Artikel ini membahas bahasa scripting deklaratif JavaPath sebagai alternatif untuk menggunakan Java Reflection dan cara untuk menghindari "neraka layanan" dalam aplikasi mandiri menggunakan struktur data yang kompleks.
Deskripsi masalah
Pertimbangkan struktur yang sangat bersarang
class A{
B b;
}
class B{
C c;
}
class C{
String name;
}
Jika kita perlu menetapkan nilai ke bidang nama kelas C tanpa memiliki akses langsung ke instance A, maka lapisan perantara API layanan biasanya datang untuk menyelamatkan.
private A a;
public void setNameService(String name) {
a.b.c.name = name;
}
, , . , .
private A a;
public void setNameService(String name) {
if(a == null) {
a = new A();
}
if(a.b == null) {
a.b = new B();
}
if(a.b.c == null) {
a.b.c = new C();
}
a.b.c.name = name;
}
, , setNameService(String name) , , a, b c, , .
API, , , API. . , . , , 'C' name, 'B' 'A' .
, - . , , , . - - . , . , , , , .
JavaPath , .
JavaPath
JavaPath.
private A a = new A();
private final JavaPath javaPath = new JavaPath(A.class);
public void setNameService(String name) {
javaPath.evalPath("b.c.name", a, name);
}
setNameService.
, JavaPath — , Java. JavaPath . , . JavaPath . -public. . JavaPath private final .
: — JavaPath!
final String str = "VALUE";
JavaPath javaPath = new JavaPath(String.class);
assertEquals("VALUE",str);
// private final byte[] value; String
javaPath.evalPath("value",str,"THE HACK".getBytes());
assertEquals("THE HACK",str);
- , , JavaPath Java Reflection .
, JavaPath . . .
JavaPath
public Object evalPath(String path, Object root, Object... values);
evalPath
, . C. .
class C{
String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
. .
A a = new A();
JavaPath javaPath = new JavaPath(A.class);
public void setNameService(String name) {
javaPath.evalPath("b.c.setName", a, name);
}
JavaPath , , , :
javaPath.evalPath("b.c.setName($)", a, name);
$ $0 — .
a0.a1.… .an
a0.a1.… .an-1
, , / null. an . , , , evalPath. , . JavaPath .
JavaPath
JavaPath , . . . , , , . , , ,
Java . , , , API.
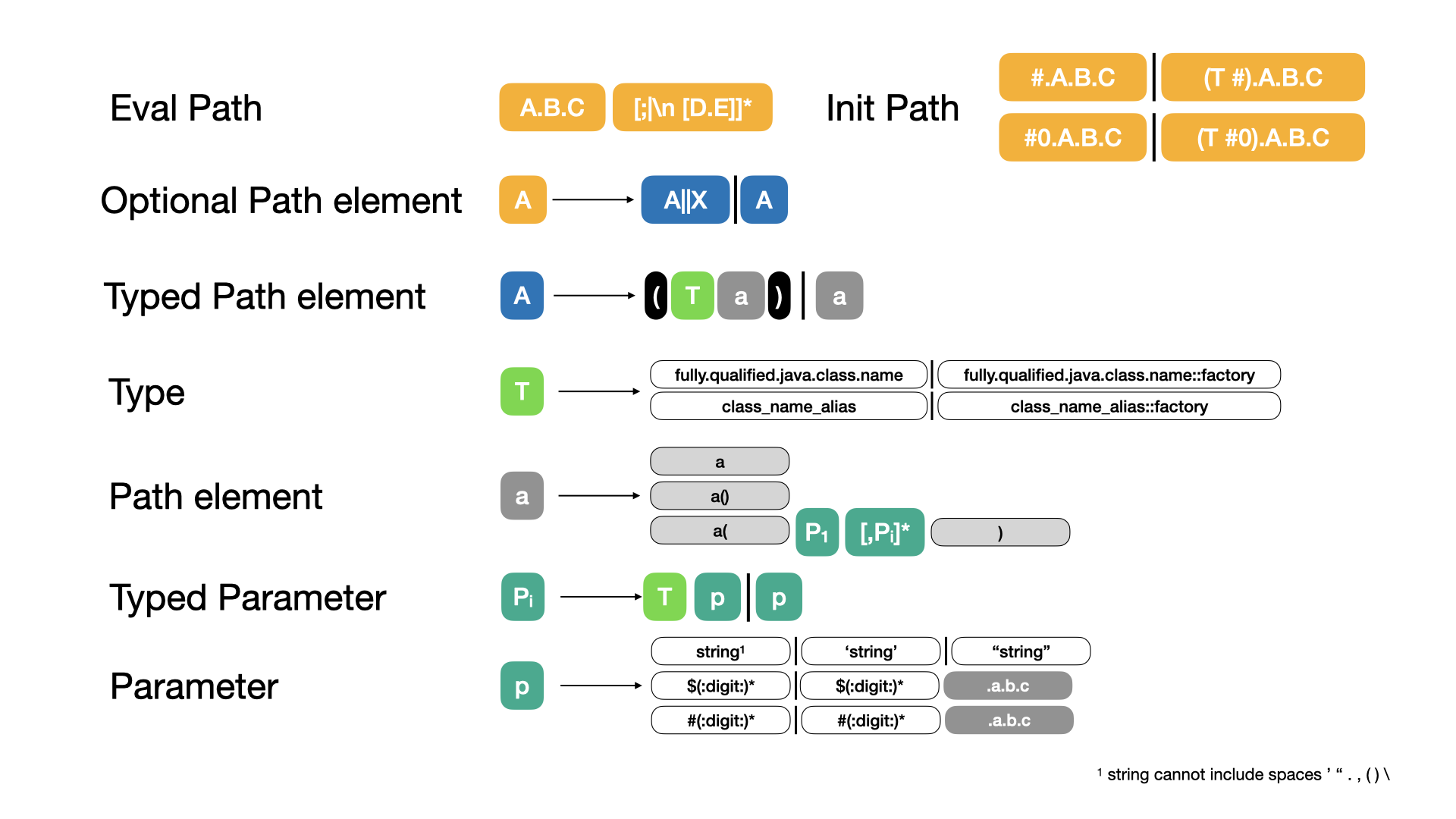
JavaPath . . , , , . . , , , .. — .
$ #

, evalPath $[:digit:]* . $ , . .
.
. : #[:digit:]* # #0
.
, -.
public class A {
A parent;
A child;
String name;
public A(A parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
}
A a = new A(null);
JavaPath javaPath = new JavaPath(A.class);
javaPath.evalPath("name",a,"PARENT");
javaPath.evalPath("child(#0).name",a,"CHILD");
javaPath.evalPath("child(#0).child(#1).name",a,"GRAND-CHILD");
assertEquals("PARENT",a.name);
assertEquals("CHILD",a.child.name);
assertEquals("GRAND-CHILD",a.child.child.name);
assertEquals("CHILD",a.child.child.parent.name);
assertEquals("PARENT",a.child.child.parent.parent.name);
— .
"a.set('$0')"
InLine :
, JavaPath. , , . .
, , valueOf ( , enum ) .
, valueOf - , StringConverter, .
- null , . .
, , , . — . Java, .
"(T a).b"
: map .
public class A {
Map<String,String> map;
}
A a = new A();
JavaPath javaPath = new JavaPath(A.class);
// map
javaPath.evalPath("(HashMap map).put(firstName,$)", a, "John");
// , .
javaPath.evalPath("map.put(lastName,$)", a, "Silver");
.
javaPath.evalPath("(HashMap map(int 100,float '0.8')).put(firstName,$)", a, "John");
, null. map .
enum PhoneType{HOME,CELL,WORK}
public static class A {
String firstName;
String lastName;
Map<PhoneType, Set<String>> phones;
Map<String, PhoneType> reversedPhones;
}
A a = new A();
ClassRegistry classRegistry = new ClassRegistry();
classRegistry.registerClass(PhoneType.class,PhoneType.class.getSimpleName());
JavaPath javaPath = new JavaPath(A.class,classRegistry);
javaPath.evalPath("(map phones).put(PhoneType WORK)", a, new HashSet<>());
javaPath.evalPath("phones.computeIfAbsent(PhoneType HOME,key->new HashSet).@", a);
javaPath.evalPath("phones.computeIfAbsent(PhoneType CELL,key->new HashSet).@", a);
javaPath.evalPath("(map reversedPhones).@", a);
javaPath.evalPath("firstName", a, "John");
javaPath.evalPath("lastName", a, "Smith");
javaPath.evalPath("phones.get(PhoneType CELL).add", a, "1-101-111-2233");
javaPath.evalPath("phones.get(PhoneType HOME).add", a, "1-101-111-7865");
javaPath.evalPath("phones.get(PhoneType WORK).add", a, "1-105-333-1100");
javaPath.evalPath("phones.get(PhoneType WORK).add($)", a, "1-105-333-1104");
javaPath.evalPath("reversedPhones.put($,PhoneType CELL)", a, "1-101-111-2233");
javaPath.evalPath("reversedPhones.put($,PhoneType HOME)", a, "1-101-111-7865");
javaPath.evalPath("reversedPhones.put($,PhoneType WORK)", a, "1-105-333-1100");
javaPath.evalPath("reversedPhones.put($,PhoneType WORK)", a, "1-105-333-1104");
@
@ . , . .
||
null, JavaPath . .
::
, -, ::
ClassRegistry
, , .. ClassRegistry , JavaPath.
ClassRegistry . ClassRegistry, JavaPath.
PhoneType
ClassRegistry classRegistry = new ClassRegistry();
classRegistry.registerClass(PhoneType.class,PhoneType.class.getSimpleName(),"Phone");
JavaPath javaPath = new JavaPath(A.class,classRegistry);
PhoneType , , Phone.
ClassRegistry . , :: .
. ClassRegistry . , StringConverter — .
public class A {
...
static {
ClassRegistry.registerGlobalStringConverter(A.class,A::stringToA);
}
public static A stringToA(String str) {
A a = new A("{"+str+"}");
return a;
}
}
public class B {
A a;
}
JavaPath javaPath = new JavaPath(B.class); // A::stringToA
@PathElement @NoPathElement
@PathElement .
public class A {
String name;
@PathElement({"name","first_name","firstName"})
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
, setName "name", . .
@NoPathElement JavaPath.
public class A {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
@NoPathElement
private final String protectedField = "IMMUTABLE BY JAVA PATH!";
public void add(String str) {
stringBuilder.append(str == null ? "N/A" : str);
}
@NoPathElement
public void add(Object val) {
stringBuilder.append(val);
}
}
.
JavaPath . .
public class A {
String firstName;
String lastName;
int age;
}
A a = new A();
JavaPath javaPath = new JavaPath(A.class);
javaPath.evalPath("firstName; lastName; age", a, "John","Smith",55);
javaPath.evalPath("firstName($); lastName($); age($)", a, "John","Smith",55);
javaPath.evalPath("firstName($0); lastName($1); age($2)", a, "John","Smith",55);
'$', , . , firstName($) "John" ( , ), age($) — 55 ( , ). .
, , .
. .
JavaPath
, . , ? initPath
.
JavaPath . , . , , root. # #0
initPath .
:
Object instanceOfA = javaPath.initPath("(com.my.project.A #0).b", "test");
A instanceOfA = javaPath.initPath(A.class, "#.b", "test");
// , # #0
A instanceOfA = javaPath.initPath(A.class, "root.b", "test");
Metode setEnablePathCaching (boolean enableCaching) dari kelas JavaPath memungkinkan Anda untuk menyimpan hasil parser di cache. Jangan bingung dengan caching hirarki bidang dan metode kelas yang tidak dapat dinonaktifkan. Tembolok jalur dinonaktifkan secara default karena dapat menyebabkan konsumsi memori yang tidak terkendali jika jalur dihitung secara dinamis.
Contoh - akan ada tiga jalur berbeda di cache:
evalPath("user.name('John'));"
evalPath("user.name('Peter'));"
evalPath("user.name('Mike'));"
Alih-alih, gunakan nilai-nilai variabel yang diteruskan secara eksplisit. Contoh di bawah akan menyimpan satu jalur.
evalPath("user.name($0)","John");
evalPath("user.name($0)","Peter");
evalPath("user.name($0)","Mike");
Ketergantungan
Java8 dan yang lebih lama
Repositori Maven
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aegisql</groupId>
<artifactId>java-path</artifactId>
<version>0.2.0</version>
</dependency>