 Eu acho que muitas pessoas gostam de se socializar. redes e use aplicativos (por exemplo, o Tinder),mas geralmente leva muito tempo para gostar e enviar as primeirasmensagens. Acredito que são ações monótonas que apenas repelem acomunicação e o namoro. Se você é um programador, por que ser como todo mundo, vamosautomatizar o processo de ações monótonas comigo e deixar nossa atenção apenaspara uma comunicação agradável, mas sobre tudo em ordem.
Eu acho que muitas pessoas gostam de se socializar. redes e use aplicativos (por exemplo, o Tinder),mas geralmente leva muito tempo para gostar e enviar as primeirasmensagens. Acredito que são ações monótonas que apenas repelem acomunicação e o namoro. Se você é um programador, por que ser como todo mundo, vamosautomatizar o processo de ações monótonas comigo e deixar nossa atenção apenaspara uma comunicação agradável, mas sobre tudo em ordem.Treinamento
Neste artigo, usarei o navegador Chrome .
- Crie uma pasta com o projeto bot_tinder .
- bot_tinder chromedriver_for_win chromedriver_for_mac, chromedriver_for_lin (.. 3 Windows, macOS, Linux).
- webdriver ( Chrome, Firefox ), .
- chromedriver_for_win, chromedriver_for_mac, chromedriver_for_lin.
, , .. .
- Na pasta bot_tinder, crie um arquivo chamado log.txt ( anotamos o número de telefone no qual ele irá para o Tinder). Formatar sem uma figura oito: 9851234567
- Na pasta bot_tinder, crie os arquivos tinder.py , function.py .
Como resultado, você deve ter o seguinte: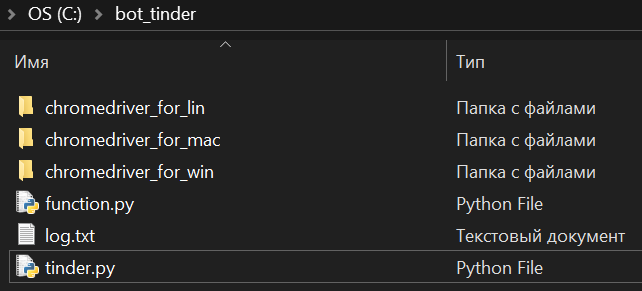 Cada pasta deve conter o arquivo do driver da web baixado anteriormente.
Cada pasta deve conter o arquivo do driver da web baixado anteriormente.Se você implementá-lo apenas para o seu sistema operacional, o arquivo do driver da web deve estar localizado em apenas uma das pastas com o nome do seu sistema operacional “chromedriver_for_seu SO ” .
Implementação
No arquivo tinder.py, importe a biblioteca:
from selenium import webdriver
No arquivo function.py , importe as bibliotecas:from selenium.common.exceptions import NoSuchElementException, ElementNotInteractableException
from sys import platform
from time import sleep
import datetime
Em seguida, no arquivo function.py , criamos as variáveis que precisaremos posteriormente:error = ''
warning = ''
ok = ''
oc = ''
like = ''
all_sleep = 3
like_sleep = 2
Os ícones foram excluídos pelo intérprete Habr, mas deve ser assim: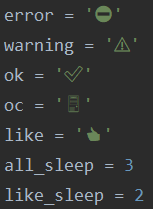 Você pode copiar os ícones do site ou usar a biblioteca de emojis .As variáveis all_sleep , like_sleep indicam o tempo de atraso em segundos.Depois de criarmos as funções no arquivo function.py :
Você pode copiar os ícones do site ou usar a biblioteca de emojis .As variáveis all_sleep , like_sleep indicam o tempo de atraso em segundos.Depois de criarmos as funções no arquivo function.py :
A primeira função determinará a data e a hora:
def get_data_time():
time_now = datetime.datetime.now()
return time_now.strftime("%d-%m-%Y %H:%M")
- A segunda função determinará seu sistema operacional e acessará o driver da web desejado :
def get_OC():
"""
Define OS.
:return: OS information and path to chromedriver.exe
"""
if platform == "linux" or platform == "linux2":
time_now = datetime.datetime.now()
information = "[" + get_data_time() + '] {} Linux'.format(oc)
put = "chromedriver_for_lin/** webdriver**"
return information, put
elif platform == "darwin":
time_now = datetime.datetime.now()
information = "[" + get_data_time() + '] {} Mac'.format(oc)
put = "chromedriver_for_mac/** webdriver**"
return information, put
elif platform == "win32":
time_now = datetime.datetime.now()
information = "[" + get_data_time() + '] {} Windows'.format(oc)
put = "chromedriver_for_win/chromedriver.exe"
return information, put
Lembre-se de escrever o caminho para o webdriver na variável put .
- A terceira função lerá o número de telefone do arquivo log.txt :
def information_from_txt_files():
"""
Read the .txt files
:return: Information. Login.
"""
information = ''
with open('log.txt', 'r') as file:
log = file.read()
information += "[" + get_data_time() + \
'] {} Tinder: {}'.format(ok, log)
return information, log
- A quarta função fechará o pop-up no site do Tinder:
def close_start_popups(browser):
"""
Close the popup.
:param browser: parameter of the running browser.
:return: information.
"""
sleep(all_sleep)
try:
browser.find_element_by_xpath('//button[@aria-label=""]').click()
return "[" + get_data_time() + "] {} .".format(ok)
except ElementNotInteractableException as err:
return "[" + get_data_time() + '] {} ' + err + ''.format(error)
except NoSuchElementException as err:
return "[" + get_data_time() + '] {} .'.format(error)
- A quinta função pressionará o botão "Login usando o número de telefone" :
def log_in_using_your_phone(browser):
"""
Click the Login button using the phone number.
:param browser: parameter of the running browser.
:return: information
"""
sleep(all_sleep)
try:
browser.find_element_by_xpath('//div[@id="modal-manager"]').find_element_by_xpath('//button[@aria-label=" "]').click()
return "[" + get_data_time() + "] {} .".format(ok)
except ElementNotInteractableException as err:
return "[" + get_data_time() + '] {} ' + err + ''.format(error)
except NoSuchElementException as err:
browser.find_element_by_xpath('//button[text()=" "]').click()
return log_in_using_your_phone(browser)
- A sexta função digitará o número de telefone:
def input_number_phone(browser, log):
"""
Enter the phone number.
:param browser: parameter of the running browser.
:param log: phone number.
:return: information.
"""
sleep(all_sleep)
try:
browser.find_element_by_name('phone_number').send_keys(log)
return "[" + get_data_time() + '] {} {}'.format(ok, log)
except NoSuchElementException:
return "[" + get_data_time() + '] {} .'.format(error)
- A sétima função pressiona o botão Continuar :
def go_on(browser):
"""
Click the Continue button.
:param browser: parameter of the running browser.
:return: information
"""
sleep(all_sleep)
try:
browser.find_element_by_xpath('//span[text()=""]').click()
return "[" + get_data_time() + '] {} '.format(ok)
except NoSuchElementException:
return "[" + get_data_time() + '] {} .'.format(error)
- A oitava função solicita que você digite o código que chegará ao seu telefone:
def code_check():
"""
Entering a code and checking the entered code.
:return: entered code
"""
kod_numbers = input("[" + get_data_time() + "] {} : ".format(warning))
if len(kod_numbers) != 6:
print("[" + get_data_time() + '] {} .'.format(error))
return code_check()
else:
print("[" + get_data_time() + '] {} .'.format(ok))
return kod_numbers
A função também verifica o número de dígitos inseridos.
- A nona função insere o código:
def input_cod(browser):
"""
Code entry.
:param browser: parameter of the running browser.
:return: information.
"""
try:
kod_numbers = code_check()
kod = browser.find_elements_by_xpath('//input[@type="tel"]')
n = 0
for i in kod:
i.send_keys(kod_numbers[n])
n += 1
return "[" + get_data_time() + '] {} .'.format(ok)
except NoSuchElementException:
return "[" + get_data_time() + '] {} .'.format(error)
- A décima função permite a definição de geolocalização:
def geolocation_ok(browser):
"""
We allow geolocation.
:param browser: parameter of the running browser.
:return: information.
"""
sleep(all_sleep)
try:
browser_button = browser.find_elements_by_tag_name("button")
button_list = {i.text: i for i in browser_button}
if "" in button_list.keys():
button = [value for key, value in button_list.items() if key == ""]
button[0].click()
return "[" + get_data_time() + '] {} .'.format(ok)
else:
return "[" + get_data_time() + '] {} .'.format(error)
except NoSuchElementException:
return "[" + get_data_time() + '] {} .'.format(error)
- A décima primeira função desativa o alerta:
def notice_off(browser):
"""
Turn off notifications.
:param browser: parameter of the running browser.
:return: information.
"""
sleep(all_sleep)
try:
browser_button = browser.find_elements_by_tag_name("button")
button_list = {i.text: i for i in browser_button}
if "" in button_list.keys():
button = [value for key, value in button_list.items() if key == ""]
button[0].click()
return "[" + get_data_time() + '] {} .'.format(ok)
else:
return "[" + get_data_time() + '] {} .'.format(error)
except NoSuchElementException:
return "[" + get_data_time() + '] {} .'.format(error)
- A décima segunda função fecha pop-ups:
def popup_windows_off(browser):
"""
Close popups.
:param browser: parameter of the running browser
:return: information
"""
sleep(like_sleep)
try:
browser_button = browser.find_elements_by_tag_name("button")
button_list = {i.text: i for i in browser_button}
if "" in button_list.keys():
button = [value for key, value in button_list.items() if key == ""]
button[0].click()
print("[" + get_data_time() + '] {} .'.format(ok))
except NoSuchElementException:
pass
- A décima terceira função coloca como:
def click_like(browser):
"""
Click LIKE.
:param browser: parameter of the running browser
:return: information
"""
sum_like = 0
while True:
try:
popup_windows_off(browser)
browser.find_element_by_xpath('//button[@aria-label=""]').click()
sum_like += 1
print("[" + get_data_time() + '] {} - {}'.format(like, str(sum_like)))
except NoSuchElementException:
print("[" + get_data_time() + '] {} .'.format(error))
Agora vá para o arquivo tinder.py e registre a importação de todas as funções:from function import get_OC, information_from_txt_files, close_start_popups, notice_off, click_like, log_in_using_your_phone, input_number_phone, go_on, input_cod, geolocation_ok
Defina o sistema operacional:
info, put = get_OC()
print(info)
Defina as opções do navegador:
chromedriver = put
options = webdriver.ChromeOptions()
options.add_argument('--start-minimize')
browser = webdriver.Chrome(executable_path=chromedriver, chrome_options=options)
Se você trabalha com o Firefox , leia como trabalhar com ele usando a biblioteca selenium.webdriver .
O navegador é iniciado e vai para a página do Tinder:
browser.get('https://tinder.com/app/recs')
Agora começamos a usar as funções preparadas anteriormente:
info_txt, log = information_from_txt_files()
print(info_txt)
print(close_start_popups(browser))
print(log_in_using_your_phone(browser))
print(input_number_phone(browser, log))
print(go_on(browser))
print(input_cod(browser))
print(go_on(browser))
print(geolocation_ok(browser))
print(notice_off(browser))
click_like(browser)
Conclusão
No final, obtenha um bot que acesse o site do Tinder e clique em Curtir.Você só precisa entrar no aplicativo em algumas horas e começar a conversar comsimpatias já mútuas .Automação é o esforço dos homens para simplificar o trabalho, para que as mulheres possam fazê-lo.
No próximo artigo, implementaremos a capacidade de enviar mensagens para gostos mútuos.