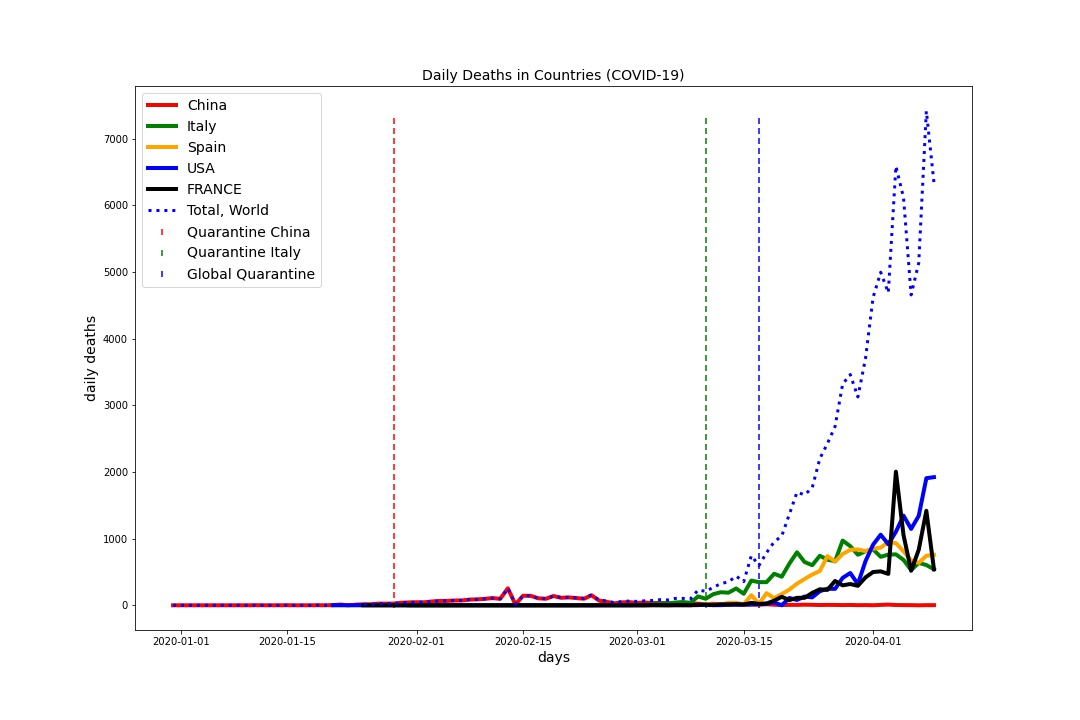
当然,这一切都始于建立欧洲疾病控制中心对COVID-19的每日数据可视化。一个简单的算法每天中午在更新的数据上绘制图形。图表提醒人们注意3月初疫情开始下降时中国采取的有效防疫行动。但是欧洲国家接力棒-首先是意大利(您还记得吗(由于经济不景气,米兰当局在2月下旬要求游客返回城市)?)然后是西班牙。
— , , -, . 30 — , , , ? ? .
“” COVID-19 — - . , (!) . . . ? — !
- — . — . — . , — . . 3 :
, , — , . . ? , — “ ” caseIssuedDate ( — ). , — “ ” severity . “” .
: - = 1 .
:
epidemy = [[0, None, 'infected', 'mild', None, False]]
*, \ ‘result’ . ‘recovered’ ‘dead’.
— , …
— . , ( “”, , ). , — .
— , “”. , 0.1 (10%) 1 10 . 100 10 , 100 10 0.1 = 100 . , : , . () :
['infectDate', 'endOfCaseDate', 'result', 'severity', 'caseDocumentedDate', 'isolated' ]
, , ( — !) .
— , , . ? , . : , , , — deathRate.
- ::
dailyTransmissionContacts = 15
contagiousness = 0.01
severityRate = 0.3
deathRate = 0.5
caseDuration = 25
closedPopulation = 10000
periodToDocumented = caseDuration * 0.6
mildDocumentedRate = 0.3
severeDocumentedRate = 0.9
isolationQualityRate = 0.1
showDays = 150
(. ) :
periodToIssued — , ,
mildDocmentedRate — 30%
severeDocumentedRate = 90%
isolationQualityRate — () . 100%
? , — … , , , , . — . . , COVID-19. — .
. :
— “” “” “”
, “” —
.2
susceptibleToday = (closedPopulation - infectedCountToday - recoveredCountToday)
newAffectedPeopleCount = int(((activeInfectedCountToday * dailyTransmissionContacts * contagiousness) // 1 * susceptibleToday/closedPopulation + 1))
* — “” . . ( ) .
.
.
, pandas.
10 . : 0 (.. ) 100%, “” .
6 . 120 ( ) ( ) — , .
totalAffected: 10000 deathsTotal: 1582 deathRate_real = 15%

( ). 10 , ,

. , . , COVID-19, — 5-7 . , , —

caseDuration :

: , , .
:
. caseIssuedDate — . “” . : “ , ”. , , - .
: “, , . > ?”
: “ , ...
: , , — . 2 : mildDocumentedRate severDocumentedRate — ( ) . : 7-9 10 , , . , . , , , , , . ? , . , .
mildIDocumentedRate = 0.3
severeDocumentedRate = 0.9

, . , : 150 50 — , , .. .
, .
, .. , . , . () .
( — — )
totalAffected: 10000 deathsTotal: 1582 deathRate_real = 15%
DocumentedTotal: 4789 deathsDocumented: 1406 deathRate_docum = 29%
. .
() : “” . — , .
periodToDocumented — . , “” , , . , — , — , , .

periodToDocumented. mildDocumentedRate = 0.3 (30% ). “” , , .
: — , .

, [20:30] .
, , — .
:
.
. , , , .

(0 — , 1 — ).
, — , “ ” . , .
( ) .
, , . . , . ( 0.7) periodToDocumented.
, periodToDocumented ( ) 60% , .. 25 * 0.6 = 15 . 10, 7, 4

, , — “” , , , , . , .
:
totalAffected: 10000 deathsTotal: 1486 deathRate_real = 14%
totalAffected: 10000 deathsTotal: 1556 deathRate_real = 15%
totalAffected: 10000 deathsTotal: 1439 deathRate_real = 14%
totalAffected: 8466 deathsTotal: 1248 deathRate_real = 14%
— — . 2 :
dailyTransmissionContacts = 15
contagiousness = 0.01
“ ” . .

totalAffected: 10000 deathsTotal: 1557 deathRate_real = 15%
totalAffected: 7727 deathsTotal: 1173 deathRate_real = 15%
totalAffected: 4597 deathsTotal: 709 deathRate_real = 15%
totalAffected: 2008 deathsTotal: 299 deathRate_real = 14%
. 5 . , “ ”. — .
, .
. : 60 80, .

, , “” , , “ ”
totalAffected: 10000 deathsTotal: 1557 deathRate_real = 15%
totalAffected: 4597 deathsTotal: 709 deathRate_real = 15%
totalAffected: 10000 deathsTotal: 1434 deathRate_real = 14%
, “” , . , , , , / (, , ). “ ” — . , . , , — , ( , , , , , — , — ).
. ! , , .
: epidemy (‘recovered’).


totalAffected: 7890 deathsTotal: 1162 deathRate_real = 11%
totalAffected: 10000 deathsTotal: 1557 deathRate_real = 15%
5 20 ( ) 30% — .
, . :
- , «». . .
- . (, , , ) , , .
- , ( “ ”).
“ ” , .
“ ” “” . , , , — . “” “ ” .
不同的抑制方法在效果上可能存在显着差异:测试的“自我隔离”甚至“早期检测”方法在模型参数接近COVID19时均未显示出预期的阳性结果。同时,任何一种在某种程度上抑制这种疾病的措施都会“消除”该流行病的高峰,这可以在该流行病的背景下积极影响医疗保健系统的工作。
最有效的措施是隔离。及时和充分的隔离不仅可以“扩大”流行病的进程,减轻医疗保健系统的负担,而且有时还可以减少病例数和死亡率。
Google Colab上的笔记本电脑链接