每个Android开发人员迟早都必须使用网络。Android有许多开源库,例如Retrofit,OkHttp或Volley等,我们今天将对其进行详细介绍。那么这个图书馆是什么样的呢?Volley是一个HTTP库,可简化和加速Android应用程序的联网。GitHub库代码。因此,要开始使用Volley,我们需要将其添加到build.gradle(模块:app)中:dependencies {
...
implementation 'com.android.volley:volley:1.1.1'
}
还需要在我们的应用程序清单中添加使用Internet的权限:<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
接下来,我们需要一个API。在本教程中,我将使用openweathermap.org/api中的weather API 。此API的示例首先,我们将创建一个简单的标记来显示从API(应用程序编程接口)获取的数据。<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tempTextView"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text=": "
android:textSize="20sp"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_marginLeft="50dp"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_marginTop="50dp"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/windTextView"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_marginLeft="50dp"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:text=" :"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
接下来,转到MainActivity并创建必要的字段:private static final String testUrl = "https://samples.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather?id=2172797&appid=b6907d289e10d714a6e88b30761fae22";
RequestQueue mRequestQueue;
TextView tempTextView,windTextView;
double temp = 0,windSpeed = 0;
我们在onCreate中初始化创建的字段字段:tempTextView = findViewById(R.id.tempTextView);
windTextView = findViewById(R.id.windTextView);
mRequestQueue = Volley.newRequestQueue(this);
现在,我们进入本教程的主题-使用Volley库从API获取数据:1)在MainActivity中,我们创建GetWeather方法:private void getWeather(String url) {
final JsonObjectRequest request = new JsonObjectRequest(Request.Method.GET,
url, null, new Response.Listener<JSONObject>() {
@Override
public void onResponse(JSONObject response) {
try {
JSONObject weather = response.getJSONObject("main"),wind = response.getJSONObject("wind");
temp = weather.getDouble("temp");
windSpeed = wind.getDouble("speed");
setValues();
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, new Response.ErrorListener() {
@Override
public void onErrorResponse(VolleyError error) {
error.printStackTrace();
}
});
mRequestQueue.add(request);
}
 jsonformatter用于将json转换为标准格式 。值得注意的是,对象名称的编写方式必须与我们的API中的编写方式完全相同,否则它们将无法获取。2)直接创建setValues方法:
jsonformatter用于将json转换为标准格式 。值得注意的是,对象名称的编写方式必须与我们的API中的编写方式完全相同,否则它们将无法获取。2)直接创建setValues方法:private void setValues() {
tempTextView.setText(": " + temp);
windTextView.setText(" : " + windSpeed);
}
3)在onCreate()中调用getWeather()和setValues()方法:@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
getWeather(testUrl);
setValues();
}
4)运行该应用程序并完成!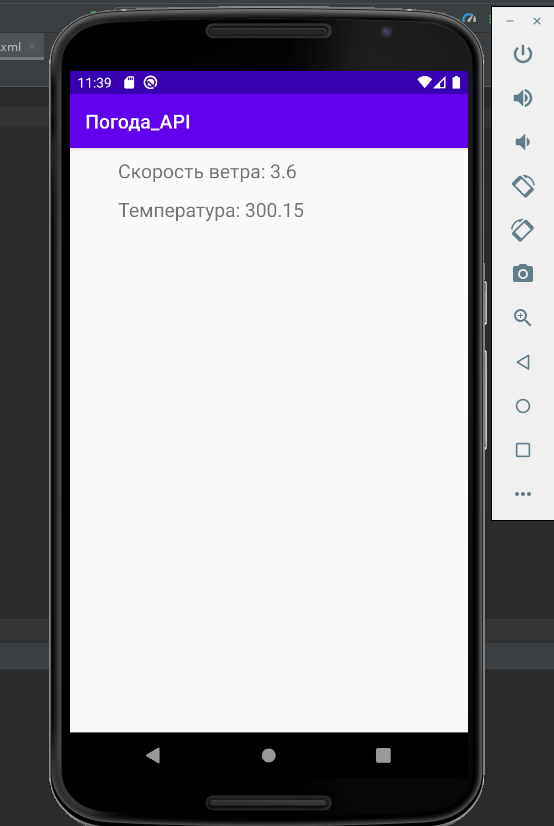 PS:一些想深入了解问题的人的有用链接:Volley库的官方文档为了更好地理解HTTP请求的API 类型的本质以JSON格式编写数据P.SS:GitHub上的应用程序文件
PS:一些想深入了解问题的人的有用链接:Volley库的官方文档为了更好地理解HTTP请求的API 类型的本质以JSON格式编写数据P.SS:GitHub上的应用程序文件