Bonjour, Habr!Cet article décrit le processus de mise à niveau d'une plate-forme automotrice basée sur l'esp8266 MK avec micropython , vers un robot simple équipé d'un capteur d'obstacles à ultrasons à balayage, d'une LED clignotante, d'un bouton marche / arrêt, ainsi que d'un serveur Web intégré, dans le cadre d'un projet de formation.KDPV: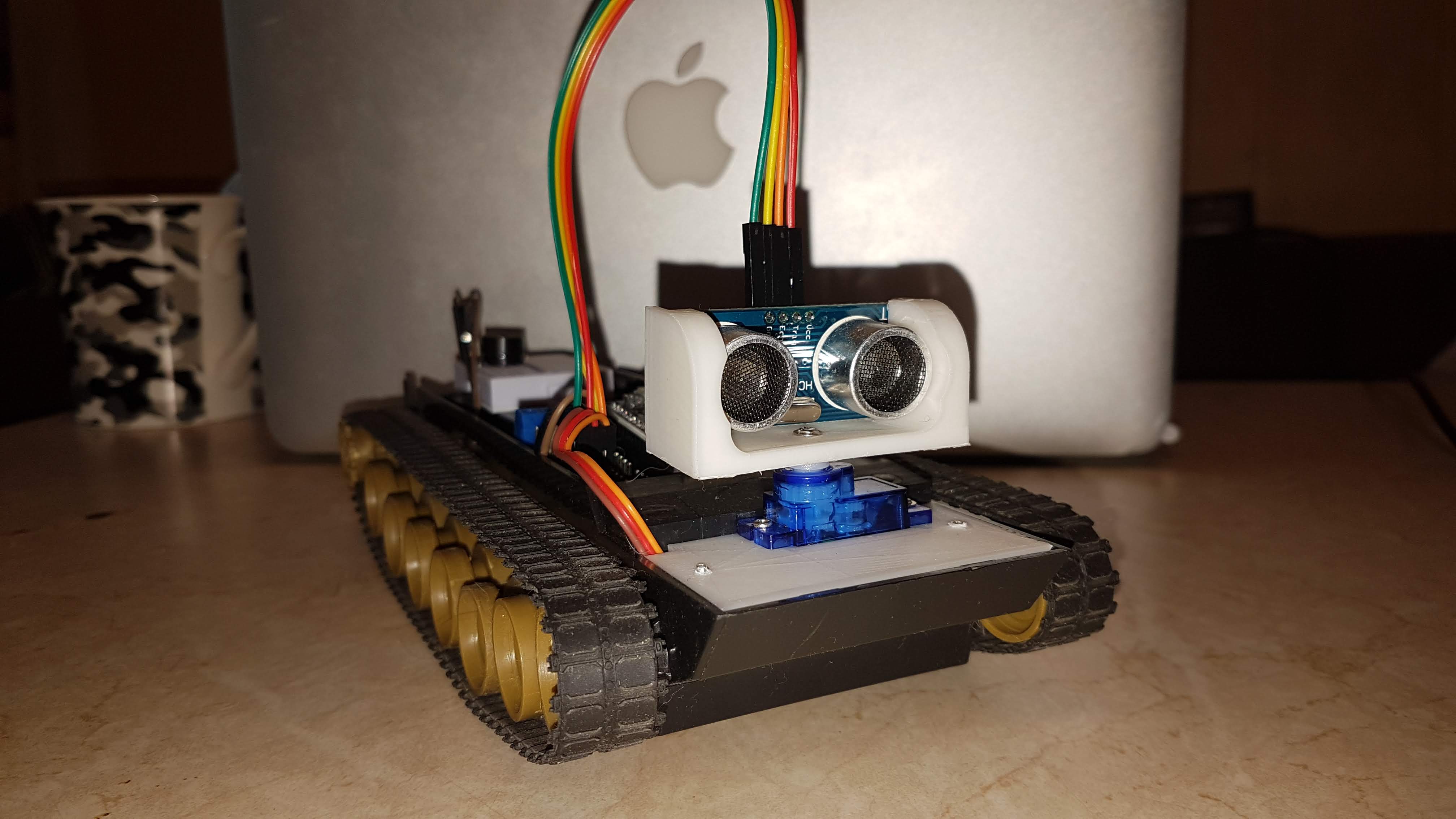 Ainsi, les deux premières parties décrivent la fabrication d'une plateforme automotrice contrôlée via une interface web wifi.La tâche de l'étape actuelle est d'équiper cette plate-forme à ultrasons du capteur HC-SR04 et d'ajouter la possibilité de travailler hors ligne.Pour commencer - la partie mécanique:il faut fixer le capteur et le servo dans le boîtier, concevoir (j'ai utilisé FreeCAD pour cela ) et fabriquer les pièces manquantes:
Ainsi, les deux premières parties décrivent la fabrication d'une plateforme automotrice contrôlée via une interface web wifi.La tâche de l'étape actuelle est d'équiper cette plate-forme à ultrasons du capteur HC-SR04 et d'ajouter la possibilité de travailler hors ligne.Pour commencer - la partie mécanique:il faut fixer le capteur et le servo dans le boîtier, concevoir (j'ai utilisé FreeCAD pour cela ) et fabriquer les pièces manquantes: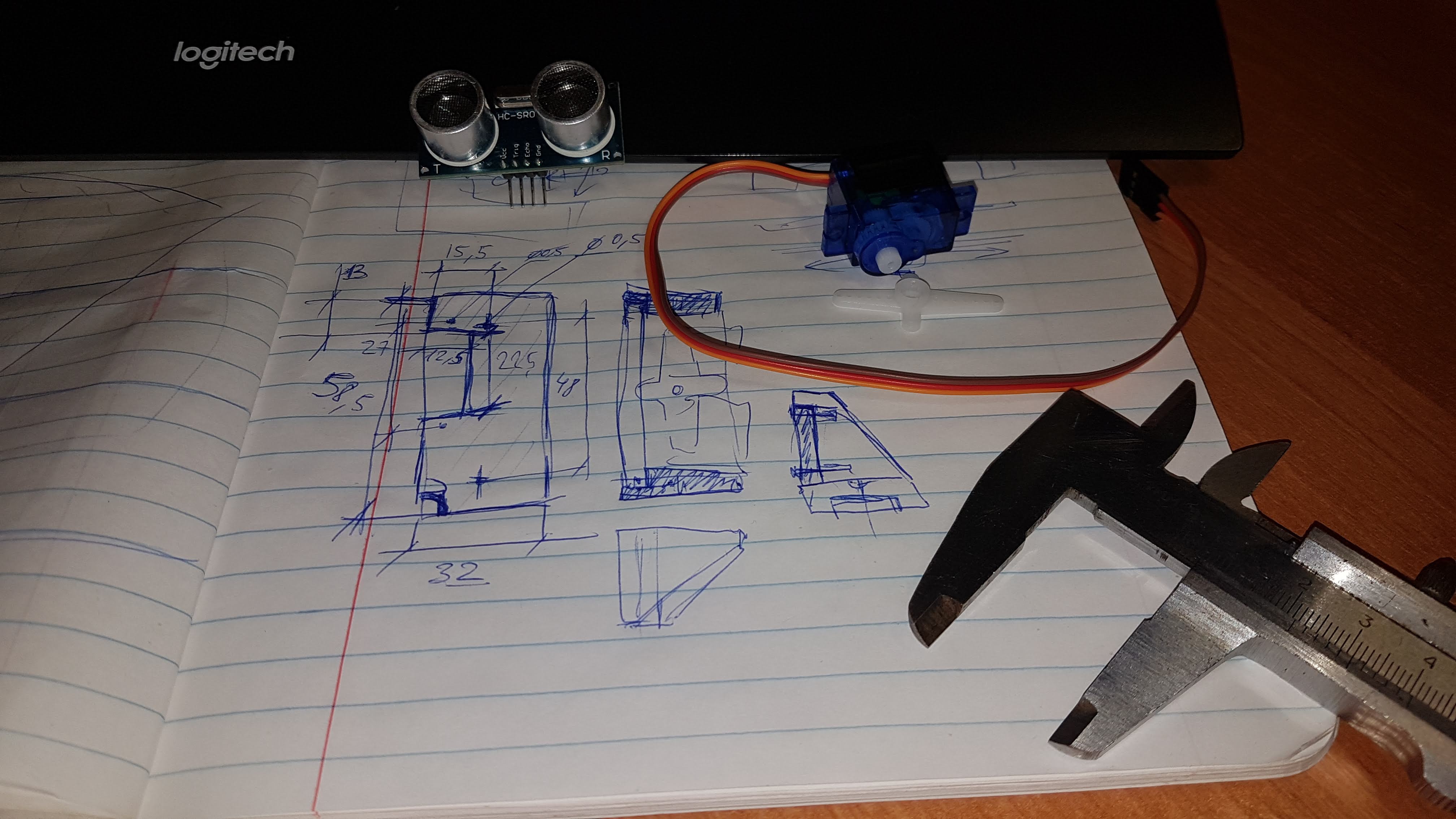
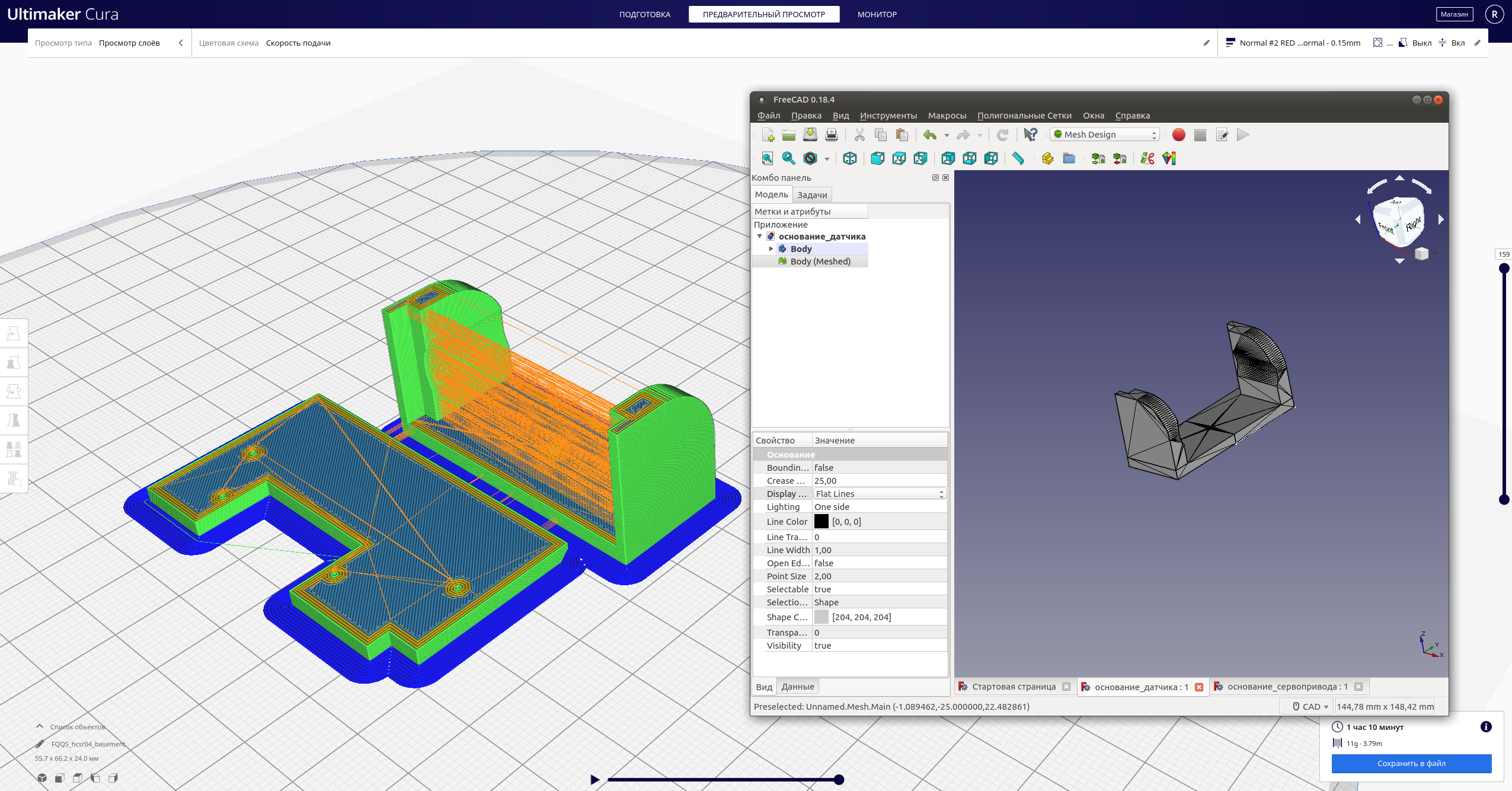 Ensuite - la partie électrique:dessiner le circuit (par exemple, à Fritzing ) et effectuer la commutation conformément à cela:
Ensuite - la partie électrique:dessiner le circuit (par exemple, à Fritzing ) et effectuer la commutation conformément à cela: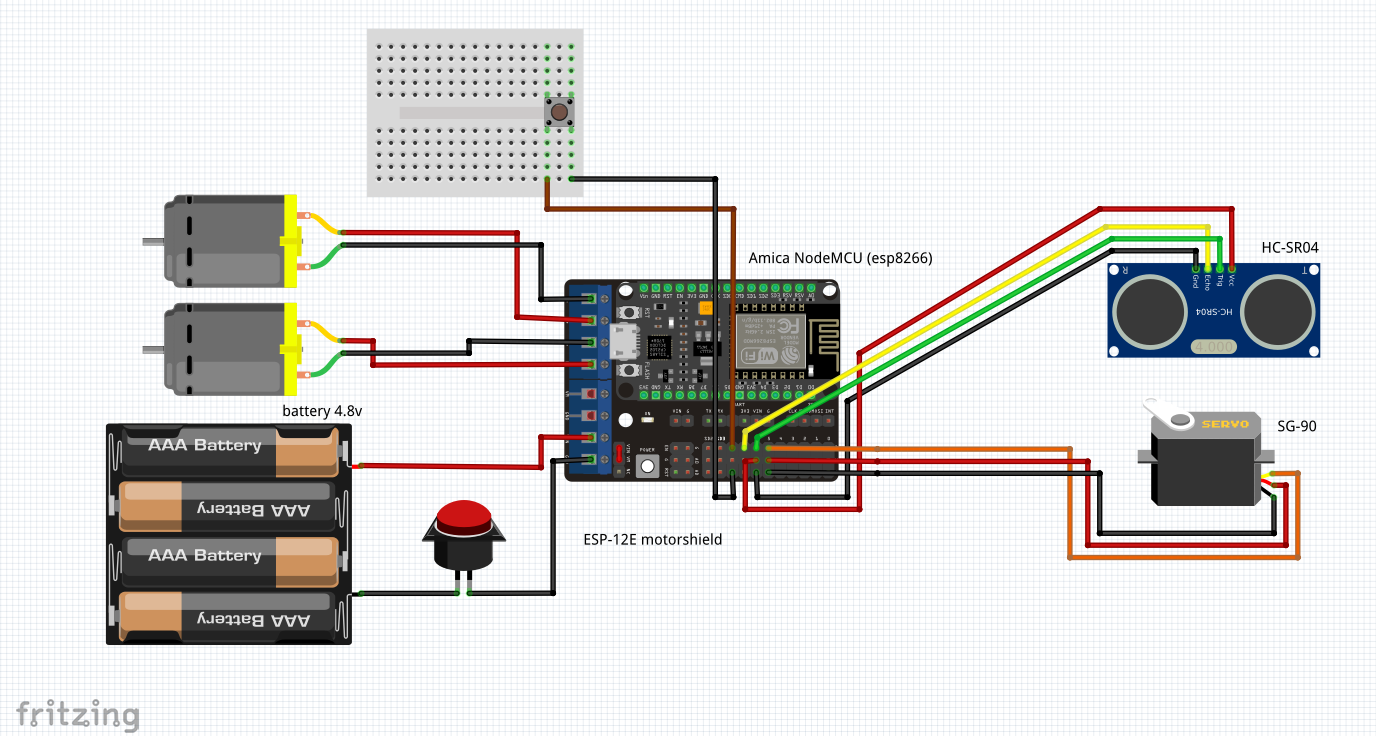 Après cela, essayez de tout faire voler ...Comme je voulais que certaines fonctions du programme robot soient exécutées en parallèle (par exemple, le processus de balayage de la distance aux obstacles et la fonction de mouvement), j'ai dû plonger dans les capacités du module asyncio . Un travail plus détaillé avec asyncio est décrit dans cet article et dans ces articles.Par exemple, pour faire clignoter une LED, vous pouvez appliquer une telle coroutine, qui n'est pratiquement pas différente de synchrone:
Après cela, essayez de tout faire voler ...Comme je voulais que certaines fonctions du programme robot soient exécutées en parallèle (par exemple, le processus de balayage de la distance aux obstacles et la fonction de mouvement), j'ai dû plonger dans les capacités du module asyncio . Un travail plus détaillé avec asyncio est décrit dans cet article et dans ces articles.Par exemple, pour faire clignoter une LED, vous pouvez appliquer une telle coroutine, qui n'est pratiquement pas différente de synchrone:import uasyncio as asyncio
from machine import Pin
syst_led = Pin(16, Pin.OUT)
async def blink_led(led, interval_ms):
led_val = True
while True:
led_val = not(led_val)
led_state = led.value(int(led_val))
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.create_task(blink_led(syst_led, interval_ms=250))
loop.run_forever()
La différence est que de telles coroutines qui effectuent différentes tâches peuvent être lancées plusieurs en même temps (les ressources seront allouées par le planificateur).Ainsi, nous écrirons des coroutines pour mesurer la distance et balayer le secteur, ainsi qu'un rappel pour une interruption matérielle (bouton) qui démarre ou arrête le balayage. Le transfert d'état entre coroutines dans le cas le plus simple peut se faire via des variables globales:Rappel du bouton:from machine import Pin
run_flag = False
button = Pin(15, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP)
def callback(p):
global run_flag
run_flag = not(run_flag)
print('set run_flag', run_flag, p)
button.irq(trigger=Pin.IRQ_FALLING, handler=callback)
Mesure de distance:import uasyncio as asyncio
from utime import sleep, sleep_us
from machine import Pin, time_pulse_us
trig=Pin(12, Pin.OUT)
echo=Pin(13, Pin.IN)
async def async_measure_range():
echo_timeout_us=500*2*30
trig.off()
sleep_us(5)
trig.on()
sleep_us(10)
trig.off()
try:
pulse_time = time_pulse_us(echo, 1, echo_timeout_us)
except:
pass
dist = (pulse_time / 2) / 29.1
return dist
Balayage de secteur (avec appel de la coroutine de mesure de distance):import uasyncio as asyncio
from machine import Pin, PWM
pos_actual = 75
dist_cm = 50
p14 = Pin(14, Pin.OUT)
servo = PWM(p14, freq=50)
async def radar_scan(interval_ms):
pos_list = [45,75,105,75]
global pos_actual
global dist_cm
while True:
if run_flag:
for pos in pos_list:
servo.duty(pos)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
dist_cm = await async_measure_range()
pos_actual = pos
print('pos_actual = %s, dist_cm = %s' % (pos_actual, dist_cm)
elif not run_flag:
await asyncio.sleep(0)
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop(
loop.create_task(radar_scan(interval_ms=250))
loop.run_forever()
Dans le processus de débogage, le capteur, de temps en temps, a donné une valeur de distance négative. Il s'est avéré - «L'électronique est la science des mauvais contacts» , lorsque le capteur a été tourné, le câble a été tiré et le contact a été perdu.Reste à fixer la logique du choix de l'action en fonction des résultats de l'analyse:avoid_left = False
avoid_right = False
avoid_backward = False
async def make_decision(interval_ms, avoid_limit_cm):
global avoid_left
global avoid_right
global avoid_backward
while True:
if run_flag:
if pos_actual == 45 and dist_cm < avoid_limit_cm :
avoid_left = True
if debug : print('avoid_left = %s' % avoid_left)
elif pos_actual == 45 and dist_cm >= avoid_limit_cm :
avoid_left = False
if debug : print('avoid_left = %s' % avoid_left)
elif pos_actual == 75 and dist_cm < avoid_limit_cm*1.25 :
avoid_backward = True
if debug : print('avoid_backward = %s' % avoid_backward)
elif pos_actual == 75 and dist_cm >= avoid_limit_cm*1.25 :
avoid_backward = False
if debug : print('avoid_backward = %s' % avoid_backward)
elif pos_actual == 105 and dist_cm < avoid_limit_cm :
avoid_right = True
if debug : print('avoid_right = %s' % avoid_right)
elif pos_actual == 105 and dist_cm >= avoid_limit_cm :
avoid_right = False
if debug : print('avoid_right = %s' % avoid_right)
if debug : print('pos = %s, dist_cm = %s' % (pos_actual,dist_cm))
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
elif not run_flag:
await asyncio.sleep(0)
loop.create_task(make_decision(interval_ms=250, avoid_limit_cm=15))
Fonctions motrices:from random import getrandbits
async def moving(interval_ms):
while True:
if run_flag:
if avoid_backward :
print('avoid_backward = %s' % avoid_backward)
await backward(interval_ms*2)
if bool(getrandbits(1)) :
await right_rotate(interval_ms+getrandbits(3)*100)
await stop_all()
else:
await left_rotate(interval_ms+getrandbits(3)*100)
await stop_all()
elif avoid_left :
print('avoid_left = %s' % avoid_left)
await left_turn(interval_ms)
elif avoid_right :
print('avoid_right = %s' % avoid_right)
await right_turn(interval_ms)
else:
print('move_forward')
await forward(interval_ms)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
elif not run_flag:
await stop_all()
await asyncio.sleep(0)
loop.create_task(moving(interval_ms=1000))
Et contrôle moteur
p5 = Pin(5, Pin.OUT)
p4 = Pin(4, Pin.OUT)
revrs_L = Pin(0, Pin.OUT, value=0)
revrs_R = Pin(2, Pin.OUT, value=0)
motor_L = PWM(p5, freq=1000, duty=0)
motor_R = PWM(p4, freq=1000, duty=0)
speed = 1023
async def stop_all():
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(0)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(0)
async def forward(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def backward(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(1)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(1)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def right_rotate(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(1)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def left_rotate(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(1)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def right_turn(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(0)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def left_turn(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(0)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
Ainsi qu'une LED clignotante pour contrôler le fonctionnement du programme:async def blink_led(led, interval_ms):
led_val = True
while True:
if run_flag:
led_val = not(led_val)
led_state = led.value(int(led_val))
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
elif not run_flag:
await asyncio.sleep(0)
loop.create_task(blink_led(syst_led, interval_ms=250))
Après quoi, il ne reste plus qu'à collecter tout celaen un seul morceauimport gc
import uasyncio as asyncio
from utime import sleep, sleep_us
from machine import Pin, PWM, time_pulse_us
from random import getrandbits
p5 = Pin(5, Pin.OUT)
p4 = Pin(4, Pin.OUT)
revrs_L = Pin(0, Pin.OUT, value=0)
revrs_R = Pin(2, Pin.OUT, value=0)
motor_L = PWM(p5, freq=1000, duty=0)
motor_R = PWM(p4, freq=1000, duty=0)
speed = 1023
p14 = Pin(14, Pin.OUT)
servo = PWM(p14, freq=50)
button = Pin(15, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP)
syst_led = Pin(16, Pin.OUT)
trig=Pin(12, Pin.OUT)
echo=Pin(13, Pin.IN)
run_flag = False
avoid_left = False
avoid_right = False
avoid_backward = False
pos_actual = 75
dist_cm = 50
debug = False
def callback(p):
global run_flag
run_flag = not(run_flag)
print('set run_flag', run_flag, p)
def stop_all_sync():
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(0)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(0)
async def stop_all():
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(0)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(0)
async def forward(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def backward(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(1)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(1)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def right_rotate(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(1)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def left_rotate(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(1)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def right_turn(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(0)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def left_turn(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(0)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def moving(interval_ms):
while True:
if run_flag:
if avoid_backward :
print('avoid_backward = %s' % avoid_backward)
await backward(interval_ms*2)
if bool(getrandbits(1)) :
await right_rotate(interval_ms+getrandbits(3)*100)
await stop_all()
else:
await left_rotate(interval_ms+getrandbits(3)*100)
await stop_all()
elif avoid_left :
print('avoid_left = %s' % avoid_left)
await left_turn(interval_ms)
elif avoid_right :
print('avoid_right = %s' % avoid_right)
await right_turn(interval_ms)
else:
print('move_forward')
await forward(interval_ms)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
elif not run_flag:
await stop_all()
await asyncio.sleep(0)
async def blink_led(led, interval_ms):
led_val = True
while True:
if run_flag:
led_val = not(led_val)
led_state = led.value(int(led_val))
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
elif not run_flag:
await asyncio.sleep(0)
async def async_measure_range():
echo_timeout_us=500*2*30
trig.off()
sleep_us(5)
trig.on()
sleep_us(10)
trig.off()
try:
pulse_time = time_pulse_us(echo, 1, echo_timeout_us)
except:
pass
dist = (pulse_time / 2) / 29.1
return dist
async def make_decision(interval_ms, avoid_limit_cm):
global avoid_left
global avoid_right
global avoid_backward
while True:
if run_flag:
if pos_actual == 45 and dist_cm < avoid_limit_cm :
avoid_left = True
if debug : print('avoid_left = %s' % avoid_left)
elif pos_actual == 45 and dist_cm >= avoid_limit_cm :
avoid_left = False
if debug : print('avoid_left = %s' % avoid_left)
elif pos_actual == 75 and dist_cm < avoid_limit_cm*1.25 :
avoid_backward = True
if debug : print('avoid_backward = %s' % avoid_backward)
elif pos_actual == 75 and dist_cm >= avoid_limit_cm*1.25 :
avoid_backward = False
if debug : print('avoid_backward = %s' % avoid_backward)
elif pos_actual == 105 and dist_cm < avoid_limit_cm :
avoid_right = True
if debug : print('avoid_right = %s' % avoid_right)
elif pos_actual == 105 and dist_cm >= avoid_limit_cm :
avoid_right = False
if debug : print('avoid_right = %s' % avoid_right)
if debug : print('pos = %s, dist_cm = %s' % (pos_actual,dist_cm))
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
elif not run_flag:
await asyncio.sleep(0)
async def radar_scan(interval_ms):
pos_list = [45,75,105,75]
global pos_actual
global dist_cm
while True:
if run_flag:
for pos in pos_list:
servo.duty(pos)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
dist_cm = await async_measure_range()
pos_actual = pos
elif not run_flag:
await asyncio.sleep(0)
stop_all_sync()
print('Move sensor to initial position...')
servo.duty(75)
sleep(1)
print('Waiting for start button...')
gc.enable()
button.irq(trigger=Pin.IRQ_FALLING, handler=callback)
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.create_task(blink_led(syst_led, interval_ms=250))
loop.create_task(radar_scan(interval_ms=250))
loop.create_task(make_decision(interval_ms=250, avoid_limit_cm=15))
loop.create_task(moving(interval_ms=1000))
loop.run_forever()
et vérifier le travail:Cependant, je voudrais garder la possibilité d'un contrôle manuel via la page web ...Pour cela, dans une coroutine séparée, ajoutez un simple serveur web:async def web_page(request):
global auto_run_flag
motor_state="Stopped"
if request.find('GET /?forward') > 0:
motor_state="Going Forward"
auto_run_flag = False
forward_sync()
elif request.find('GET /?left_rotate') > 0:
motor_state="Rotate Left"
auto_run_flag = False
left_rotate_sync()
elif request.find('GET /?right_rotate') > 0:
motor_state="Rotate Right"
auto_run_flag = False
right_rotate_sync()
elif request.find('GET /?left_turn') > 0:
motor_state="Turn Left"
auto_run_flag = False
left_turn_sync()
elif request.find('GET /?right_turn') > 0:
motor_state="Turn Right"
auto_run_flag = False
right_turn_sync()
elif request.find('GET /?backward') > 0:
motor_state="Going Backward"
auto_run_flag = False
backward_sync()
elif request.find('GET /?stop') > 0:
motor_state="Stopped"
auto_run_flag = False
stop_all_sync()
elif request.find('GET /?auto') > 0:
auto_run_flag = not auto_run_flag
if auto_run_flag :
motor_state="Autopilot"
elif not auto_run_flag :
motor_state="Stopped"
stop_all_sync()
html = """<html><head><title>RoboTank WEB</title>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<link rel="icon" href="data:,"> <style>
html{font-family: Helvetica; display:inline-block; margin: 0px auto; text-align: center;}
h1{color: #0F3376; padding: 2vh;}p{font-size: 1.5rem;}
.button{display: inline-block; background-color: #33c080; border: none;
border-radius: 4px; color: white; text-decoration: none; font-size: 30px; width:100%}
.button2{background-color: #4286f4; width:30%}
.button3{background-color: #eb2b10; width:35%}
.button4{background-color: #8386f4; width:44%}
</style></head>
<body> <h1>RoboTank WEB</h1>
<p>Status : <strong>""" + motor_state + """</strong></p>
<p><a href='/?forward'><button class="button">Forward</button></a></p>
<p><a href='/?left_turn'><button class="button button2">LEFT</button></a>
<a href='/?stop'><button class="button button3">STOP</button></a>
<a href='/?right_turn'><button class="button button2">RIGHT</button></a>
<p><a href='/?backward'><button class="button">Backward</button></a></p>
<p><a href='/?left_rotate'><button class="button button4">L-rotate</button></a>
<a href='/?right_rotate'><button class="button button4">R-rotate</button></a></p>
<p><a href='/?auto'><button class="button button3">AUTO</button></a></p>
</body></html>"""
return html
async def web_handler(reader, writer):
try:
request = str(await reader.read(1024))
header = """HTTP/1.1 200 OK\nContent-Type: text/html\nConnection: close\n\n"""
response = await web_page(request)
await writer.awrite(header)
await writer.awrite(response)
await writer.aclose()
print("Finished processing request")
except Exception as e:
print(e)
async def tcp_server(host, port):
server = await asyncio.start_server(web_handler, host, port)
loop.create_task(tcp_server('0.0.0.0', 80))
Et des fonctions de mouvement synchrones pour un contrôle manuel.def stop_all_sync():
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(0)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(0)
def backward_sync():
revrs_L.value(1)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(1)
motor_R.duty(speed)
def forward_sync():
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(speed)
def right_rotate_sync():
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(1)
motor_R.duty(speed)
def left_rotate_sync():
revrs_L.value(1)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(speed)
def right_turn_sync():
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(0)
def left_turn_sync():
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(0)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(speed)
Apparence de l'interface: Tests de la version finale:Les sources sont disponibles ici.Sources d'inspiration:docs.micropython.org/en/latest/library/uasyncio.htmlhabr.com/en/post/484446habr.com/en/post/337420habr.com/en/post/484472github.com/peterhinch /micropython-async/blob/master/TUTORIAL.mdgithub.com/rsc1975/micropython-hcsr04medium.com/@pgjones/an-asyncio-socket-tutorial-5e6f3308b8b0
Tests de la version finale:Les sources sont disponibles ici.Sources d'inspiration:docs.micropython.org/en/latest/library/uasyncio.htmlhabr.com/en/post/484446habr.com/en/post/337420habr.com/en/post/484472github.com/peterhinch /micropython-async/blob/master/TUTORIAL.mdgithub.com/rsc1975/micropython-hcsr04medium.com/@pgjones/an-asyncio-socket-tutorial-5e6f3308b8b0