Olá Habr! Apresento a você a tradução do artigo "Web2Text: Remoção de clichês estruturados em profundidade" por uma equipe de autores Thijs Vogels, Octavian-Eugen Ganea e Carsten Eickhof.
As páginas da Web são uma fonte valiosa de informações para muitas tarefas de processamento de linguagem natural e recuperação de informações. A extração eficaz do conteúdo principal desses documentos é fundamental para o desempenho de aplicativos derivados. Para resolver esse problema, introduzimos um novo modelo que classifica e rotula blocos de texto em uma página HTMLcomo blocos de modelo ou blocos contendo conteúdo principal. Nosso método usa o modelo Hidden Markov sobre os potenciais obtidos a partir dos recursos do modelo de objeto do HTMLdocumento ( Document Object Model, DOM) usando redes neurais convolucionais ( Convolutional Neural Network, CNN). O método proposto melhora qualitativamente o desempenho para extrair dados de texto de páginas da web.
1. Introdução
Os métodos modernos de processamento de linguagem natural e recuperação de informações são altamente dependentes de grandes coleções de texto. A World Wide Web é uma fonte inesgotável de conteúdo para esses aplicativos. No entanto, um problema comum é que as páginas da Web incluem não apenas o conteúdo principal (texto), mas também anúncios, listas de hiperlinks, navegação, visualizações de outros artigos, banners etc. Esse conteúdo de modelo geralmente tem um impacto negativo no desempenho de um aplicativo derivado [15,24]. A tarefa de separar o texto principal em uma página da Web do conteúdo restante (modelo) na literatura é conhecida como "excluir um modelo padrão", "segmentar uma página da Web" ou "extrair conteúdo". Os métodos populares conhecidos para esse problema usam algoritmos baseados em regras ou aprendizado de máquina.As abordagens mais bem-sucedidas primeiro dividem a página da Web de entrada em blocos de texto e, em seguida, binárias{1, 0}Rotular cada bloco como o conteúdo ou modelo principal. Neste artigo, propomos o Modelo de Markov Oculto sobre os potenciais neurais para a tarefa de remover padrões. Utilizamos a capacidade das redes neurais convolucionais de estudar potenciais unários e emparelhar em blocos com base em combinações complexas não lineares de sinais baseadas em DOM. Durante a previsão, encontramos o rótulo de bloco mais provável {1, 0}, maximizando a probabilidade conjunta da sequência de rótulos usando o algoritmo de Viterbi [23]. A eficácia do nosso método é demonstrada em conjuntos padrão de dados comparativos.
. 2 . 3 , . 4 -.
2.
HTML- [7] Body Text Extractor (BTE). BTE , , HTML- -. , BTE , . , : (1) HTML, , , (2) , -.
DOM, HTML [11,19,6]. , , <table>, .
DOM . . [24] [22]. , -, -, -. .
. [10] , . HTML , , , . , , (), , (). DOM [4,21]. . [3] DOM, , . . [21] / , DOM .
«», . FIASCO . [2] (SVM) HTML- , DOM , . . [17] SVM . . [20] , , . , . CleanEval [1].
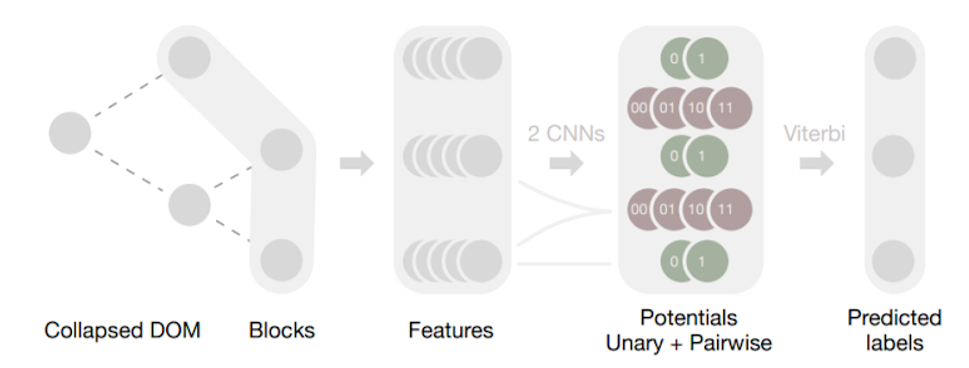
. 1. Web2Text. DOM (Collapsed DOM) - , . DOM. , , : . . , , , .
, DOM. , , . , - , .
3.
— - (- ) [1]. . 1.
3.1.
, - (X) HTML-. ( DOM) Jsoup [12].

. 2. DOM. : HTML, — DOM, — DOM.
DOM, i) , , ii) , , : , <br>, <checkbox>, <head>, <hr>, <iframe>, <img>, <input>. DOM. DOM- . 2 DOM, (<ul>), DOM. (, « »), . Collapsed () DOM (CDOM).
3.2.
. - , , . - , : i) HTML, ii) DOM, iii) DOM . DOM, . , , HTML. , DOM- ( #text) . , , . , Web2Text , , — .
3.3.
— , , , . , CDOM . .
. , CDOM, , CDOM. 128 , , « - <p>», « », « », « », « - » .. , , .
. 25 . . , , , 2, 3, 4 > 4. , HTML-, ..
3.4. (Convolutional Neural Network, CNN)
, , . , . pi (li = 1), pi (li = 0) , li i , . . pi, i + 1 (li = 1, li + 1 = 1), pi, i + 1 (li = 1, li + 1 = 0), pi, i + 1 (li = 0, li + 1 = 1) pi, i + 1 (li = 0, li + 1 = 0) — . .
CNN 5 , ReLU , (50, 50, 50, 10, 2) (50, 50, 50, 10, 4) . 1 (1, 1, 3, 3, 3) . CNN , , , . CNN , , , . , , . 2 , softmax. 4 , . , i . (dropout) 0,2 L2 10-4.
-:

l∗i — i, θunary — , n — .
-:

θpairwise — .
3.5.
- . (b0, b1, ..., bn) (l0, l1, ..., ln) ∈ {0, 1}n :

λ — . λ = 0,1 . [23], CNN.
4.
. Web2Text - . , . Web2Text .
4.1.
CleanEval 2007 [1] . 188 -. (60 ) (676 ). (55 ) (5 ). 10000 , , . CleanEval : (531 ), (58 ) (148 ).
. , ( CleanEval) . “- — ” ( ). , , . (, [20]) . (, ) (-, ). .
-, 10 . - ( ). , - , « ». -. , , , , 2/3 .
4.2.
[14] 10–3 5000 . - 128 - 9 . , . , .
4.3.
Web2Text , . BTE [7] Unfluff [8] . [17,16] — , , (. 1). CRF [20] CleanEval. (Conditional Random Field, CRF) , . , 4.1, CRF - . , , , , CleanEval. CleanEval, , .
. CRF [20] 9 705 . , CNN 17 960 , CNN 12 870 . 30 830. , .
4.4.
1 . , . , Web2Text (Accuracy), Recall F1 , CleanEval. , , , 3.2. , , Web2Text CNN, .

1. - CleanEval. : (55 — , 5 — , 676 — ) (531 — , 58 — , 148 — ). , .
. Web2Text 54 -; 35 DOM , 19 . Macbook Intel Core i5 2,8 .
4.5.
, , , . HTML, .
- ClueWeb12. . CW12-A 733M - (27,3 ) CW12-B 52M (1,95 ). Indri. 50 TREC Web Track 2013 [5].

2. . (*) HTML. (†) , .
2 , -. HTML . , , †. , , CW12-A, , , CW12-B. - . , (QL) , (RM). , . , (BTE, article-ext, large-ext, Unfluff) , . (CRF, Web2Text) . , Web2Text 0,05. , Web2Text CleanEval, 4.1.
5.
Web2Text -. , CRF [9], , DOM . CleanEval . , , , .
6.
, - .
, .
- Marco Baroni, Francis Chantree, Adam Kilgarriff, and Serge Sharoff. CleanEval: a competition for cleaning web pages. In LREC, 2008.
- Daniel Bauer, Judith Degen, Xiaoye Deng, Priska Herger, Jan Gasthaus, Eugenie Giesbrecht, Lina Jansen, Christin Kalina, Thorben Kräger, Robert Märtin, Martin Schmidt, Simon Scholler, Johannes Steger, Egon Stemle, and Stefan Evert. FIASCO: Filtering the internet by automatic subtree classification, osnabruck. In Building and Exploring Web Corpora: Proceedings of the 3rd Web as Corpus Workshop, incorporating CleanEval, volume 4, pages 111–121, 2007.
- Deepayan Chakrabarti, Ravi Kumar, and Kunal Punera. Page-level template detection via isotonic smoothing. In Proceedings of the 16th international conference on World Wide Web, pages 61–70. ACM, 2007.
- Deepayan Chakrabarti, Ravi Kumar, and Kunal Punera. A graph-theoretic approach to webpage segmentation. In Proceedings of the 17th international conference on World Wide Web, pages 377–386. ACM, 2008.
- Kevyn Collins-Thompson, Paul Bennett, Fernando Diaz, Charlie Clarke, and Ellen Voorhees. Overview of the TREC 2013 web track. In Proceedings of the 22nd Text Retrieval Conference (TREC’13), 2013.
- Sandip Debnath, Prasenjit Mitra, Nirmal Pal, and C Lee Giles. Automatic identification of informative sections of web pages. IEEE transactions on knowledge and data engineering, 17(9):1233–1246, 2005.
- Aidan Finn, Nicholas Kushmerick, and Barry Smyth. Fact or fiction: Content classification for digital libraries. Unrefereed, 2001.
- Adam Geitgey. Unfluff – an automatic web page content extractor for node.js!, 2014.
- John Gibson, Ben Wellner, and Susan Lubar. Adaptive web-page content identification. In Proceedings of the 9th annual ACM international workshop on Web information and data management, pages 105–112. ACM, 2007.
- Thomas Gottron. Content code blurring: A new approach to content extraction. In Database and Expert Systems Application, 2008. DEXA’08. 19th International Workshop on, pages 29–33. IEEE, 2008.
- Suhit Gupta, Gail Kaiser, David Neistadt, and Peter Grimm. DOM-based content extraction of HTML documents. In Proceedings of the 12th international conference on World Wide Web, pages 207–214. ACM, 2003.
- Jonathan Hedley. Jsoup HTML parser, 2009.
- Rong Jin, Alex G Hauptmann, and ChengXiang Zhai. Language model for information retrieval. In Proceedings of the 25th annual international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in information retrieval, pages 42–48. ACM, 2002.
- Diederik Kingma and Jimmy Ba. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980, 2014.
- Christian Kohlschütter. A densitometric analysis of web template content. In Proceedings of the 18th international conference on World wide web, pages 1165– 1166. ACM, 2009.
- Christian Kohlschütter et al. Boilerpipe – boilerplate removal and fulltext extraction from HTML pages. Google Code, 2010.
- Christian Kohlschütter, Peter Fankhauser, and Wolfgang Nejdl. Boilerplate detection using shallow text features. In Proceedings of the third ACM international conference on Web search and data mining, pages 441–450. ACM, 2010.
- Victor Lavrenko and W Bruce Croft. Relevance based language models. In Proceedings of the 24th annual international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in information retrieval, pages 120–127. ACM, 2001.
- Shian-Hua Lin and Jan-Ming Ho. Discovering informative content blocks from web documents. In Proceedings of the eighth ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, pages 588–593. ACM, 2002.
- Miroslav Spousta, Michal Marek, and Pavel Pecina. Victor: the web-page cleaning tool. In 4th Web as Corpus Workshop (WAC4)-Can we beat Google, pages 12–17, 2008.
- Fei Sun, Dandan Song, and Lejian Liao. Dom based content extraction via text density. In Proceedings of the 34th international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in Information Retrieval, pages 245–254. ACM, 2011.
- Karane Vieira, Altigran S Da Silva, Nick Pinto, Edleno S De Moura, Joao Cavalcanti, and Juliana Freire. A fast and robust method for web page template detection and removal. In Proceedings of the 15th ACM international conference on Information and knowledge management, pages 258–267. ACM, 2006.
- Andrew J Viterbi. Error bounds for convolutional codes and an asymptotically optimum decoding algorithm. In The Foundations Of The Digital Wireless World: Selected Works of AJ Viterbi, pages 41–50. World Scientific, 2010.
- Lan Yi, Bing Liu, and Xiaoli Li. Eliminating noisy information in web pages for data mining. In Proceedings of the ninth ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, pages 296–305. ACM, 2003.