Oi Oi! Mais uma vez, preparamos para você uma seleção de perguntas e tarefas interessantes a partir de entrevistas nas principais empresas de TI! A propósito, as respostas para os problemas da edição anterior já foram publicadas . Os problemas serão exibidos toda semana - fique ligado! A coluna é suportada pela agência de recrutamento Spice IT .Nesta semana, coletamos tarefas de entrevistas com a empresa holandesa Philips.
Os problemas serão exibidos toda semana - fique ligado! A coluna é suportada pela agência de recrutamento Spice IT .Nesta semana, coletamos tarefas de entrevistas com a empresa holandesa Philips.Questões
1. Veneno e RatoExistem 1000 garrafas de vinho. Uma das garrafas contém vinho envenenado. Um rato morre uma hora depois de beber o vinho envenenado. Quantos ratos mínimos são necessários para descobrir qual frasco contém veneno em uma hora.
Transferir1000 . . , . , , .
2. 5 piratas e 100 moedas de ouroThere are 5 pirates, they must decide how to distribute 100 gold coins among them. The pirates have seniority levels, the senior-most is A, then B, then C, then D, and finally the junior-most is E.
Rules of distribution are:
- The most senior pirate proposes a distribution of coins.
- All pirates vote on whether to accept the distribution.
- If the distribution is accepted, the coins are disbursed and the game ends.
- If not, the proposer is thrown and dies, and the next most senior pirate makes a new proposal to begin the system again.
- In case of a tie vote the proposer can has the casting vote
Rules every pirates follows:
- Every pirate wants to survive
- Given survival, each pirate wants to maximize the number of gold coins he receives.
What is the maximum number of coins that pirate A might get?
5 , , 100 . , — A, B, C, D, , , — E.
:
, :
?Dado um número inteiro, a tarefa é encontrar o fatorial do número.
Entrada:
A primeira linha de entrada contém um número inteiro T, indicando o número de casos de teste.
A primeira linha de cada caso de teste é N, o número cujo fatorial deve ser encontrado
Saída:
Imprima o fatorial do número em uma linha separada.
Restrições: Exemplo: Entrada de Saída
1 ≤ T ≤ 100
1 ≤ N ≤ 1000
3
5
10
2
120
3628800
2
Transferir, , .
:
T, .
— N, ,
:
.
:
1 ≤ T ≤ 100
1 ≤ N ≤ 1000
:
3
5
10
2
:
120
3628800
2
2. Diâmetro da árvore bináriaGiven a Binary Tree, find diameter of it.
+The diameter of a tree is the number of nodes on the longest path between two leaves in the tree. The diagram below shows two trees each with diameter nine, the leaves that form the ends of a longest path are shaded (note that there is more than one path in each tree of length nine, but no path longer than nine nodes).
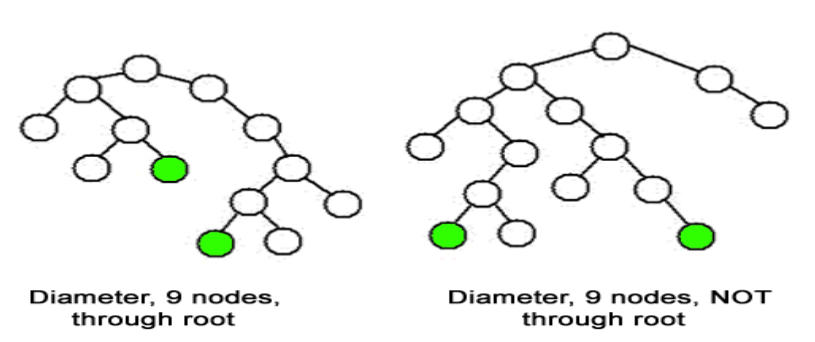
Input Format:
First line of input contains the number of test cases T. For each test case, there will be only a single line of input which is a string representing the tree as described below:
1. The values in the string are in the order of level order traversal of the tree where, numbers denotes node values, and a character “N” denotes Filho nulo .
2. Por exemplo:

Para a árvore acima, a sequência será: 1 2 3 NN 4 6 N 5 NN 7 N
Formato de saída:
Para cada caixa de teste, em uma nova linha, imprima o diâmetro.
Sua tarefa:
você precisa concluir a função diâmetro () que toma o nó como parâmetro e retorna o diâmetro.
Restrições: Exemplo: Entrada: Saída: Explicação: Testcase1: A árvore é O diâmetro é de 3 comprimentos. Testcase2: A árvore é O diâmetro é de 4 comprimento.
1 <= T <= 100
1 <= Number of nodes <= 100
1 <= Data of a node <= 100
2
1 2 3
10 20 30 40 60
3
4
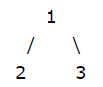
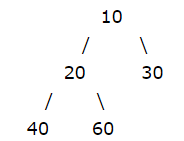
Transferir,
.
+
— . , , , , ( , , ).
 :
:T. ,
, , :
1. , , “N” .
2. :

: 1 2 3 N N 4 6 N 5 N N 7 N
:.
:diameter(), node .
:1 < = T <= 100
1 < = < = 100
1 < = <= 100:
:2
1 2 3
10 20 30 40 60:3
4:1: :
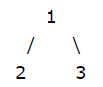
3.
2: :
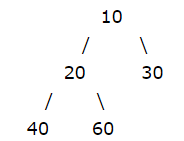
4 .
3. preto e brancoHow many ways are there to place a black and a white knight on an N * M chessboard such that they do not attack each other? The knights have to be placed on different squares. A knight can move two squares horizontally and one square vertically (L shaped), or two squares vertically and one square horizontally (L shaped). The knights attack each other if one can reach the other in one move.
Input:
The first line contains the number of test cases T. Each of the next T lines contains two integers N and M which is size of matrix.
Output:
For each testcase, print the required answer, i.e, number of possible ways to place knights.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 100
1 <= N, M <= 105
Example:
Input:
3
2 2
2 3
4 5
Output:
12
26
312
Explanation:
Testcase 1: We can place a black and a white knight in 12 possible ways such that none of them attracts each other.
N * M , ? . (L- ), (L- ). , .
:
T. T N M, .
:
, .
:
1 < = T <= 100
1 <= N, M < = 105
:
:
3
2 2
2 3
4 5
:
12
26
312
:
1: 12 , .
1. 10 , . . 10, Log2(1000).
, 1 1000 . , . . 1 , 2 . 5, 7 9 , 42 ( 0000101010) .
2— 98.
1. , A, B C , D E. , (D (100, 0). , E - , 0.
2. , A B , C, D E . D , (C (99, 0, 1), E C).
3. , A . B, C, D E . , B 1 D. (99, 0, 1, 0)
4. A 3, 1 C 1 E, . - (98, 0, 1, 0, 1).
, B , (B , a ). A 2 , B , .
1:
using namespace boost::multiprecision;
int main()
{
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
cpp_int n, res = 1;
cin >> n;
while (n != 1)
{
res = res * n;
n = n - 1;
}
cout << res << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
2int find(Node* root, int &h)
{
if (root == NULL) return 0;
int lh = find(root->left, h);
int rh = find(root->right, h);
h = max(h, lh + rh + 1);
return max(lh, rh) + 1;
}
int diameter(Node* root)
{
int h = -1;
find(root, h);
return h;
}
3#include <iostream>
#include <cstdint>
typedef unsigned __int128 uint128_t;
int main()
{
unsigned t;
uint64_t n, m, upper, lower;
uint128_t res;
std::cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
std::cin >> n >> m;
res = n*m;
res *= (n*m-1);
if (n>1 && m>1)
res -= 4*(2*n*m-3*n-3*m+4);
upper = (uint64_t)(res/1000000000000000000);
lower = (uint64_t)(res%1000000000000000000);
if (upper)
{
std::cout << upper;
uint64_t digitChecker = 100000000000000000;
while (lower/digitChecker == 0 && digitChecker)
{
std::cout << 0;
digitChecker /= 10;
}
}
std::cout << lower << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}