呈现数据以进行深度学习的复杂性每天都在增长。图神经网络(GNN)已成为近年来的突破之一。但是,为什么图形在机器学习中越来越受欢迎呢?
我的叙述的最终目标是机器学习技术中图形的一般呈现。本文并非伪装成足以描述图的全部功能的科学著作,而只是向读者介绍了这个惊人而复杂的世界。对于不熟悉深度学习图形表示的,经过艰苦训练的专业人士以及该领域的初学者而言,该出版物都是理想的选择。
介绍
自动突出显示解决问题所需的重要功能是成功使用机器学习的主要原因之一。但是传统上,当使用图时,机器学习方法依赖于用户定义的启发式方法来提取结构图信息的编码特征。尽管如此,近年来的趋势已发生变化:越来越多的方法不断涌现,这些方法可以使用深度学习和非线性降维方法自动学习对低维投资中的图形结构进行编码。
在图上的机器学习中,可以区分两个主要问题:在模型中包含有关图的结构的信息(即,在特征向量中对该信息进行编码的简单方法)以及特征向量的维数减少。
为了从图提取结构信息,传统的机器方法通常基于图的摘要统计量(例如,聚类系数),核函数或用于测量局部邻域结构的精心设计的函数。但是,这些方法受到限制,因为这些工程解决方案无法适应学习过程,并且它们的开发是费力且昂贵的过程。
为什么是图?
说到图形作为数据表示的结构单元,您可以问自己一个简单的问题:为什么选择图形?
— . , , ( ) [1], [2], ( [3], [4] [5]), [6] [7].
CV/ML , , . , , [8].
, . . , , , .
, (embeddings), . , , , , (), . , , . , .
, . , , . , , , .
, (direct encoding), . . , , -. , , , .
DeepWalk node2vec . , . , .
( ). (DNGR SDNE), , [9].
, , , — ( ) , .
(.1). :

, , , ( , ). .
, . , ( , ). , , , , .
, , . , , . (, )
- , , / . ; ( ) , ( ). , .
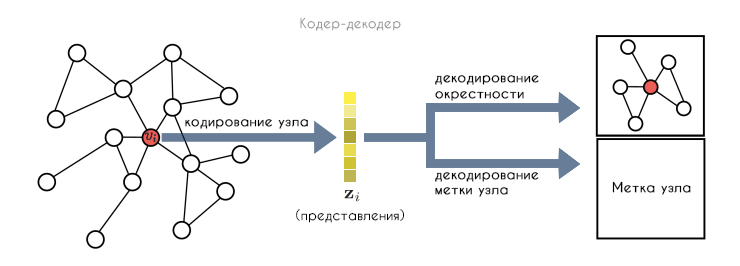
, , , . , (, ) . 2 , , .
, — , , ( ):
— , :
. , , . , , . , :
— , . , , 1, 0. . ( 1) :
— , (.. ) .
, -, , . , , , , , .
seq2seq , , . , seq2seq, GNN [10].
, :
- : , .
- ENC, . , .
- DEC, .
- , , .

. , . , .
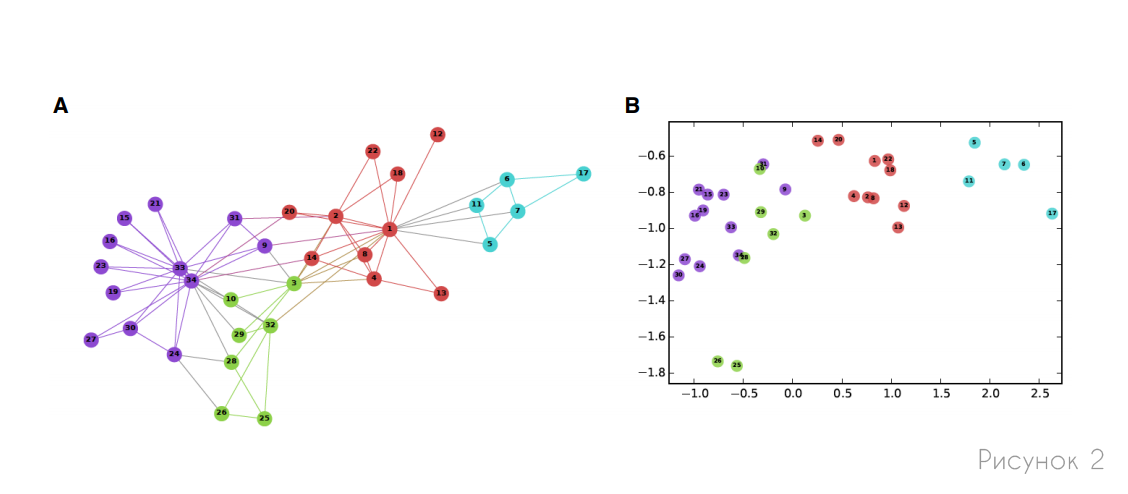
, , . , , (.3). , , , .

DeepWalk node2vec, , , . , , . , , :
— , , . , . , :
, (.. . — ( (2) ). , DeepWalk node2vec (3). DeepWalk softmax , . , node2vec (3), : , , " ".
, node2vec DeepWalk , , . , node2vec : , (.4). , . , node2vec , .
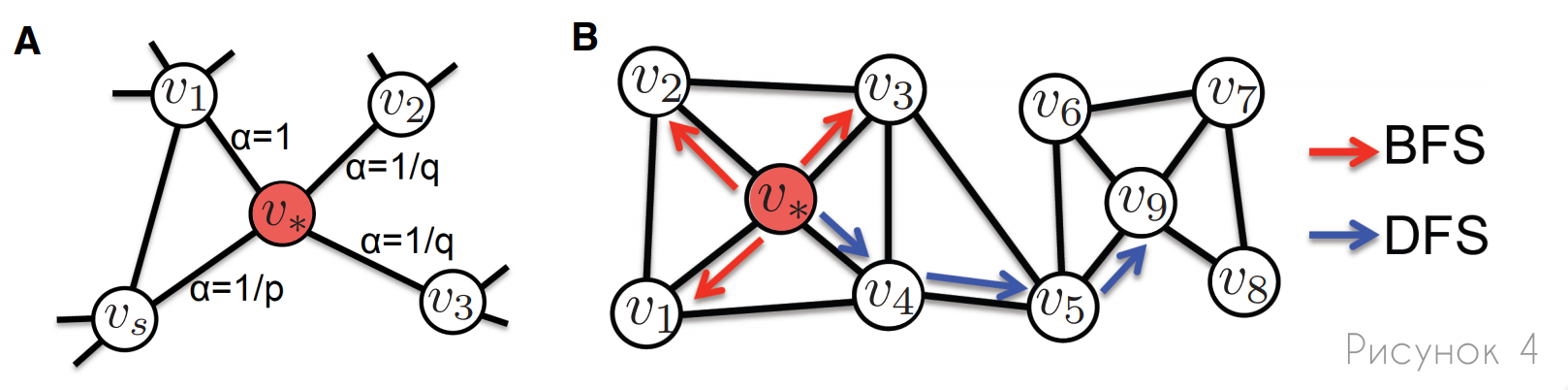
A: , node2vec , p q. , , (α) , .
B: , (BFS) (DFS). , BFS, , , . , , DFS, .
, . , :
- (.. ). , , .
- . (, ), .
- . , , ( , ). , , , , .
/ . -, , , .
(DNGR) (SDNE) , : , . , — , (.5). DNGR SDNE , .

, ( — ). . DNGR SDNE , , :
, :
, , ( ), , . SDNE, DNGR, : , (.5).
SDNE DNGR , , , . DNGR , , DeepWalk node2vec. SDNE , .
, SDNE DNGR , ( ), - . , .
, . . , , , [9], . , .
. , , , , , , .
, , , .
. (. ), ( ). . , , , , , , — , , , . , , , .
. , , - , , . , , , , .
. , , , . , , , . , .
. , , . , , . , , , . , , , , .
, — . , , .
[1] — W. L. Hamilton, Z. Ying, and J. Leskovec, "Inductive representation learning on large graphs," NIPS 2017, pp. 1024–1034, 2017.
[2] — T. N. Kipf and M. Welling, "Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks," ICLR 2017, 2017.
[3] — A. Sanchez-Gonzalez, N. Heess, J. T. Springenberg, J. Merel, M. Riedmiller, R. Hadsell, and P. Battaglia, "Graph networks as learnable physics engines for inference and control," arXiv
preprint arXiv:1806.01242, 2018.
[4] — P. Battaglia, R. Pascanu, M. Lai, D. J. Rezende et al., "Interaction networks for learning about objects, relations and physics," in NIPS 2016, 2016, pp. 4502–4510.
[5] — A. Fout, J. Byrd, B. Shariat, and A. Ben-Hur, "Protein interface prediction using graph convolutional networks," in NIPS 2017, 2017, pp. 6530–6539.
[6] — T. Hamaguchi, H. Oiwa, M. Shimbo, and Y. Matsumoto, "Knowledge transfer for out-of-knowledge-base entities: A graph neural network approach," in IJCAI 2017, 2017, pp. 1802–1808.
[7] — H. Dai, E. B. Khalil, Y. Zhang, B. Dilkina, and L. Song, "Learning combinatorial optimization algorithms over graphs," arXiv preprint arXiv:1704.01665, 2017.
[8] — X. Liang, X. Shen, J. Feng, F. Lin, S. Yan, "Semantic Object Parsing with Graph LSTM", arXiv:1603.07063v1 [cs.CV] 23 Mar 2016.
[9] — Z. Wu, S. Pan, F. Chen, G. Long, C. Zhang, Philip S. Yu, "A Comprehensive Survey on Graph Neural Networks", arXiv:1901.00596v4 [cs.LG] 4 Dec 2019.
[10]-P.Veličković,G。Cucurull,A。Casanova,A。Romero,P。Liò,Y。Bengio,“图注意力网络”,arXiv:1710.10903v3 [stat.ML] 2018年2月4日。
参考文献
图神经网络:方法和应用的回顾
图上的表示学习:方法和应用