 क्या यह ध्वनि परिचित है: "मैंने पाठ्यक्रम लेने के बाद वेब विकास करना शुरू किया"?शायद आप डेटा संरचनाओं और एल्गोरिदम के संदर्भ में कंप्यूटर विज्ञान की मूल बातें के बारे में अपने ज्ञान में सुधार करना चाहते हैं। आज हम JS उदाहरण का उपयोग करते हुए कुछ सबसे सामान्य डेटा संरचनाओं के बारे में बात करेंगे।
क्या यह ध्वनि परिचित है: "मैंने पाठ्यक्रम लेने के बाद वेब विकास करना शुरू किया"?शायद आप डेटा संरचनाओं और एल्गोरिदम के संदर्भ में कंप्यूटर विज्ञान की मूल बातें के बारे में अपने ज्ञान में सुधार करना चाहते हैं। आज हम JS उदाहरण का उपयोग करते हुए कुछ सबसे सामान्य डेटा संरचनाओं के बारे में बात करेंगे।1. स्टैक (कॉल) (स्टैक)
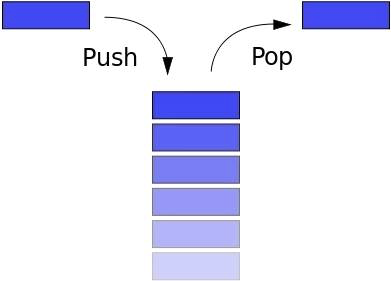 स्टैक लिफो सिद्धांत का अनुसरण करता है (लास्ट इन फर्स्ट आउट - लास्ट इन, फर्स्ट आउट)। यदि आपने पुस्तकों को एक-दूसरे के ऊपर ढेर कर दिया है और सबसे कम पुस्तक लेना चाहते हैं, तो पहले शीर्ष पर ले जाएँ, फिर अगले एक पर, आदि। ब्राउज़र में "बैक" बटन आपको पिछले पृष्ठ पर जाने (वापसी) की अनुमति देता है।स्टैक में निम्न विधियाँ हैं:
स्टैक लिफो सिद्धांत का अनुसरण करता है (लास्ट इन फर्स्ट आउट - लास्ट इन, फर्स्ट आउट)। यदि आपने पुस्तकों को एक-दूसरे के ऊपर ढेर कर दिया है और सबसे कम पुस्तक लेना चाहते हैं, तो पहले शीर्ष पर ले जाएँ, फिर अगले एक पर, आदि। ब्राउज़र में "बैक" बटन आपको पिछले पृष्ठ पर जाने (वापसी) की अनुमति देता है।स्टैक में निम्न विधियाँ हैं:- धक्का: नया आइटम जोड़ें
- पॉप: शीर्ष तत्व को हटा दें, इसे वापस करें
- झांकना: शीर्ष तत्व लौटना
- लंबाई: स्टैक पर तत्वों की संख्या लौटाएं
JS में एक सरणी में स्टैक विशेषताएँ हैं, लेकिन हम फ़ंक्शन स्टैक () का उपयोग करके इसे स्क्रैच से बनाएंगे:function Stack() {
this.count = 0
this.storage = {}
this.push = function(value) {
this.storage[this.count] = value
this.count++
}
this.pop = function() {
if (this.count === 0) return undefined
this.count--
let result = this.storage[this.count]
delete this.storage[this.count]
return result
}
this.peek = function() {
return this.storage[this.count - 1]
}
this.size = function() {
return this.count
}
}
2. कतार (कतार)
 एक कतार एक ढेर जैसा दिखता है। अंतर यह है कि कतार एफआईएफओ सिद्धांत (फर्स्ट इन फर्स्ट आउट - फ़र्स्ट इन, फ़र्स्ट आउट) का अनुसरण करती है। जब आप लाइन में खड़े होते हैं, तो उसमें पहले वाला हमेशा पहला होगा।कतार में निम्नलिखित विधियाँ हैं:
एक कतार एक ढेर जैसा दिखता है। अंतर यह है कि कतार एफआईएफओ सिद्धांत (फर्स्ट इन फर्स्ट आउट - फ़र्स्ट इन, फ़र्स्ट आउट) का अनुसरण करती है। जब आप लाइन में खड़े होते हैं, तो उसमें पहले वाला हमेशा पहला होगा।कतार में निम्नलिखित विधियाँ हैं:- enqueue: कतार में प्रवेश करें, अंत में एक आइटम जोड़ें
- dequeue: कतार छोड़ें, पहला तत्व हटाएं और उसे वापस करें
- सामने: पहला तत्व प्राप्त करें
- isEmpty: जाँच करें कि क्या कतार खाली है
- आकार: कतार में वस्तुओं की संख्या प्राप्त करें
JS में एक सरणी में कुछ कतार विशेषताएँ हैं, इसलिए हम इसे प्रदर्शन के लिए उपयोग कर सकते हैं:function Queue() {
let collection = []
this.print = function() {
console.log(collection)
}
this.enqueue = function(element) {
collection.push(element)
}
this.dequeue = function() {
return collection.shift()
}
this.front = function() {
return collection[0]
}
this.isEmpty = function() {
return collection.length === 0
}
this.size = function() {
return collection.length
}
}
प्राथमिकता का क्रम (प्राथमिकता)
कतार का एक उन्नत संस्करण है। प्रत्येक आइटम को प्राथमिकता दें और आइटम उसी के अनुसार क्रमबद्ध होंगे:function PriorityQueue() {
...
this.enqueue = function(element) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
collection.push(element)
} else {
let added = false
for (let i = 0; i < collection.length; i++) {
if (element[1] < collection[i][1]) {
collection.splice(i, 0, element)
added = true
break;
}
}
if (!added) {
collection.push(element)
}
}
}
}
परिक्षण:let pQ = new PriorityQueue()
pQ.enqueue([gannicus, 3])
pQ.enqueue([spartacus, 1])
pQ.enqueue([crixus, 2])
pQ.enqueue([oenomaus, 4])
pQ.print()
परिणाम:[
[spartacus, 1],
[crixus, 2],
[gannicus, 3],
[oenomaus, 4]
]
3. एक लिंक्ड सूची (नोड्स और लिंक या पॉइंटर्स की लिंक्ड सूची) (लिंक्ड सूची)
 वस्तुतः, एक लिंक की गई सूची एक जंजीर डेटा संरचना है, जहां प्रत्येक नोड में दो भाग होते हैं: नोड डेटा और अगले नोड के लिए एक सूचक। लिंक की गई सूची और सशर्त सरणी क्रमबद्ध भंडारण के साथ रैखिक डेटा संरचनाएं हैं। अंतर इस प्रकार हैं:एक एकल लिंक की गई सूची में निम्नलिखित विधियाँ हैं:
वस्तुतः, एक लिंक की गई सूची एक जंजीर डेटा संरचना है, जहां प्रत्येक नोड में दो भाग होते हैं: नोड डेटा और अगले नोड के लिए एक सूचक। लिंक की गई सूची और सशर्त सरणी क्रमबद्ध भंडारण के साथ रैखिक डेटा संरचनाएं हैं। अंतर इस प्रकार हैं:एक एकल लिंक की गई सूची में निम्नलिखित विधियाँ हैं:- आकार: नोड्स की संख्या लौटाएं
- सिर: पहला तत्व लौटाओ (सिर - सिर)
- जोड़ें: अंत में एक तत्व जोड़ें (पूंछ - पूंछ)
- निकालें: कई नोड्स निकालें
- indexOf: रिटर्न नोड इंडेक्स
- elementAt: इंडेक्स द्वारा रिटर्न नोड
- addAt: किसी विशिष्ट स्थान पर एक नोड डालें (अनुक्रमणिका द्वारा)
- निष्कासन: किसी विशिष्ट नोड को हटाएं (अनुक्रमणिका द्वारा)
function Node(element) {
this.element = element
this.next = null
}
function LinkedList() {
let length = 0
let head = null
this.size = function() {
return length
}
this.head = function() {
return head
}
this.add = function(element) {
let node = new Node(element)
if (head === null) {
head = node
} else {
let currentNode = head
while (currentNode.next) {
currentNode = currentNode.next
}
currentNode.next = node
}
length++
}
this.remove = function(element) {
let currentNode = head
let previousNode
if (currentNode.element !== element) {
head = currentNode.next
} else {
while (currentNode.element !== element) {
previousNode = currentNode
currentNode = currentNode.next
}
previousNode.next = currentNode.next
}
length--
}
this.isEmpty = function() {
return length === 0
}
this.indexOf = function(element) {
let currentNode = head
let index = -1
while (currentNode) {
index++
if (currentNode.element === element) {
return index
}
currentNode = currentNode.next
}
return -1
}
this.elementAt = function(index) {
let currentNode = head
let count = 0
while (count < index) {
count++
currentNode = currentNode.next
}
return currentNode.element
}
this.addAt = function(index, element) {
let node = new Node(element)
let currentNode = head
let previousNode
let currentIndex = 0
if (index > length) return false
if (index === 0) {
node.next = currentNode
head = node
} else {
while (currentIndex < index) {
currentIndex++
previousNode = currentNode
currentNode = currentNode.next
}
node.next = currentNode
previousNode.next = node
}
length++
}
this.removeAt = function(index) {
let currentNode = head
let previousNode
let currentIndex = 0
if (index < 0 || index >= length) return null
if (index === 0) {
head = currentIndex.next
} else {
while (currentIndex < index) {
currentIndex++
previousNode = currentNode
currentNode = currentNode.next
}
previousNode.next = currentNode.next
}
length--
return currentNode.element
}
}
4. संग्रह (मूल्यों का) (सेट)
 एक संग्रह (कई) गणित की मूल अवधारणाओं में से एक है: अच्छी तरह से परिभाषित और अलग-थलग वस्तुओं का एक सेट। ES6 ने एक संग्रह पेश किया जो एक सरणी के लिए कुछ समानता रखता है। हालांकि, संग्रह डुप्लिकेट तत्वों को शामिल करने की अनुमति नहीं देता है और इसमें अनुक्रमित नहीं होते हैं।मानक संग्रह में निम्नलिखित विधियाँ हैं:
एक संग्रह (कई) गणित की मूल अवधारणाओं में से एक है: अच्छी तरह से परिभाषित और अलग-थलग वस्तुओं का एक सेट। ES6 ने एक संग्रह पेश किया जो एक सरणी के लिए कुछ समानता रखता है। हालांकि, संग्रह डुप्लिकेट तत्वों को शामिल करने की अनुमति नहीं देता है और इसमें अनुक्रमित नहीं होते हैं।मानक संग्रह में निम्नलिखित विधियाँ हैं:- मान: संग्रह में सभी आइटम लौटाते हैं
- आकार: तत्वों की संख्या लौटाएं
- है: अगर एक आइटम संग्रह में है की जाँच करें
- जोड़ें: आइटम जोड़ें
- निकालें: एक आइटम निकालें
- संघ: दो संग्रह के चौराहे क्षेत्र वापस
- अंतर: दो संग्रहों के बीच अंतर लौटाएं
- सबसेट: जाँच करें कि क्या एक संग्रह दूसरे का उपसमूह है
function MySet() {
let collection = []
this.has = function(element) {
return (collection.indexOf(element) !== -1)
}
this.values = function() {
return collection
}
this.size = function() {
return collection.length
}
this.add = function(element) {
if (!this.has(element)) {
collection.push(element)
return true
}
return false
}
this.remove = function(element) {
if (this.has(element)) {
index = collection.indexOf(element)
collection.splice(index, 1)
return true
}
return false
}
this.union = function(otherSet) {
let unionSet = new MySet()
let firstSet = this.values()
let secondSet = otherSet.values()
firstSet.forEach(i => unionSet.add(i))
secondSet.forEach(i => unionSet.add(i))
}
this.intersection = function(otherSet) {
let intersectionSet = new MySet()
let firstSet = this.values()
firstSet.forEach(function(e) {
if (otherSet.has(e)) {
intersectionSet.add(e)
}
})
return intersectionSet
}
this.difference = function(otherSet) {
let differenceSet = new MySet()
let firstSet = this.values()
firstSet.forEach(function(e) {
if (!otherSet.has(e)) {
differenceSet.add(e)
}
})
return differenceSet
}
this.subset = function(otherSet) {
lat firstSet = this.values()
return firstSet.every(value => otherSet.has(value))
}
}
5. हैश टेबल (हैश टेबल)
 एक हैश तालिका एक डेटा संरचना है जो कुंजी-मूल्य के आधार पर बनाई गई है। कुंजी द्वारा मूल्यों की खोज की उच्च गति के कारण, इसका उपयोग मानचित्र, शब्दकोश और ऑब्जेक्ट जैसी संरचनाओं में किया जाता है। जैसा कि चित्र में दिखाया गया है, हैश तालिका में एक हैश फ़ंक्शन होता है जो कुंजी को संख्याओं की एक सूची में परिवर्तित करता है जो कुंजी के नाम (मान) के रूप में उपयोग किए जाते हैं। प्रमुख मूल्य खोज समय ओ (1) तक पहुंच सकता है। समान कुंजी को समान मान लौटना चाहिए - यह हैश फ़ंक्शन का सार है।एक हैश तालिका में निम्नलिखित विधियाँ हैं:
एक हैश तालिका एक डेटा संरचना है जो कुंजी-मूल्य के आधार पर बनाई गई है। कुंजी द्वारा मूल्यों की खोज की उच्च गति के कारण, इसका उपयोग मानचित्र, शब्दकोश और ऑब्जेक्ट जैसी संरचनाओं में किया जाता है। जैसा कि चित्र में दिखाया गया है, हैश तालिका में एक हैश फ़ंक्शन होता है जो कुंजी को संख्याओं की एक सूची में परिवर्तित करता है जो कुंजी के नाम (मान) के रूप में उपयोग किए जाते हैं। प्रमुख मूल्य खोज समय ओ (1) तक पहुंच सकता है। समान कुंजी को समान मान लौटना चाहिए - यह हैश फ़ंक्शन का सार है।एक हैश तालिका में निम्नलिखित विधियाँ हैं:- जोड़ें: एक कुंजी / मूल्य जोड़ी जोड़ें
- निकालें: एक जोड़ी निकालें
- लुकअप: मान को कुंजी से खोजें
function hash(string, max) {
let hash = 0
for (let i = 0; i < string.length; i++) {
hash += string.charCodeAt(i)
}
return hash % max
}
function HashTable() {
let storage = []
const storageLimit = 4
this.add = function(key, value) {
let index = hash(key, storageLimit)
if (storage[index] === undefined) {
storage[index] = [
[key, value]
]
} else {
let inserted = false
for (let i = 0; i < storage[index].len; i++) {
if (storage[index][i][0] === key) {
storage[index][i][1] = value
inserted = true
}
}
if (inserted === false) {
storage[index].push([key, value])
}
}
}
this.remove = function(key) {
let index = hash(key, storageLimit)
if (storage[index].length === 1 && storage[index][0][0] === key) {
delete storage[index]
} else {
for (let i = 0; i < storage[index]; i++) {
if (storage[index][i][0] === key) {
delete storage[index][i]
}
}
}
}
this.lookup = function(key) {
let index = hash(key, storageLimit)
if (storage[index] === undefined) {
return undefined
} else {
for (let i = 0; i < storage[index].length; i++) {
if (storage[index][i][0] === key) {
return storage[index][i][1]
}
}
}
}
}
6. पेड़
 एक पेड़ संरचना एक बहुपरत (बहु-स्तरीय) संरचना है। यह भी एक सरणी, स्टैक और कतार के विपरीत, एक nonlinear संरचना है। तत्वों को जोड़ने और खोजने के मामले में यह संरचना बहुत प्रभावी है। यहां पेड़ की संरचना की कुछ अवधारणाएं दी गई हैं:
एक पेड़ संरचना एक बहुपरत (बहु-स्तरीय) संरचना है। यह भी एक सरणी, स्टैक और कतार के विपरीत, एक nonlinear संरचना है। तत्वों को जोड़ने और खोजने के मामले में यह संरचना बहुत प्रभावी है। यहां पेड़ की संरचना की कुछ अवधारणाएं दी गई हैं:- मूल: मूल तत्व, कोई माता-पिता नहीं है
- मूल नोड: शीर्ष परत (स्तर) का एक सीधा नोड, केवल एक ही हो सकता है
- बाल नोड: निचले स्तर के प्रत्यक्ष नोड (ओं), कई हो सकते हैं
- भाई-बहन: एक माता-पिता के बच्चे
- पत्ती: "बच्चों" के बिना गाँठ
- बढ़त: नोड्स के बीच की शाखा या लिंक (लिंक)
- पथ: पथ (लिंक का सेट) प्रारंभ नोड से लक्ष्य तत्व तक
- पेड़ की ऊँचाई: एक विशिष्ट तत्व से नोड तक सबसे लंबे पथ के लिंक की संख्या जिसमें बच्चे नहीं हैं
- नोड की गहराई: रूट नोड से एक विशिष्ट तत्व के लिंक की संख्या।
- नोड की डिग्री: वंशज की संख्या
यहां बाइनरी सर्च ट्री (BST) का एक उदाहरण दिया गया है। प्रत्येक नोड में केवल दो वंशज हैं, बाएं (बच्चे) नोड वर्तमान (माता-पिता) नोड से छोटा है, दायां बड़ा है: इस पेड़ की विधियां निम्नानुसार हैं:
इस पेड़ की विधियां निम्नानुसार हैं:- जोड़ें: नोड जोड़ें
- findMin: न्यूनतम नोड प्राप्त करें
- findMax: अधिकतम नोड प्राप्त करें
- खोज: एक विशिष्ट नोड खोजें
- isPresent: एक विशिष्ट नोड के लिए जाँच करें
- निकालें: नोड निकालें
class Node {
constructor(data, left = null, right = null) {
this.data = data
this.left = left
this.right = right
}
}
class BST {
constructor() {
this.root = null
}
add(data) {
const node = this.root
if (node === null) {
this.root = new Node(data)
return
} else {
const searchTree = function(node) {
if (data < node.data) {
if (node.left === null) {
node.left = new Node(data)
return
} else if (node.left !== null) {
return searchTree(node.left)
}
} else if (data > node.data) {
if (node.right === null) {
node.right = new Node(data)
return
} else if (node.right !== null) {
return searchTree(node.right)
}
} else {
return null
}
}
return searchTree(node)
}
}
findMin() {
let current = this.root
while (current.left !== null) {
current = current.left
}
return current.data
}
findMax() {
let current = this.root
while (current.right !== null) {
current = current.right
}
return current.data
}
find(data) {
let current = this.root
while (current.data !== data) {
if (data < current.data) {
current = current.left
} else {
current = current.right
}
if (current === null) {
return null
}
}
return current
}
isPresent(data) {
let current = this.root
while (current) {
if (data === current.data) {
return true
}
data < current.data ? current = current.left : current = current.right
}
return false
}
remove(data) {
const removeNode = function(node, data) {
if (node === null) return null
if (data === node.data) {
if (node.left === null && node.right === null) return null
if (node.left === null) return node.right
if (node.right === null) return node.left
let tempNode = node.right
while (tempNode.left !== null) {
tempNode = tempNode.left
}
node.data = tempNode.data
node.right = removeNode(node.right, tempNode.data)
return node
} else if (data < node.data) {
node.left = removeNode(node.right, data)
return node
} else {
node.right = removeNode(node.right, data)
return node
}
}
this.root = removeNode(this.root, data)
}
}
परिक्षण:const bst = new BST()
bst.add(4)
bst.add(2)
bst.add(6)
bst.add(1)
bst.add(3)
bst.add(5)
bst.add(7)
bst.remove(4)
console.log(bst.findMin())
console.log(bst.findMax())
bst.remove(7)
console.log(bst.findMax())
console.log(bst.isPresent(4))
परिणाम:1
7
6
false
7. लोड (उपसर्ग) पेड़ (ट्राइ, "कोशिश" के रूप में पढ़ा)
 उपसर्ग वृक्ष एक प्रकार का खोज वृक्ष है। इसमें डेटा क्रमिक रूप से संग्रहीत किया जाता है (चरण दर चरण) - प्रत्येक ट्री नोड एक चरण का प्रतिनिधित्व करता है। उपसर्ग वृक्ष का उपयोग शब्दकोशों में किया जाता है, क्योंकि यह खोज को तेज करता है।प्रत्येक ट्री नोड वर्णमाला का एक अक्षर है, एक शाखा के बाद एक शब्द का निर्माण होता है। इसमें एक "बूलियन संकेतक" भी शामिल है, यह निर्धारित करने के लिए कि वर्तमान नोड अंतिम पत्र है।उपसर्ग वृक्ष के निम्नलिखित तरीके हैं:
उपसर्ग वृक्ष एक प्रकार का खोज वृक्ष है। इसमें डेटा क्रमिक रूप से संग्रहीत किया जाता है (चरण दर चरण) - प्रत्येक ट्री नोड एक चरण का प्रतिनिधित्व करता है। उपसर्ग वृक्ष का उपयोग शब्दकोशों में किया जाता है, क्योंकि यह खोज को तेज करता है।प्रत्येक ट्री नोड वर्णमाला का एक अक्षर है, एक शाखा के बाद एक शब्द का निर्माण होता है। इसमें एक "बूलियन संकेतक" भी शामिल है, यह निर्धारित करने के लिए कि वर्तमान नोड अंतिम पत्र है।उपसर्ग वृक्ष के निम्नलिखित तरीके हैं:- जोड़ें: शब्दकोश में एक शब्द जोड़ें
- isWord: एक शब्द के लिए जाँच करें
- प्रिंट: सभी शब्दों को वापस करें
function Node() {
this.keys = new Map()
this.end = false
this.setEnd = function() {
this.end = true
}
this.isEnd = function() {
return this.end
}
}
function Trie() {
this.root = new Node()
this.add = function(input, node = this.root) {
if (input.length === 0) {
node.setEnd()
return
} else if (!node.keys.has(input[0])) {
node.keys.set(input[0], new Node())
return this.add(input.substr(1), node.key.get(input[0]))
} else {
return this.add(input.substr(1), node.keys.get(input[0]))
}
}
this.isWord = function(word) {
let node = this.root
while (word.length > 1) {
if (node.keys.has(word[0])) {
return false
} else {
node = node.keys.get(word[0])
word = word.substr(1)
}
}
return (node.keys.has(word) && node.keys.get(word).isEnd()) ? true : false
}
this.print = function() {
let words = new Array()
let search = function(node = this.root, string) {
if (node.keys.size !== 0) {
for (let letter of node.keys.keys()) {
search(node.keys.get(letter), string.concat(letter))
}
if (node.isEnd()) {
words.push(string)
}
} else {
string.length > 0 ? words.push(string) : undefined
return
}
}
search(this.root, new String())
return words.length > 0 ? words : null
}
}
8. ग्राफ (ग्राफ) (ग्राफ)
 एक ग्राफ, जिसे एक नेटवर्क के रूप में भी जाना जाता है, इंटरकनेक्टेड नोड्स का एक संग्रह है। दो प्रकार के रेखांकन हैं - उन्मुख और गैर-उन्मुख, इस पर निर्भर करता है कि लिंक की दिशा है या नहीं। ग्राफ़ का उपयोग हर जगह किया जाता है, उदाहरण के लिए, नेविगेशन अनुप्रयोगों में सर्वोत्तम मार्ग की गणना या सामाजिक नेटवर्क पर सिफारिशों की सूची बनाने के लिए।ग्राफ़ को एक सूची या मैट्रिक्स के रूप में प्रस्तुत किया जा सकता है।
एक ग्राफ, जिसे एक नेटवर्क के रूप में भी जाना जाता है, इंटरकनेक्टेड नोड्स का एक संग्रह है। दो प्रकार के रेखांकन हैं - उन्मुख और गैर-उन्मुख, इस पर निर्भर करता है कि लिंक की दिशा है या नहीं। ग्राफ़ का उपयोग हर जगह किया जाता है, उदाहरण के लिए, नेविगेशन अनुप्रयोगों में सर्वोत्तम मार्ग की गणना या सामाजिक नेटवर्क पर सिफारिशों की सूची बनाने के लिए।ग्राफ़ को एक सूची या मैट्रिक्स के रूप में प्रस्तुत किया जा सकता है।सूची
इस मामले में, सभी मूल नोड्स बाईं ओर स्थित हैं, और उनके बच्चे दाईं ओर हैं।
साँचा
इस मामले में, नोड्स को पंक्तियों और स्तंभों में वितरित किया जाता है, पंक्ति और स्तंभ के चौराहे को नोड्स के बीच संबंध दिखाता है: 0 का मतलब है कि नोड्स जुड़े नहीं हैं, 1 - नोड्स जुड़े हुए हैं। ग्राफ को दो तरीकों से खोजा जाता है - चौड़ाई-पहली खोज (ब्रीथ-फर्स्ट-सर्च, बीएफएस) और गहन-गहन खोज (डेप्थ-फर्स्ट-सर्च, डीएफएस)।BFS पर विचार करें:
ग्राफ को दो तरीकों से खोजा जाता है - चौड़ाई-पहली खोज (ब्रीथ-फर्स्ट-सर्च, बीएफएस) और गहन-गहन खोज (डेप्थ-फर्स्ट-सर्च, डीएफएस)।BFS पर विचार करें:function bfs(graph, root) {
let nodesLen = {}
for (let i = 0; i < graph.length; i++) {
nodesLen[i] = Infinity
}
nodesLen[root] = 0
let queue = [root]
let current
while (queue.length !== 0) {
current = queue.shift()
let curConnected = graph[current]
let neighborIdx = []
let idx = curConnected.indexOf(1)
while (idx !== -1) {
neighborIdx.push(idx)
idx = curConnected.indexOf(1, idx + 1)
}
for (let i = 0; i < neighborIdx.length; i++) {
if (nodesLen[neighborIdx[i]] === Infinity) {
nodesLen[neighborIdx[i]] = nodesLen[current] + 1
queue.push(neighborIdx[i])
}
}
}
return nodesLen
}
परिक्षण:let graph = [
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0]
]
console.log(bfs(graph, 1))
परिणाम:{
0: 2,
1: 0,
2: 1,
3: 3,
4: Infinity
}
मेरे लिए बस इतना ही मुझे आशा है कि आप अपने लिए कुछ उपयोगी पाएंगे। हैप्पी कोडिंग!