Esta nota es una visión general de la conexión entre la filosofía de la conciencia y la inteligencia artificial. Ella no pretende ser un estudio original, pero el autor espera una discusión fructífera y críticas aniquiladoras.
Introducción
En la actualidad, es difícil encontrar un tema que sea más relevante y de rápido desarrollo que la inteligencia artificial. Los problemas que surgen y los resultados alcanzados, tocando aspectos que son agudos para muchos, como el monopolio del hombre sobre la mente y la conciencia, requieren investigación filosófica, por ejemplo, el problema de distinguir entre inteligencia artificial "fuerte" y "débil" y, en particular, el problema de la posibilidad de crear "conciencia artificial" . Esta nota intenta proporcionar una visión general de las relaciones actuales entre las teorías filosóficas de la conciencia y el estado actual de la inteligencia artificial (IA).
Los filósofos existen mucho más tiempo que las computadoras e intentan resolver algunos problemas relacionados con la IA: ¿cómo funciona la mente? ¿Es posible que las máquinas actúen razonablemente como humanos, y si es así, tenían mentes reales, "conscientes"? ¿Cuáles son las implicaciones éticas de las máquinas inteligentes (Russel y Norvig, 2016)?
Sin embargo, debe tenerse en cuenta que será incorrecto considerar el nivel actual de desarrollo de IA como algo estable y aún más definitivo. Es posible encontrar completamente, al parecer, pronósticos razonables que no pueden soportar la prueba del tiempo. Entonces, en su libro muy popular "Gödel, Escher, Bach: This Endless Garland" (Hofstadter, 2001), el matemático y filósofo Douglas Hofstadter escribe que "se pueden crear programas que puedan vencer a cualquiera [en el ajedrez], pero [... ] serán programas de la mente [...] general y tendrán carácter ". Después de solo un par de décadas, los programas de ajedrez vencieron a cualquiera, mientras que, en primer lugar, no son sistemas de inteligencia artificial en el sentido completo (desde el punto de vista del estado actual de la informática), y en segundo lugar, sin mostrar, por supuesto,no es el menor signo de conciencia en la comprensión intuitiva del término.
:
«» .
, « , » (Samuel, 1756).
«» . «» : , , ( , ) . , — , : , , (Sutherland, 1989). «» , ; , , -, — . . , - , , (Vimal, 2006).
, , , . (Schneider & Velmans, 2008):
- : , , . , . .
- : , .
- : (, ) . — .
- : , , , , , , .
- : , .
.
«»
, , , , .
. , , . , — , . , (Descartes, 2008). , . . «», «». , , (Gennaro, 1999).
, . , - . , . : , , , , - , .
, , «» ( «») « ». (Skirry, 2016): « - , ?».
, . .
, , . , , , - . , , . , , , . , . .
, , , , . « ».
« » — (, 2009) , - . :
, .
- , - , (Jackson, 1982).
, . ( ), ( , , ) ().
, , . , . .
, , , , — . , , , (. « »).
, , , , , .
« » « » (Chalmers, 1996).
, : , , , . , — , . ? « », . , .
, (Salazar, et al., 2019), , : , , , , , — . — ; , . , , , : , , , , .
, , , , , ( ), . (. « ») — , , , , .
, « », (Jackson, 1982). , , - . , , , ( , ). - . , - , — , . , , , , , .
( ), , , , — , . , , , , . -, « » , - . « - ». , , , — , , , , , , . -, - « » . , - , . , , , , , , , — , .
, , , :
« » (Philosophy Index, 2020) , . , — , .
, , — . , «, , » ( – «» «») ( «» «»).
()
- , . . - , , , . -, , , , , ( ) ( ) — , , , .
(, 2000) , . , , , — , . - , , «» . — , «», «», «», «». , , , ( ) ( ) . . , , .
, . , , , . , , . , , , .
() . (Tononi, 2004; Fallon, 2020) 2004 , , , , , ϕ-.
, , - . , , , , , , . , . . , - , . .
, , , . . ϕ- , , , .
Φ — - , . — φ>0, ϕ. , , . , , , , .
(Dennett D., 1991) , . , ϕ-. , . , , , . , , . , , , . , , , .
, , . , , . , .
, « » , , .
«»
, «» .
, : , , . , , -. . — , - , , , . , , .
, .
, , ( ) , ; . , (Gallup, 1970). 50 , . , , , , .
, , .
, , , . , , .
, , (. « »).
, , , . ( . . — « , , » (, 1964) , - , .
, (Searle, 1983) — .
, , , «» (Allen, 2001). , , -, , -. «». «» , . («») , , . «-» , .
. , , . , « » (., , (Churchland, 1986), . , , .
«qualia» 1929 . . . .
, , , . . , , , , . , , . . , , , . (. « »).
, «» , , .
.
1950 (Turing, Computing Machinery and Intelligence, 1950), : " « ?». , , , , « », .
, ( ) . , ; , 30% . , 2000 109 , . — .
, , , . ELIZA -, MGONZ NATACHATA, , - CYBER LOVER - « » (Russel & Norvig, 2016). , 1991 , , « ». . , , .
(McCarthy, 2007).
— , . , , .
«» . , .
«», . , , . , .
« ?» — . , , . , . «».
. , - , , , . , , , . , , , .
, , , . , , , , , . , , . , .
, 2007 , 1970 , «», «». , , , « », . , AlphaZero , (Silver, 2017).
, .
1949 (Jefferson, 1949): « , , , , , , .. , , . ( , ) , , , - , , , ».
, -, « ». , , , , , . , , , . , , , , , , . .
(« — , » (Gardner, 1983).
, , , . , , , .
, , , , , .
. , «» , , «» . , , (Joshi, 2016):
, . . , . , , . . «». . . IBM Deep Blue, 1997 .
— , , . , , . , , , , , .
, , . — , . , , , , . - , , , , «» .
, . , , . , , , . , , , , .
, , « », « » « -».
, , - . , , , .
() — , , . , , .
-
- (), , , , , , . , .
« » «» «» .
: ?
, , , , , , , ( ), .
, — , , , .
— . , , , « ?» « ?» (Russel & Norvig, 2016).
, , (Turing, Computing Machinery and Intelligence, 1950). . (Kurzweil, 2005), — , . , , . - , , , .
, , , , .
: ?
« » , - , -, , , — . .
. , ( , ). , , : « ?». , ? . , : « , , , ».
, , : . , . . , , «» - . , , .
, «» (. . (Holland, 2003) . , , .
, : « «» , ?» . , 10 , . , « » . , « » . (. « »).
, , . , . . , , . , .
.
, , , (. Theory of Mind). .
.
theory of mind ( « ») . .
— , , , , — (Premack & Woodruff, 1978).
, , , .
, (« »).
, — , (). , , , , , , «». — , «» .
, — , , (, , ) — , (Rescorla, 2020).
, . , . , , . , , - . , . , (, , ). , .
:
- . , . , (, ) (, ). , ;
- . . , ;
- : , . - . . . , (Gallistel & King, 2009);
- , , . , . , , (Fodor & Pylyshyn, Connectionism and Cognitive Architecture: A Critical Analysis, 1988);
- : . . . , , .
, «- », .
, .
(Putnam, 1967) « ». . , (, ), (, ) (, ). , . , — . , . , , . — , . , . (. « »).
1980- , . , . , , .
«», (. . -) . :
- . , , - , ;
- . - . - (Graves, Wayne, & Danihelka, 2014).
, « », . , «» , . : , - . , « » (. ).
. . (Scassellati, 2002) , , - (Simon Baron-Cohen) (Alan M. Leslie).
, , .
, , . , ; , . , , , , . , .
- , . , Cog, , - ( , ), , , , , , , .
, , , , , . -, , - . , , . , Cog , 2002 . , .
(Blum, Hafner, & Winfield, 2018).
« », , , ( ), . , , .
« , », — . « [...] — ». , .
, , , , , . , , , , .
, , . , , « ». , , , «, » . , , , , . , , , . « ».
. , , , , — . , , , . , : « », : .
, (Schreiber, 2020), , , «», , , , , . , , . « », , , . , , . , . , , , , — .
, (Allen, 2001). , , ( ) . , , , , , , . (Davidson, 1975) , , , , .
, . : .
, , , . (Zhu, 2009), :
« » (intentional stance).
« » (Dennett D. C., 1987): « : , , ; , , . , , , , , , . , ; , ».
, , , , , , . « » ( 1) — , (Braitenberg, 1984). , , « , , , ». , , , « », « », « ». , , , .
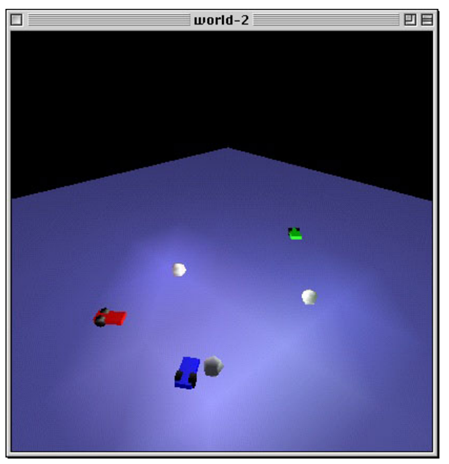
, , . (, Adobe Photoshop) (, Microsoft Clippy). , . , Voyager — , (Lewis, 2000). . , «» -, « ». Voyager’ , «» , .
. , , . , , , , , , .
, , , . , , . , «» . , .
, (Chella & Gaglio, 2009). , ( 2). , . . , , 3D . - . «» «», .
. , - . , . , - . , . , , , , , 2D, , , . 2D , . , , .
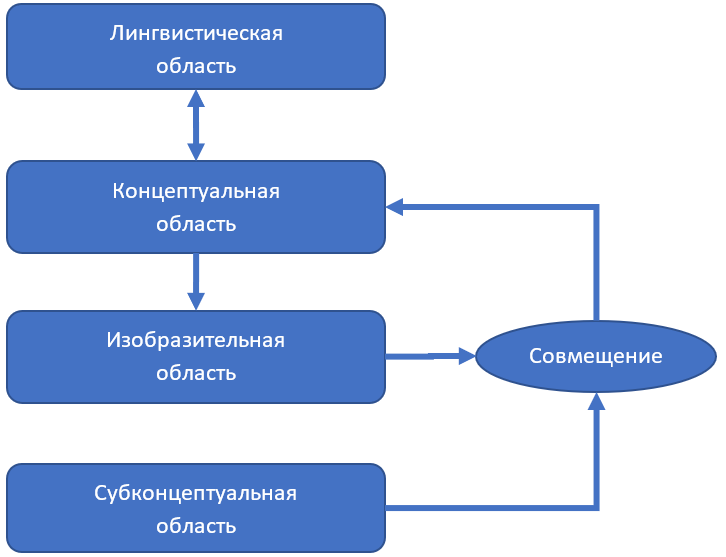
, , . (Gärdenfors, 2000). , , . — , — , , , , . , . , , : , , , . , . , - .
, - . « », , , . .
, Situation (), Action (), Time_Instant ( ) . «» , (, precond (), part_of ().
.
«, — », , (Woods & Schmolze, 1992):
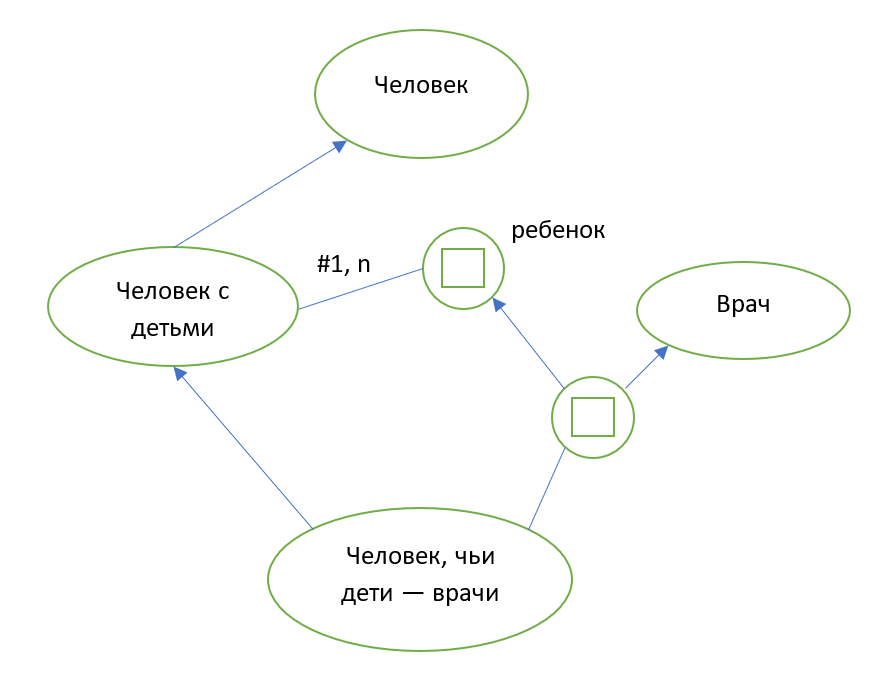
, 2D ( 3D), , .
, (), «» , . . ( 4).

— , , , , , .
, ( 4) «» , , , — , — :
" " . , :
- ;
- ;
- , , .
, , . , , - , :
- — , ;
- , , .
, , , :
- ;
- / ;
- /.
(Bringsjord & Govindarajulu, 2013) R, , :
- R;
- , R;
- , R;
- , .
, , , .
(Yampolskiy, 2017) , , , . . , . , , , , , . «» (, , . .), , , , , , . , . . , , , . .
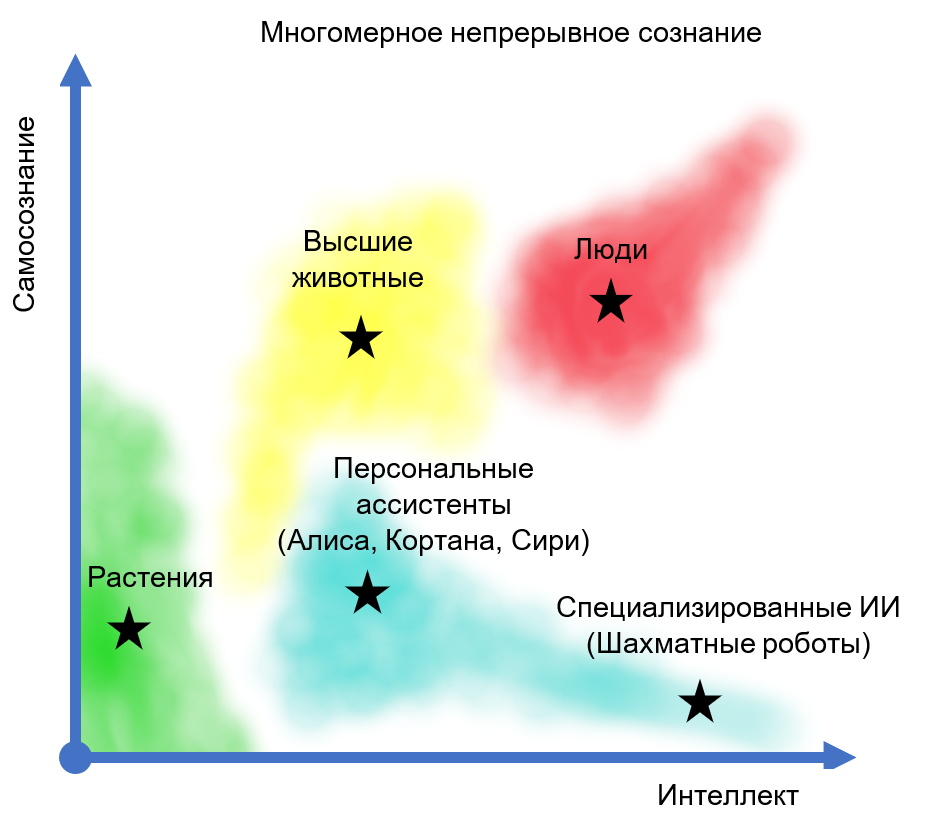
— , ( 5). , , , : « ? ? ?» , , . , . , : «, , ». , , .
(Koch, 2019), OpenAI GPT-2 (Radford, et al., 2019). GPT-2 — , , : - , . «» . , , , , . . , -, DeepL (Coldeway & Lardinois, 2017) :
, , , .
, .
.
. .
(Fodor & Block, What Psychological States Are Not, 1972). « ». . . , , . , . , , - , . , . -, , .
« ». . , , « », « ». , , . . , . . , . , , . .
(Rescorla, 2020). .
, , . , , , . , , , .
, , « » (, 1989).
, . , , .
? ? , ? , , . , , .
:
- - «» , .
- , (), «» , , .
- , , , -.
- , , .
́
. , (, ). , , , . - , . , , .
, . , « », , . , , , ́, , . , , .
« » , , . , . , , . , , . , .
.
(Graziano, 2016) .
, . — . . ́ , . , .
, , . , , – . , , . , « ».
, . , , , , .
, . . , , . , . . . . , : «, !». .
, , , . . . . . , , . , . , , .
?
— . , . . , .
, - — . . , , , . , , , — , . . — .
-, , , , , , , , .
, - « » — « ?». , , , , ?
:
- , ;
- , , , ;
- " ", , , ;
- .
, , , , ( ) -, , ".
, . , (Fretten, 2017).
, , , , , , , , , . , , , . , , , - , .
«» « » , - , . «» , , - , , - - , , , , , , .
, «» . « ».
« », (Searle, 1983; Hauser, 2020) , , «» «» , . ; «» ( «») , . , , . , , «», «», «»; , « ». «»: .
, , , . , , -.
, , , : « , . , , , , ».
« — » (Kugel, 2004) . « »,
- , ,
- ,
- , «».
, — — (1) (2) «» . , : .
, . , (1) — , — . , (2) — — .
, , , ( ):
- : « «» «», . ?»
- : «.»
- : « , — ?»
- : «.»
, , , , (). , , . , «».
, . « », . , « ».
« » , : , , , . , «, , », , « , ».
, « », , . « », — , — « , , , ».
« » , , .
, . , , « », . . , , , .
, , , . : , , . «» , .
(Holloway, 2019), , . , (Turing, On Computable Numbers, with an Application to the Entscheidungsproblem, 1937). , , , . , , « ». , , .
:
- .
- , , , .
- , , .
:
- , .
- , .
- « », . . , , , , , , .
, ? , , . , , . , , , . , , , .
, , , . — .
, , , - , , . , .
, , .
(Mumford, 2019) , , «, ». , . , , , . , , , , , , , . , , , , . . , , , : « , ». : « , , ». , . , : « , ». — , , , .
, () ( ), . « » , , , . , , , , , , - , .
, , . , , , , . , , - .
(Nguyen, Yosinski, & Clune, 2014) , , , , ImageNet, , 99,6% , . , DNN (. 6).
, , « » , , 35% . , 20% , .
(Manzotti & Chella, 2018) , «» ( — Good Old-Fashioned Artificial Consciousness, GOFAC) .
— , . , , , « ».
GOFAC , . , , , , . , , , , , , . , , , : . « », , , .
, . , , . , . , - — . . « » , — . .
, , « ». -, , , , , , . , - -. , . , . , , , — -, -, / .
Actualmente, el desarrollo de teorías de IA y algunas teorías de conciencia van de la mano. Sin embargo, vemos que la adopción de la hipótesis de la inteligencia artificial "fuerte" conduce a la incompatibilidad de muchas teorías de conciencia existentes, especialmente las idealistas.
A pesar de que la cuestión de la posibilidad de inteligencia artificial "fuerte" sigue abierta, los principales argumentos en su contra, como la "sala china", son cada vez más inferiores bajo la presión de los nuevos desarrollos en el campo de las "máquinas inteligentes".
Bibliografía
Referencias- Allen, C. (2001). Intentionality: Natural and Artificial. Department of History & Philosophy of Science. University of Pittsburgh:
- Blum, C., Hafner, V., & Winfield, A. (2018). Simulation-Based Internal Models for Safer Robots. Front. Robot. AI.
- Braitenberg, V. (1984). Vehicles: Experiments in synthetic psychology. Cambridge: MIT Press.
- Bringsjord, S., & Govindarajulu, N. (2013). Toward a Modern Geography of Minds, Machines, and Math. Philosophy and Theory of Artificial Intelligence, 151-165.
- Chalmers, D. (1996). The Conscious Mind: In Search of a Fundamental Theory. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Chella, A., & Gaglio, S. (2009). In Search of Computational Correlates of Artificial Qualia. Proceedings of the 2nd Conference on Artificial General Intelligence.
- Churchland, P. (1986). Neurophilosophy: toward a unified science of the mind/brain. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- Coldeway, D., & Lardinois, F. (2017). DeepL schools other online translators with clever machine learning. TechCrunch
- Davidson, D. (1975). Thought and talk. Mind and Language, Oxford University Press.
- Dennett, D. (1991). Consciousness Explained. New York: Little, Brown.
- Dennett, D. C. (1987). The Intentional Stance. Cambridge: MIT Press.
- Descartes, R. (2008). Descartes and the Pineal Gland. Stanford University.
- Fallon, F. (2020). Integrated Information Theory of Consciousness. Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy
- Fodor, J., & Block, N. (1972). What Psychological States Are Not. The Philosophical Review, 81, 159–181.
- Fodor, J., & Pylyshyn, Z. (1988). Connectionism and Cognitive Architecture: A Critical Analysis. Cognition, 28, 3–71.
- Fretten, R. (2017). How Artificial Intelligence is Making Us Rethink Consciousness. Medium
- Gallistel, C., & King, A. (2009). Memory and the Computational Brain. Malden: Wiley-Blackwell.
- Gallup, G. G. (1970). Chimpanzees: Self-Recognition. Science, 86–87.
- Gärdenfors, P. (2000). Conceptual Spaces. Cambridge: MIT Press.
- Gardner, M. (1983). The Whys of a Philosophical Scrivener. New York: Quill.
- Gennaro, R. (1999). Leibniz on Consciousness and Self Consciousness”. R. Gennaro, & C. Huenemann, New Essays on the Rationalists. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Graves, A., Wayne, G., & Danihelka, I. (2014). Neural Turing Machines. arXiv
- Graziano, M. (2016). Most Popular Theories of Consciousness Are Worse Than Wrong. The Atlantic
- Hauser, L. (2020). Chinese Room Argument. The Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy
- Holland, O. (2003). Machine Consciousness. New York: Imprint Academic.
- Holloway, E. (2019). Artificial Intellegence Must Be Possible. Mind Matters
- Jackson, F. (1982). Epiphenomenal Qualia. Philosophical Quarterly, 32.
- Jacob, P. (2019). Intentionality. The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy
- Jefferson, G. (1949). The Mind of Mechanical Man. British Medical Journal, i, 1105-1121.
- Joshi, N. (2016). 7 Types Of Artificial Intelligence. ]Forbes Cognitive World
- Koch, C. (2019). Will Machines Ever Become Conscious? Scientific American
- Kugel, P. (2004). The Chinese room is a trick. BEHAVIORAL AND BRAIN SCIENCES 27, 153–168.
- Kurzweil, R. (2005). Long Live AI. Forbes
- Lewis, G. E. (2000). Too many notes: Computers, complexity and culture in voyager. Leonardo Music Journal, vol. 10, 33–39.
- Manzotti, R., & Chella, A. (2018). Good old-fashioned artificial consciousness and the intermediate level fallacy. Frontiers in Robotics and AI.
- McCarthy, J. (12 11 2007 .). What Is Artificial Intelligence:
- Mumford, D. (11 April 2019 .). Can an artificial intelligence machine be conscious? David Mumford. Archive for Reprints, Notes, Talks, and Blog:
- Nguyen, A., Yosinski, J., & Clune, J. (2014). Deep Neural Networks are Easily Fooled: High Confidence Predictions for Unrecognizable Images. arXiv.
- Philosophy Index. (2020). Type Identity Theory.
- Premack, D., & Woodruff, G. (1978). Does the chimpanzee have a theory of mind? Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 1, 515—526.
- Putnam, H. (1967). Psychophysical Predicates. Art, Mind, and Religion.
- Radford, A., Wu, J., Child, R., Luan, D., Amodei, D., & Sutskever, I. (2019). Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners. Computer Science.
- Rescorla, M. (2020). The Computational Theory of Mind. Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy
- Russel, S. J., & Norvig, P. (2016). Artificial Intelligence. A Modern Approach. Third Edition. Harlow: Pearson Education Limited.
- Salazar, H., Hendricks, C., Vintiadis, E., Asoulin, E., Blum, P., Haas, D., Cheng, T. (2019). Introduction to Philosophy: Philosophy of Mind. Rebus Community. Introduction to Philosophy: PPhilosophy of Mind.
- Samuel, J. (1756). A Dictionary of the English language. London.
- Scassellati, B. (2002). Theory of Mind for a Humanoid Robot. Autonomous Robots.
- Schneider, S., & Velmans, M. (2008). The Blackwell Companion to Consciousness.
- Schreiber, A. (2020). AI Theory of Mind. Medium — Artificial Intelligence:
- Searle, J. (1983). Intentionality. An essay in the philosophy of mind. Cambridge.
- Silver, D. e. (2017). Mastering Chess and Shogi by Self-Play with a General Reinforcement Learning Algorithm. arXiv:1712.01815.
- Skirry, J. (2016). Rene Descartes: The Mind-Body Distinction. Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy
- Sutherland, S. (1989). Consciousness. Macmillan Dictionary of Psychology. Macmillan.
- Tononi, G. (2004). An information integration theory of consciousness. BMC Neuroscience, 5: 42.
- Turing, A. M. (1937). On Computable Numbers, with an Application to the Entscheidungsproblem. Proceedings of the London Mathematical Society, Vol. 42, 230–265.
- Turing, A. M. (1950). Computing Machinery and Intelligence. Mind, v.59, pp. 433 — 460.
- Vimal, R. L. (2006). Meanings attributed to the term "consciousness". Journal of Consciousness Studies.
- Woods, W., & Schmolze, J. (1992). The KL-ONE Family. Computers Mathematical Applications, 133-177.
- Yampolskiy, R. V. (2017). Detecting Qualia in Natural and Artificial Agents. arXiv
- Zhu, J. (2009). Intentional Systems and the Artificial Intelligence Hermeneutic Network. Georgia Institute of Technology.
- , . . (2009). . : -.
- , . . (1964). . : .
- , . (1989). The Emperor's New Mind: Concerning Computers, Minds and The Laws of Physics. .
- , . (2000). . : -.
- , . . (2001). , , : . : "-".