Jupyter Notebook est un environnement d'outils préféré pour les scientifiques des données, les analystes, les ingénieurs, les mathématiciens, les étudiants et même pour nous - les scientifiques les plus ordinaires en physique expérimentale.
Cet outil est conçu pour fonctionner avec des langages interprétés et une représentation graphique pratique des données. Pendant longtemps, nous avons simplement compté dessus en utilisant Python et des bibliothèques mathématiques (numpy, SciPy, matplot, etc.). Mais il s'avère que cet environnement n'est pas si simple et a un potentiel beaucoup plus grand. De manière très inattendue, mais Jupyter facilite la manipulation des appareils électroniques sur les microcontrôleurs, il peut servir comme une sorte d'environnement REPL pour MK uniquement sans MicroPython faible et un support impressionnant pour la périphérie de la puce, le tout presque hors de la boîte.
Une petite intro.
Un jour, un appareil de mesure nous est venu d'un institut de recherche fraternel, bien que l'appareil soit dit haut et fort, plutôt un capteur primitif, dont les données doivent encore être traitées. L'algorithme est simple, il suffit de mesurer le temps de montée du front du signal. Quelque chose comme ça:
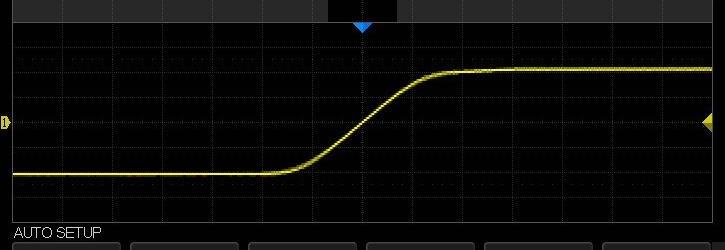
, , , .
, , .
. - USB Ethernet , , . Python.
: sample rate — 10,000 times a second , 8,000 times a second. 40,000 -50,000 times a second.
, . ( ) , . , , , x , computer vision rocket science. .
, , . , , . .
, . . Jupyter Notebook. Jupyter REPL , MicroPython. MicroPython , COM-.

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5LbgyDmRu9s
Jupyter . Jupyter Notebook , . STM32 STM8, — STMicroelectronics. Standard Peripheral Library
: STM8 - .
uint16_t ADC_GetConversionValue(ADC_TypeDef* ADCx);
. Jupyter:

ADC_GetConversionValue /++ -, Jupyter?! xeus-cling, Jupyter ++. , Windows . , Microsoft, c Ubuntu. MacOS, MacBook ...
xeus-cling /++ , - Jupyter NoteBook REMCU. , API, Standard Peripheral Library .. (header) Standard Peripheral Library, STM8LDiscovery :
#include "stm8l15x.h"
, , . .
, Jupyter , . , , :
GPIOC->DDR |= 0x80;
GPIOC->CR1 |= 0x80;
GPIOC->CR2 |= 0x80;
WavesGenerator
Jupyter . Standard Peripheral Library .
. :
- ( ) Ubuntu MacOS Anaconda, Jupyter Notebook xeus-cling xplots( )
- STM8LDiscovery — , . , c STM32.
- REMCU STM8LDiscovery, . .
STM8LDiscovery STM8L152C6 MCU name:, StdPeriph_Driver 1.4.0
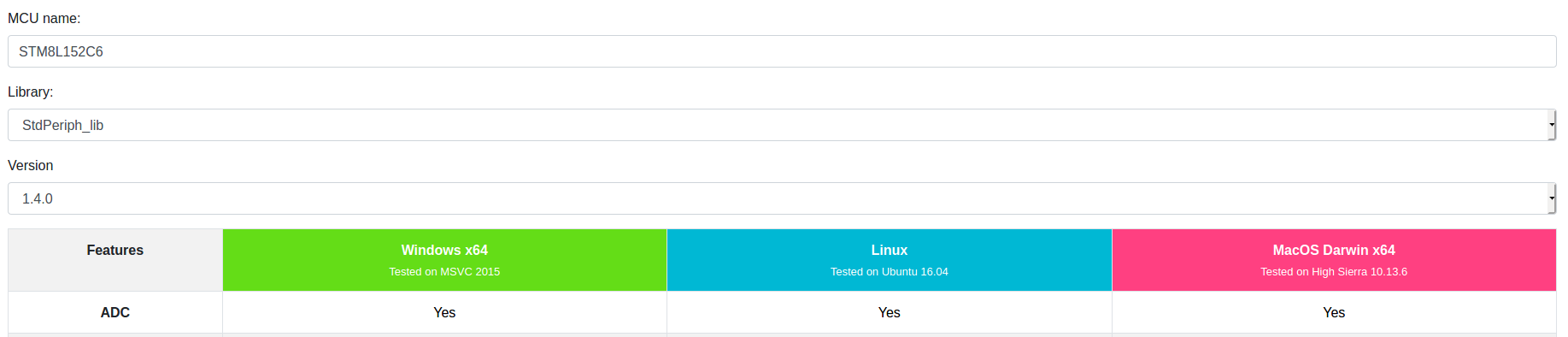
.

- OpenOCD , REMCU. , OpenOCD, Ubuntu apt install STM8LDiscovery.
- ST-Link stick — STM8LDiscovery, . STM8LDiscovery , OpenOCD.
UPD. ST-Link
ST-Link STM8LDiscovery .
OpenOCD :
./openocd -f interface/stlink-v2.cfg -f target/stm8l.cfg
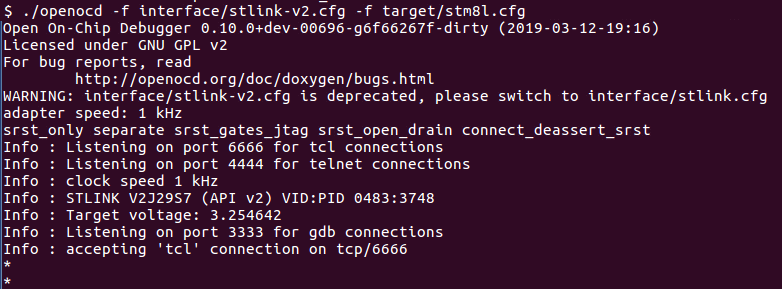
Jupyter STM8LDiscovery. Standard Peripheral Library Arduino. , - , . - , .
GPIO_Toggle — . c REMCU , GitHub REMCU. notebook:
:STM8L-Discovery GPIO example
Load REMCU shared libray
.L libremcu.so
Add path with header files
.I remcu_include
Including necessary header files. The “remcu.h” header must be always included before any MCU header files.
#include "remcu.h"
#include "stm8l15x.h"
remcu_connect2OpenOCD(debug_server_ip, default_openocd_port, timeout_sec)
remcu_resetRemoteUnit(__HALT)
Setting up microcontroller peripherals:
GPIO_Init(GPIOE, GPIO_Pin_7, GPIO_Mode_Out_PP_High_Fast)
GPIO_Init(GPIOC, GPIO_Pin_7, GPIO_Mode_Out_PP_High_Fast)
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOE, GPIO_Pin_7);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC, GPIO_Pin_7);
notebook Jupyter.
6 c REMCU. Standard Peripheral Library . STM8L-Discovery, -:
void GPIO_Init(GPIO_TypeDef* GPIOx, uint8_t GPIO_Pin, GPIO_Mode_TypeDef GPIO_Mode);
void GPIO_ResetBits(GPIO_TypeDef* GPIOx, uint8_t GPIO_Pin);
SDK, . STM8L15X_EVAL. :
GPIO_Init(GPIOE, GPIO_Pin_7, GPIO_Mode_Out_PP_High_Fast);
GPIO_Init(GPIOC, GPIO_Pin_7, GPIO_Mode_Out_PP_High_Fast);
, REMCU notebook .

OpenOCD .
notebook, - GPIO_Init :

- GPIO_ResetBits,
Arduino. :
ADC code
CLK_PeripheralClockConfig(CLK_Peripheral_ADC1, ENABLE);
ADC_Init(ADC1, ADC_ConversionMode_Continuous, ADC_Resolution_12Bit, ADC_Prescaler_2);
ADC_SamplingTimeConfig(ADC1, ADC_Group_SlowChannels, ADC_SamplingTime_384Cycles);
ADC_Cmd(ADC1, ENABLE);
ADC_SoftwareStartConv(ADC1);
ADCData = ADC_GetConversionValue(ADC1);
- STM8 40,000 sample rate . , STM8L DMA — , ( ) . Jupyter Notebook — . .
, , . , , .
DMA ADC_DMA, notebook
Xplots . PC7 STM8LDiscovery.
( ):
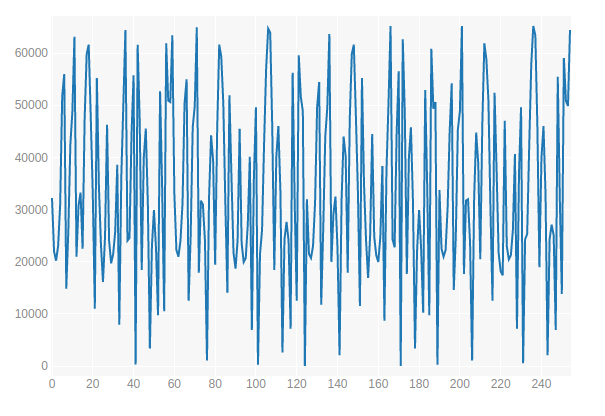
. , - , little-endian big-endian. , little-endian, STM8LDiscovery, big-endian! , . , .
#include <netinet/in.h>
for(int i = 0; i < 0xFF; i++){
uint16_t temp = adc_data[i];
temp = htons(temp);
adc_data[i] = temp;
}
line.y = adc_data;
fig
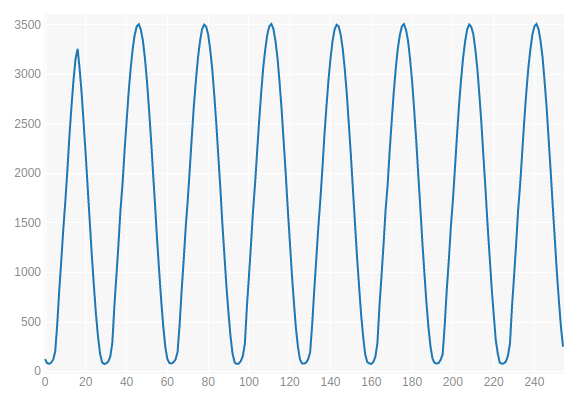
, .

- . - STM8LDiscovery . , , . , .
, , .
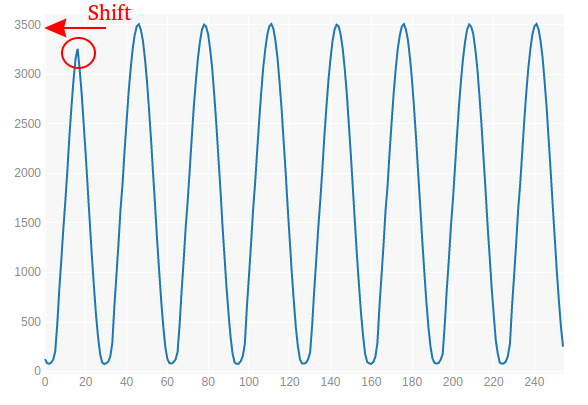
. :
int osc_data[ADC_BUFFER_SIZE] = {0};
size_t shift = DMA_GetCurrDataCounter(DMA1_Channel0);
for(int i = 0; i < ADC_BUFFER_SIZE; i++){ osc_data[i] = adc_data[i];}
shift = ADC_BUFFER_SIZE - shift;
for(size_t i = 0; i < ADC_BUFFER_SIZE; i++){
int shift_pos = (i + shift) % ADC_BUFFER_SIZE;
adc_data[i] = osc_data[shift_pos];
}
line.y = adc_data;
fig

. 8. — !
DMA STM8LDiscovery. 255 . , . 10.000 . , STM8LDiscovery — STM32F4Discovery. STM32F4 DMA 64 , . , sample rate , 255 .
, TIM1. - :
void TIM1_TimeBaseInit(uint16_t TIM1_Prescaler,
TIM1_CounterMode_TypeDef TIM1_CounterMode,
uint16_t TIM1_Period,
uint8_t TIM1_RepetitionCounter);
, . -, . . TIM1_Period, . TIM1_Period , .
, , :
SamplingTime = ADC_SamplingTime_4Cycles;
TIM1_Prescaler = 0x0;
TIM1_Period = 0x2;
TIM1_RepetitionCounter = 0;
, , 600-660 . .
, , notebook, ( DAC) STM8LDiscovery. , , DMA PF0 , , , , PC7( ) PF0( ) . notebook, :
DAC-DMA example
const uint16_t MEM_ADDRESS = ADC_BUFFER_SIZE*sizeof(adc_data.front()) + 1;
const uint8_t MEM_SIZE = 130;
uint8_t SINUS_TABLE[130] = {110,115,121,126,131,137,142,147,
152,157,161,166,171,175,179,183,187,191,195,198,201,204,207,209,
211,213,215,216,218,219,219,220,220,220,220,219,218,217,216,214,
212,210,208,205,202,199,196,193,189,185,181,177,173,168,164,159,
154,149,144,139,134,129,123,118,113,107,102,97,91,86,81,76,
71,66,61,56,52,47,43,39,35,31,27,24,21,18,15,12,
10,8,6,4,3,2,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,2,4,5,7,9,11,13,16,19,22,25,29,33,37,41,45,49,54,59,
63,68,73,78,83,89,94,99,105,110, };
CLK_PeripheralClockConfig(CLK_Peripheral_DAC, ENABLE);
CLK_PeripheralClockConfig(CLK_Peripheral_TIM4, ENABLE);
for(int i = 0 ; i < 130*sizeof(SINUS_TABLE[0]); i+=10){
remcu_store2mem(MEM_ADDRESS + i, (uint8_t*)SINUS_TABLE + i, 10);
}
/* DMA channel3 Config -----------------------------------------------------*/
#define DAC_CH1RDHRH_ADDRESS 0x5388
#define DAC_CH1RD8_ADDRESS 0x5390
#define DAC_CH1RDHLH_ADDRESS 0x538C
DMA_DeInit(DMA1_Channel3);
DMA_Init(DMA1_Channel3, MEM_ADDRESS,
DAC_CH1RD8_ADDRESS,
MEM_SIZE, DMA_DIR_MemoryToPeripheral, DMA_Mode_Circular,
DMA_MemoryIncMode_Inc, DMA_Priority_High,
DMA_MemoryDataSize_Byte
);
/* DMA1 Channel 3 enable */
DMA_Cmd(DMA1_Channel3, ENABLE);
DMA_GlobalCmd(ENABLE);
/* DAC Channel1 Config: 12bit right ----------------------------------------*/
/* DAC deinitialize */
DAC_DeInit();
/* Fill DAC Init param DAC_Trigger_T4_TRGO and DAC Channel1 Init */
DAC_Init(DAC_Channel_1, DAC_Trigger_T4_TRGO, DAC_OutputBuffer_Enable);
/* Enable DAC Channel1 */
DAC_Cmd(DAC_Channel_1, ENABLE);
/* Enable DMA for DAC Channel1 */
DAC_DMACmd(DAC_Channel_1, ENABLE);
TIM4_DeInit();
/* Time base configuration */
TIM4_TimeBaseInit(TIM4_Prescaler_1, 0x1);
/* TIM4 TRGO selection */
TIM4_SelectOutputTrigger(TIM4_TRGOSource_Update);
/* TIM4 enable counter */
TIM4_Cmd(ENABLE);
. big-endian, 8-bit.
, Standard Peripheral Library . , DAC_Noise&TriangleGenerator , -:
DAC_SetTriangleWaveAmplitude
- Standard Peripheral Library 1.4.0. , 1.4.0 REMCU.
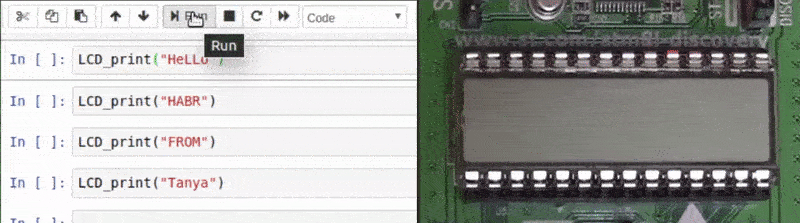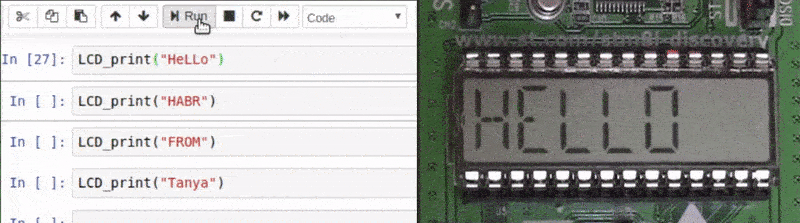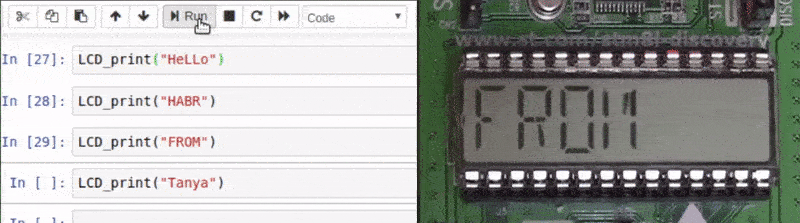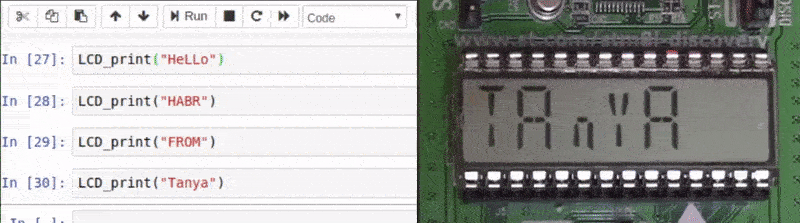
LCD , gif-. , . , 15 . STM8LDiscovery LCD . -:
void LCD_print(std::string str);
.
notebook' Github.
STM8L151 Jupyter Notebok. - , . , big-endian. , , , .
Je considère que l'expérience acquise est réussie, nous prévoyons d'utiliser STM8LDiscovery et le modèle plus professionnel STM32F4Discovery pour automatiser les expériences. Et maintenant, même les liants de la bibliothèque REMCU pour Python sont déjà apparus. Par conséquent, vous pouvez déjà vous passer d'une machine virtuelle avec Linux ou MacOS et écrire des scripts dans votre système de fenêtre natif.
Toutes les expériences intéressantes, que
Jupyter vous accompagne!