Oi Oi! Mais uma vez, preparamos para você uma seleção de perguntas e tarefas interessantes a partir de entrevistas nas principais empresas de TI! Os problemas serão exibidos toda semana - fique ligado! A coluna é suportada pela agência de recrutamento Spice IT .Nesta semana, coletamos tarefas de entrevistas na empresa americana PayPal. A propósito, as respostas para os problemas da edição anterior já foram publicadas .
Os problemas serão exibidos toda semana - fique ligado! A coluna é suportada pela agência de recrutamento Spice IT .Nesta semana, coletamos tarefas de entrevistas na empresa americana PayPal. A propósito, as respostas para os problemas da edição anterior já foram publicadas .Questões
1. Quebra-cabeça de prisioneiro e policialO policial decidiu punir o prisioneiro e pediu que ele fizesse uma declaração. O prisioneiro deve fazer tal declaração para que ele estivesse vivo.
Se a declaração for mantida verdadeira pelo policial, o prisioneiro será enforcado até a morte e se a declaração for falsa, o prisioneiro será morto a tiros.
2. Quebra-cabeça com palito de fósforoComo fazer 4 triângulos equilaterais com 6 palitos de fósforo idênticos?
Tarefas
1. Interseção de duas matrizesGiven two arrays A and B respectively of size N and M. The task is to print the count of elements in the intersection (or common elements) of the two arrays.
For this question, intersection of two arrays can be defined as the set containing distinct common elements between the two arrays.
Input:
The first line of input contains an integer T denoting the number of test cases. The first line of each test case is N and M, N is the size of array A and M is size of array B. The second line of each test case contains N input A[i].
The third line of each test case contains M input B[i].
Output:
Print the count of intersecting elements.
Constraints:
1 ≤ T ≤ 100
1 ≤ N, M ≤ 105
1 ≤ A[i], B[i] ≤ 105
Exemplo:
Entrada: Saída: Explicação: O Testcase 1: 89 é o único elemento na interseção de duas matrizes. Testcase 2: 3 4 5 e 6 são os elementos na interseção de duas matrizes. Caso de teste 3: Como nenhum dos elementos é comum, a saída será -1. O Testcase 4: 10 é o único elemento que está na interseção de duas matrizes.
4
5 3
89 24 75 11 23
89 2 4
6 5
1 2 3 4 5 6
3 4 5 6 7
4 4
10 10 10 10
20 20 20 20
3 3
10 10 10
10 10 10
1
4
0
1
TransferirA B N M. , ( ) .
, .
:
T, . — N M, N- A, M- B. N A[i].
M B[i].
:
.
:
1 ≤ T ≤ 100
1 ≤ N, M ≤ 105
1 ≤ A[i], B[i] ≤ 105
:
:
4
5 3
89 24 75 11 23
89 2 4
6 5
1 2 3 4 5 6
3 4 5 6 7
4 4
10 10 10 10
20 20 20 20
3 3
10 10 10
10 10 10
:
1
4
0
1
:
1: 89 — .
2: 3 4 5 6 — .
3: , 0.
4: 10 — , .
2. Concatenação da seqüência de zig-zag nas linhas 'n'Dada uma sequência e o número de linhas 'n'. Imprima a string formada concatenando n linhas quando a string de entrada for escrita no modo Zig-Zag em linhas.
Exemplos: Entrada:
A primeira linha de entrada consiste no número de casos de teste. A descrição dos casos de teste T é a seguinte: A primeira linha de cada caso de teste contém a sequência e a segunda linha 'n' o número de linhas. Saída:
em cada linha separada, imprima a sequência após concatenar n linhas em um formato de zig zag. Restrições: Exemplo: Entrada: Saída:
Input:
str = "ABCDEFGH"
n = 2
Output: "ACEGBDFH"
Explanation: Let us write input string in Zig-Zag fashion in 2 rows.
A___C___E___G
__B___D___F___H
Now concatenate the two rows and ignore spaces
in every row. We get "ACEGBDFH"
Input:
str = "SPICEITRECRUITMENT"
n = 3
Output: SEEINPCIRCUTETITRM
Explanation: Let us write input string in Zig-Zag fashion in 3 rows.
S_______E_______E_______I_______N
__P___C___I___R___C___U___T___E___T
____I_______T_______R_______M
Now concatenate the two rows and ignore spaces
in every row. We get "SEEINPCIRCUTETITRM"
1 ≤ T ≤ 70
1 ≤ N ≤ size of string
2
qrrc
3
rfkqyuqfjkxy
2
qrcr
rkyqjxfqufky
Transferir‘n'. , n , .
:
:
str = "ABCDEFGH"
n = 2
: "ACEGBDFH"
: 2 .
A___C___E___G
__B___D___F___H
. "ACEGBDFH"
: SEEINPCIRCUTETITRM
str = "SPICEITRECRUITMENT"
n = 3
:
: 3 .
S_______E_______E_______I_______N
__P___C___I___R___C___U___T___E___T
____I_______T_______R_______M
. "SEEINPCIRCUTETITRM"
:
. t :
, 'n' — .
:
n .
:
1 ≤ T ≤ 70
1 ≤ N ≤
:
:
2
qrrc
3
rfkqyuqfjkxy
2
:
qrcr
rkyqjxfqufky
3. Resolva o SudokuGiven an incomplete Sudoku configuration in terms of a 9 x 9 2-D square matrix (mat[][]). The task to print a solved Sudoku. For simplicity you may assume that there will be only one unique solution.
Sample Sudoku for you to get the logic for its solution:
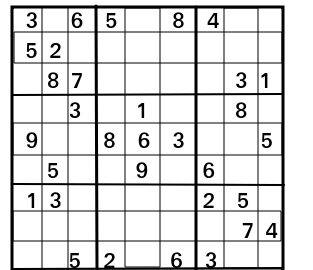
Input:
The first line of input contains an integer T denoting the no of test cases. Then T test cases follow. Each test case contains 9*9 space separated values of the matrix mat[][] representing an incomplete Sudoku state where a 0 represents empty block.
Output:
For each test case, in a new line, print the space separated values of the solution of the the sudoku.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 10
0 <= mat[] <= 9
Example:
Input:
1
3 0 6 5 0 8 4 0 0
5 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 8 7 0 0 0 0 3 1
0 0 3 0 1 0 0 8 0
9 0 0 8 6 3 0 0 5
0 5 0 0 9 0 6 0 0
1 3 0 0 0 0 2 5 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 7 4
0 0 5 2 0 6 3 0 0
Output:
3 1 6 5 7 8 4 9 2 5 2 9 1 3 4 7 6 8 4 8 7 6 2 9 5 3 1 2 6 3 4 1 5 9 8 7 9 7 4 8 6 3 1 2 5 8 5 1 7 9 2 6 4 3 1 3 8 9 4 7 2 5 6 6 9 2 3 5 1 8 7 4 7 4 5 2 8 6 3 1 9
Explanation:
Testcase 1: The solved sudoku is:
3 1 6 5 7 8 4 9 2
5 2 9 1 3 4 7 6 8
4 8 7 6 2 9 5 3 1
2 6 3 4 1 5 9 8 7
9 7 4 8 6 3 1 2 5
8 5 1 7 9 2 6 4 3
1 3 8 9 4 7 2 5 6
6 9 2 3 5 1 8 7 4
7 4 5 2 8 6 3 1 9
9 x 9 2D (mat [] []). . , .
, :
 :
:T, . T . 9 * 9 mat [] [], , 0 .
:.
:1 <= T <= 10
0 <= mat[] <= 9:
:1
3 0 6 5 0 8 4 0 0
5 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 8 7 0 0 0 0 3 1
0 0 3 0 1 0 0 8 0
9 0 0 8 6 3 0 0 5
0 5 0 0 9 0 6 0 0
1 3 0 0 0 0 2 5 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 7 4
0 0 5 2 0 6 3 0 0:3 1 6 5 7 8 4 9 2 5 2 9 1 3 4 7 6 8 4 8 7 6 2 9 5 3 1 2 6 3 4 1 5 9 8 7 9 7 4 8 6 3 1 2 5 8 5 1 7 9 2 6 4 3 1 3 8 9 4 7 2 5 6 6 9 2 3 5 1 8 7 4 7 4 5 2 8 6 3 1 9:1: :
3 1 6 5 7 8 4 9 2
5 2 9 1 3 4 7 6 8
4 8 7 6 2 9 5 3 1
2 6 3 4 1 5 9 8 7
9 7 4 8 6 3 1 2 5
8 5 1 7 9 2 6 4 3
1 3 8 9 4 7 2 5 6
6 9 2 3 5 1 8 7 4
7 4 5 2 8 6 3 1 92.

1t=0
try:
t=int(input().strip())
except:
pass
if __name__ == "__main__":
while t:
t-=1
n, m = map(int, input().strip().split())
a = list(map(int, input().strip().split()))
b = list(map(int, input().strip().split()))
a.sort()
count=0;x=0
for i in a:
if i==x:
pass
else:
if i in b:
count+=1
x=i
print(count)
2#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
string str;
cin>>str;
int row;
cin>>row;
vector<char> v[row];
int flag=1,k=0;
while(1)
{
if(flag==1 && k<str.length())
{
for(int i=0;i<row && k<str.length();i++)
{
v[i].push_back(str[k]);
k++;
}
flag=0;
}
if(flag==0 && k<str.length())
{
for(int i=row-2;i>0 && k<str.length();i--)
{
v[i].push_back(str[k]);
k++;
}
flag=1;
}
if(k==str.length())
break;
}
string res="";
for(int i=0;i<row;i++)
{
for(char ch:v[i])
{
res+=ch;
}
}
cout<<res<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
3#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
int grid[9][9];
int row[9][10];
int col[9][10];
int box[3][3][10];
bool flag;
vector<pair<int,int> >V;
void call(int I)
{
if(V.size()==I)
{
flag=false;
for(int i=0;i<9;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<9;j++)
cout<<grid[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
return;
}
int x=V[I].first,y=V[I].second;
int boxx,boxy;
if(x<3)
boxx=0;
else if(x<6)
boxx=1;
else
boxx=2;
if(y<3)
boxy=0;
else if(y<6)
boxy=1;
else
boxy=2;
for(int i=1;i<=9 && flag;i++)
{
if(row[x][i]==0 && col[y][i]==0 && box[boxx][boxy][i]==0)
{
row[x][i]=1; col[y][i]=1; box[boxx][boxy][i]=1;
grid[x][y]=i;
call(I+1);
row[x][i]=0; col[y][i]=0; box[boxx][boxy][i]=0;
grid[x][y]=0;
}
}
return;
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
for(int i=0;i<9;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<9;j++)
grid[i][j]=0;
}
for(int i=0;i<9;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=9;j++)
{
row[i][j]=0;
col[i][j]=0;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
for(int k=1;k<=9;k++)
box[i][j][k]=0;
}
flag=true;
V.clear();
for(int i=0;i<9;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<9;j++)
{
cin>>grid[i][j];
if(grid[i][j]==0)
{
V.push_back(make_pair(i,j));
continue;
}
row[i][grid[i][j]]=1;
col[j][grid[i][j]]=1;
if(i<3)
{
if(j<3)
{
box[0][0][grid[i][j]]=1;
}
else if(j<6)
{
box[0][1][grid[i][j]]=1;
}
else
{
box[0][2][grid[i][j]]=1;
}
}
else if(i<6)
{
if(j<3)
{
box[1][0][grid[i][j]]=1;
}
else if(j<6)
{
box[1][1][grid[i][j]]=1;
}
else
{
box[1][2][grid[i][j]]=1;
}
}
else
{
if(j<3)
{
box[2][0][grid[i][j]]=1;
}
else if(j<6)
{
box[2][1][grid[i][j]]=1;
}
else
{
box[2][2][grid[i][j]]=1;
}
}
}
}
call(0);
}
return 0;
}