La détection d'anomalies est une tâche d'apprentissage automatique intéressante. Il n'y a pas de moyen spécifique de le résoudre, car chaque ensemble de données a ses propres caractéristiques. Mais en même temps, plusieurs approches contribuent à réussir. Je veux parler de l'une de ces approches - les encodeurs automatiques.
Quel jeu de données choisir?
Le problème le plus urgent dans la vie de tout scientifique des données. Pour simplifier l'histoire, j'utiliserai un simple ensemble de données en structure, que nous allons générer ici.
import os
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.colors import Normalize
def gen_normal_distribution(mu, sigma, size, range=(0, 1), max_val=1):
bins = np.linspace(*range, size)
result = 1 / (sigma * np.sqrt(2*np.pi)) * np.exp(-(bins - mu)**2 / (2*sigma**2))
cur_max_val = result.max()
k = max_val / cur_max_val
result *= k
return result
Prenons un exemple de fonction. Créez une distribution normale avec μ = 0,3 et σ = 0,05:
dist = gen_normal_distribution(0.3, 0.05, 256, max_val=1)
print(dist.max())
>>> 1.0
plt.plot(np.linspace(0, 1, 256), dist)
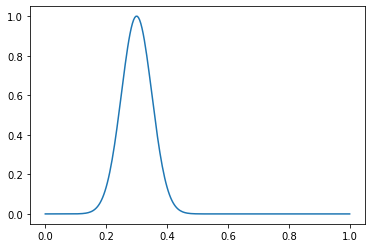
Déclarez les paramètres de notre jeu de données:
in_distribution_size = 2000
out_distribution_size = 200
val_size = 100
sample_size = 256
random_generator = np.random.RandomState(seed=42)
Et les fonctions de génération d'exemples sont normales et anormales. Les distributions avec un maximum seront considérées comme normales, anormales - avec deux:
def generate_in_samples(size, sample_size):
global random_generator
in_samples = np.zeros((size, sample_size))
in_mus = random_generator.uniform(0.1, 0.9, size)
in_sigmas = random_generator.uniform(0.05, 0.5, size)
for i in range(size):
in_samples[i] = gen_normal_distribution(in_mus[i], in_sigmas[i], sample_size, max_val=1)
return in_samples
def generate_out_samples(size, sample_size):
global random_generator
out_samples = generate_in_samples(size, sample_size)
out_additional_mus = random_generator.uniform(0.1, 0.9, size)
out_additional_sigmas = random_generator.uniform(0.01, 0.05, size)
for i in range(size):
anomaly = gen_normal_distribution(out_additional_mus[i], out_additional_sigmas[i], sample_size, max_val=0.12)
out_samples[i] += anomaly
return out_samples
Voici à quoi ressemble un exemple normal:
in_samples = generate_in_samples(in_distribution_size, sample_size)
plt.plot(np.linspace(0, 1, sample_size), in_samples[42])

Et anormal - comme ceci:
out_samples = generate_out_samples(out_distribution_size, sample_size)
plt.plot(np.linspace(0, 1, sample_size), out_samples[42])
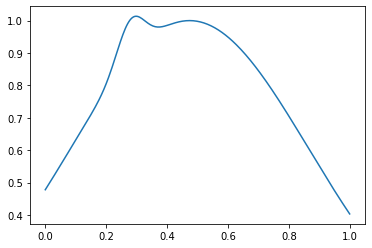
Créez des tableaux avec des balises et des balises:
x = np.concatenate((in_samples, out_samples))
y = np.concatenate((np.zeros(in_distribution_size), np.ones(out_distribution_size)))
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.2, shuffle=True, random_state=42)
. , , 2 1 (). , ( ), :
x_val_out = generate_out_samples(val_size, sample_size)
x_val_in = generate_in_samples(val_size, sample_size)
x_val = np.concatenate((x_val_out, x_val_in))
y_val = np.concatenate((np.ones(val_size), np.zeros(val_size)))
, , Sklearn: SVM . , , .
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
from sklearn.metrics import f1_score
One class SVM
from sklearn.svm import OneClassSVM
OneClassSVM nu — .
out_dist_part = out_distribution_size / (out_distribution_size + in_distribution_size)
svm = OneClassSVM(nu=out_dist_part)
svm.fit(x_train, y_train)
>>> OneClassSVM(cache_size=200, coef0=0.0, degree=3, gamma='scale', kernel='rbf',
max_iter=-1, nu=0.09090909090909091, shrinking=True, tol=0.001,
verbose=False)
:
svm_prediction = svm.predict(x_val)
svm_prediction[svm_prediction == 1] = 0
svm_prediction[svm_prediction == -1] = 1
sklearn — classification_report, Anomaly detection , precision recall, :
print(classification_report(y_val, svm_prediction))
>>> precision recall f1-score support
0.0 0.57 0.93 0.70 100
1.0 0.81 0.29 0.43 100
accuracy 0.61 200
macro avg 0.69 0.61 0.57 200
weighted avg 0.69 0.61 0.57 200
, . f1-score , .
Isolation forest
, , - ?
from sklearn.ensemble import IsolationForest
, . :
out_dist_part = out_distribution_size / (out_distribution_size + in_distribution_size)
iso_forest = IsolationForest(n_estimators=100, contamination=out_dist_part, max_features=100, n_jobs=-1)
iso_forest.fit(x_train)
>>> IsolationForest(behaviour='deprecated', bootstrap=False,
contamination=0.09090909090909091, max_features=100,
max_samples='auto', n_estimators=100, n_jobs=-1,
random_state=None, verbose=0, warm_start=False)
Classification report? — Classification report!
iso_forest_prediction = iso_forest.predict(x_val)
iso_forest_prediction[iso_forest_prediction == 1] = 0
iso_forest_prediction[iso_forest_prediction == -1] = 1
print(classification_report(y_val, iso_forest_prediction))
>>> precision recall f1-score support
0.0 0.50 0.91 0.65 100
1.0 0.53 0.10 0.17 100
accuracy 0.51 200
macro avg 0.51 0.51 0.41 200
weighted avg 0.51 0.51 0.41 200
RandomForestClassifier
, - " ?" , :
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
random_forest = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, max_features=100, n_jobs=-1)
random_forest.fit(x_train, y_train)
>>> RandomForestClassifier(bootstrap=True, ccp_alpha=0.0, class_weight=None,
criterion='gini', max_depth=None, max_features=100,
max_leaf_nodes=None, max_samples=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None,
min_samples_leaf=1, min_samples_split=2,
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, n_estimators=100,
n_jobs=-1, oob_score=False, random_state=None, verbose=0,
warm_start=False)
random_forest_prediction = random_forest.predict(x_val)
print(classification_report(y_val, random_forest_prediction))
>>> precision recall f1-score support
0.0 0.57 0.99 0.72 100
1.0 0.96 0.25 0.40 100
accuracy 0.62 200
macro avg 0.77 0.62 0.56 200
weighted avg 0.77 0.62 0.56 200
Autoencoder
, : . .
, "" , . 2 : Encoder' Decoder', .
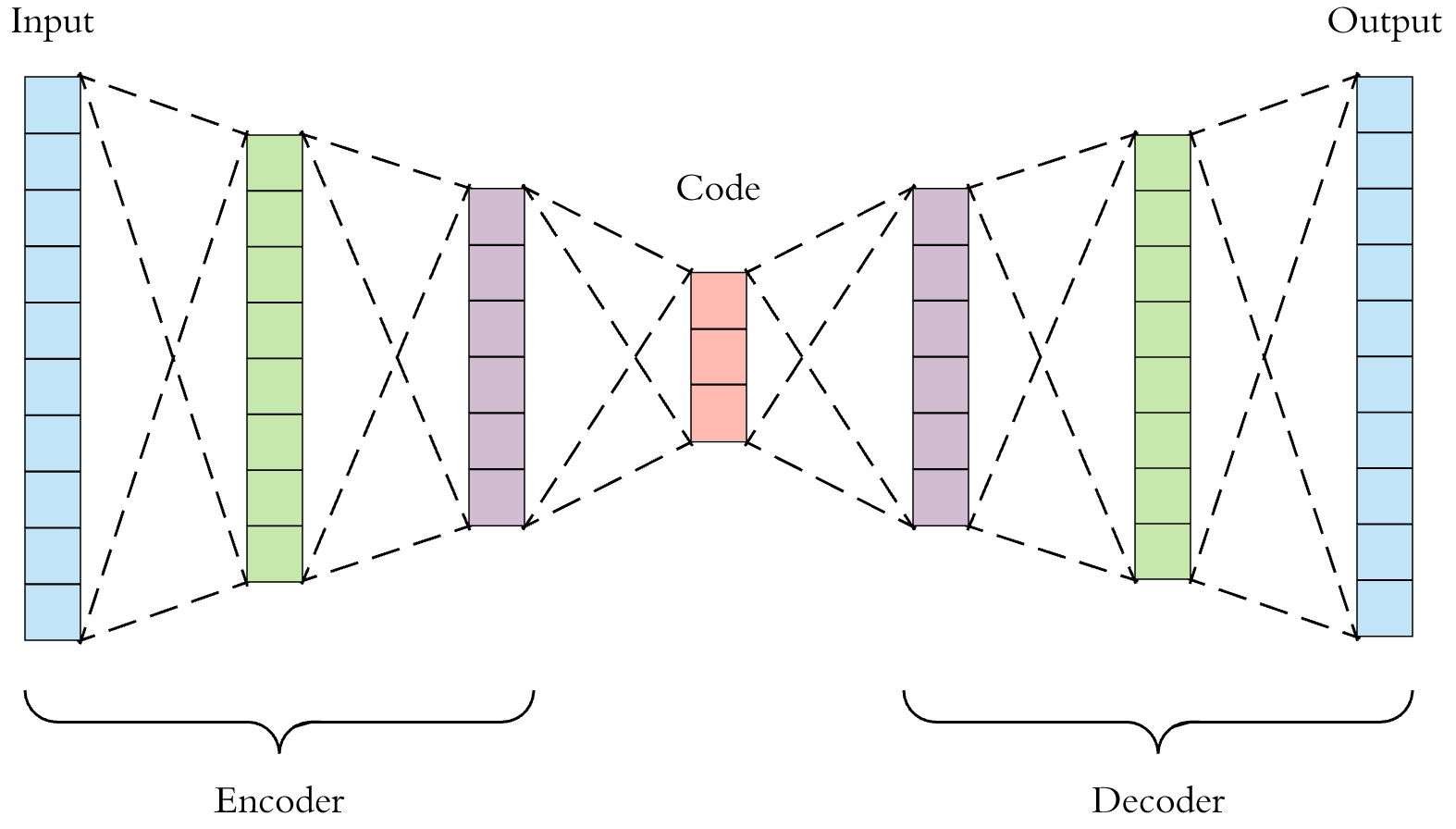
"" , , .
? , , , . , 9% 91% . , . , , : .
.
PyTorch, :
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.utils.data import TensorDataset, DataLoader
from torch.optim import Adam
:
batch_size = 32
lr = 1e-3
. , , "" . , ( , learning rate, ) , , .
train_in_distribution = x_train[y_train == 0]
train_in_distribution = torch.tensor(train_in_distribution.astype(np.float32))
train_in_dataset = TensorDataset(train_in_distribution)
train_in_loader = DataLoader(train_in_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
test_dataset = TensorDataset(
torch.tensor(x_test.astype(np.float32)),
torch.tensor(y_test.astype(np.long))
)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)
val_dataset = TensorDataset(torch.tensor(x_val.astype(np.float32)))
val_loader = DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)
. 4 , ( 2 : μ, — σ, ; 4 , ).
class Autoencoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size):
super(Autoencoder, self).__init__()
self.encoder = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(input_size, 128),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
nn.Linear(128, 64),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
nn.Linear(64, 16),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
nn.Linear(16, 4),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
)
self.decoder = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(4, 16),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
nn.Linear(16, 64),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
nn.Linear(64, 128),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
nn.Linear(128, 256),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.encoder(x)
x = self.decoder(x)
return x
model = Autoencoder(sample_size).cuda()
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
per_sample_criterion = nn.MSELoss(reduction="none")
optimizer = Adam(model.parameters(), lr=lr, weight_decay=1e-5)
- loss' , , boxplot' :
def save_score_distribution(model, data_loader, criterion, save_to, figsize=(8, 6)):
losses = []
labels = []
for (x_batch, y_batch) in data_loader:
x_batch = x_batch.cuda()
output = model(x_batch)
loss = criterion(output, x_batch)
loss = torch.mean(loss, dim=1)
loss = loss.detach().cpu().numpy().flatten()
losses.append(loss)
labels.append(y_batch.detach().cpu().numpy().flatten())
losses = np.concatenate(losses)
labels = np.concatenate(labels)
losses_0 = losses[labels == 0]
losses_1 = losses[labels == 1]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, figsize=figsize)
ax.boxplot([losses_0, losses_1])
ax.set_xticklabels(['normal', 'anomaly'])
plt.savefig(save_to)
plt.close(fig)
:
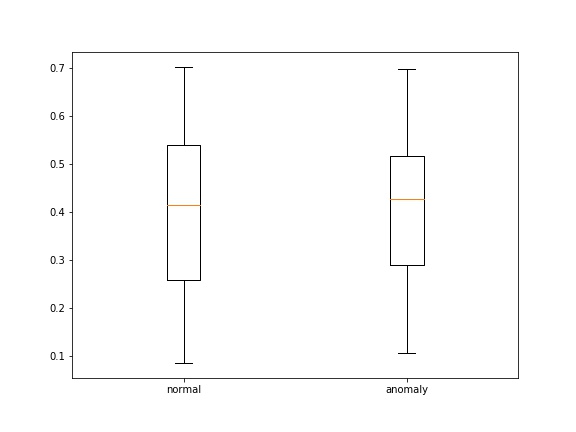
:
experiment_path = "ood_detection"
!rm -rf $experiment_path
os.makedirs(experiment_path, exist_ok=True)
epochs = 100
for epoch in range(epochs):
running_loss = 0
for (x_batch, ) in train_in_loader:
x_batch = x_batch.cuda()
output = model(x_batch)
loss = criterion(output, x_batch)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
running_loss += loss.item()
print("epoch [{}/{}], train loss:{:.4f}".format(epoch+1, epochs, running_loss))
plot_path = os.path.join(experiment_path, "{}.jpg".format(epoch+1))
save_score_distribution(model, test_loader, per_sample_criterion, plot_path)
>>>
epoch [1/100], train loss:8.5728
epoch [2/100], train loss:4.2405
epoch [3/100], train loss:4.0852
epoch [4/100], train loss:1.7578
epoch [5/100], train loss:0.8543
...
epoch [96/100], train loss:0.0147
epoch [97/100], train loss:0.0154
epoch [98/100], train loss:0.0117
epoch [99/100], train loss:0.0105
epoch [100/100], train loss:0.0097

50

100
, . , :
def get_prediction(model, x):
global batch_size
dataset = TensorDataset(torch.tensor(x.astype(np.float32)))
data_loader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)
predictions = []
for batch in data_loader:
x_batch = batch[0].cuda()
pred = model(x_batch)
predictions.append(pred.detach().cpu().numpy())
predictions = np.concatenate(predictions)
return predictions
def compare_data(xs, sample_num, data_range=(0, 1), labels=None):
fig, axes = plt.subplots(len(xs))
sample_size = len(xs[0][sample_num])
for i in range(len(xs)):
axes[i].plot(np.linspace(*data_range, sample_size), xs[i][sample_num])
if labels:
for i, label in enumerate(labels):
axes[i].set_ylabel(label)
:
x_test_pred = get_prediction(model, x_test)
compare_data([x_test[y_test == 0], x_test_pred[y_test == 0]], 10, labels=["real", "encoded"])
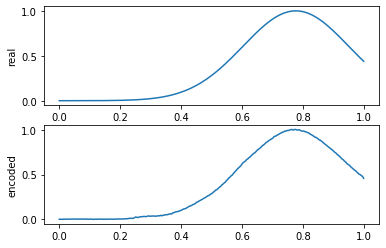
:

X? .
Difference score
— . , , , . .
def get_difference_score(model, x):
global batch_size
dataset = TensorDataset(torch.tensor(x.astype(np.float32)))
data_loader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)
predictions = []
for (x_batch, ) in data_loader:
x_batch = x_batch.cuda()
preds = model(x_batch)
predictions.append(preds.detach().cpu().numpy())
predictions = np.concatenate(predictions)
return (x - predictions)
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
test_score = get_difference_score(model, x_test)
score_forest = RandomForestClassifier(max_features=100)
score_forest.fit(test_score, y_test)
>>> RandomForestClassifier(bootstrap=True, ccp_alpha=0.0, class_weight=None,
criterion='gini', max_depth=None, max_features=100,
max_leaf_nodes=None, max_samples=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None,
min_samples_leaf=1, min_samples_split=2,
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, n_estimators=100,
n_jobs=None, oob_score=False, random_state=None,
verbose=0, warm_start=False)
, : 2 — . , 2 : , — difference_score, — . , , .
? . difference_score , ( ) , , . , , difference_score , ( ). .
:
val_score = get_difference_score(model, x_val)
prediction = score_forest.predict(val_score)
print(classification_report(y_val, prediction))
>>> precision recall f1-score support
0.0 0.76 1.00 0.87 100
1.0 1.00 0.69 0.82 100
accuracy 0.84 200
macro avg 0.88 0.84 0.84 200
weighted avg 0.88 0.84 0.84 200
. :
indices = np.arange(len(prediction))
wrong_indices = indices[(prediction == 0) & (y_val == 1)]
x_val_pred = get_prediction(model, x_val)
compare_data([x_val, x_val_pred], wrong_indices[0])
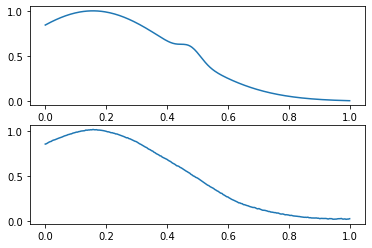
? :
plt.imshow(val_score[wrong_indices], norm=Normalize(0, 1, clip=True))

:
plt.imshow(val_score[(prediction == 1) & (y_val == 1)], norm=Normalize(0, 1, clip=True))

:
plt.imshow(val_score[(prediction == 0) & (y_val == 0)], norm=Normalize(0, 1, clip=True))

, : .
Difference histograms
. . — , "", .
, difference score
print("test score: [{}; {}]".format(test_score.min(), test_score.max()))
>>> test score: [-0.2260764424351479; 0.26339245919832344]
, :
def score_to_histograms(scores, bins=10, data_range=(-0.3, 0.3)):
result_histograms = np.zeros((len(scores), bins))
for i in range(len(scores)):
hist, bins = np.histogram(scores[i], bins=bins, range=data_range)
result_histograms[i] = hist
return result_histograms
test_histogram = score_to_histograms(test_score, bins=10, data_range=(-0.3, 0.3))
val_histogram = score_to_histograms(val_score, bins=10, data_range=(-0.3, 0.3))
plt.title("normal histogram")
plt.bar(np.linspace(-0.3, 0.3, 10), test_histogram[y_test == 0][0])

plt.title("anomaly histogram")
plt.bar(np.linspace(-0.3, 0.3, 10), test_histogram[y_test == 1][0])
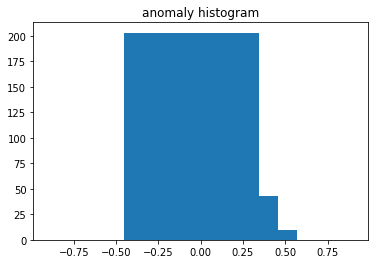
, "", .
histogram_forest = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=10)
histogram_forest.fit(test_histogram, y_test)
>>> RandomForestClassifier(bootstrap=True, ccp_alpha=0.0, class_weight=None,
criterion='gini', max_depth=None, max_features='auto',
max_leaf_nodes=None, max_samples=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None,
min_samples_leaf=1, min_samples_split=2,
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, n_estimators=10,
n_jobs=None, oob_score=False, random_state=None,
verbose=0, warm_start=False)
val_prediction = histogram_forest.predict(val_histogram)
print(classification_report(y_val, val_prediction))
>>> precision recall f1-score support
0.0 0.83 0.99 0.90 100
1.0 0.99 0.80 0.88 100
accuracy 0.90 200
macro avg 0.91 0.90 0.89 200
weighted avg 0.91 0.90 0.89 200
— . , , , , . () .
— . ? VAE, ( 4 ) . . CVAE, - . , , , ..
GAN', (), . ( ).
, , .
Statistical parametric
- GMM — Gaussian mixture modelling + Akaike or Bayesian Information Criterion
- HMM — Hidden Markov models
- MRF — Markov random fields
- CRF — conditional random fields
Robust statistic
- minimum volume estimation
- PCA
- estimation maximisation (EM) + deterministic annealing
- K-means
Non-parametric statistics
- histogram analysis with density estimation on KNN
- local kernel models (Parzen windowing)
- vector of feature matching with similarity distance (between train and test)
- wavelets + MMRF
- histogram-based measures features
- texture features
- shape features
- features from VGG-16
- HOG
Neural networks
- self organisation maps (SOM) or Kohonen's
- Radial Basis Functions (RBF) (Minhas, 2005)
- LearningVector Quantisation (LVQ)
- ProbabilisticNeural Networks (PNN)
- Hopfieldnetworks
- SupportVector Machines (SVM)
- AdaptiveResonance Theory (ART)
- Relevance vector machine (RVM)
, Data science' . Computer vision, . ( — !) — FARADAY Lab. — , .
c:
