Bloc de notas CoLab con ejemplos.
Es posible hacer una ventana móvil ( ventana móvil, ventana deslizante , ventana móvil) sobre matrices NumPy en el lenguaje de programación Python sin bucles explícitos . Este artículo aborda la creación de ventanas deslizantes de una, dos, tres y N dimensiones sobre matrices NumPy. Como resultado, los datos de velocidad de procesamiento aumenta en varios miles de veces y es comparable en velocidad con el C lenguaje de programación .
Se utiliza una ventana deslizante en: procesamiento de imágenes, redes neuronales artificiales, protocolo de Internet TCP, procesamiento de datos genómicos, predicción de series temporales, etc.
Descargo de responsabilidad : ¡ Puede haber errores en el código fuente! Si ve un error, escríbame.
Introducción
Este artículo es una continuación de mi respuesta en el sitio web StackOverflow. Mis primeros experimentos con una ventana deslizante aquí y aquí .
La implementación práctica de una ventana bidimensional deslizante en una matriz de imágenes bidimensionales está en función del rollarchivo del logic_tools.pyproyecto: marcado manual de imágenes utilizando polígonos .
Los algoritmos para una ventana deslizante unidimensional ya están implementados aquí , aquí y aquí .
, , (strides, ).
- Pandas, Pandas, , . , . , Cython, - , NumPy.
1. 1D ND Numpy

:
def roll(a,
b,
dx=1):
shape = a.shape[:-1] + (int((a.shape[-1] - b.shape[-1]) / dx) + 1,) + b.shape
strides = a.strides[:-1] + (a.strides[-1] * dx,) + a.strides[-1:]
return np.lib.stride_tricks.as_strided(a, shape=shape, strides=strides)
numpy.lib.stride_tricks.as_strided (view) (shape) (strides).
(shape) , , . (strides) .
(shape) :
a.shape[:-1] — ND-, N > 1. N == 1, t == (), N == 1.(int((a.shape[-1] - b.shape[-1]) / dx) + 1,) — [-1] . dx : 1, 2, 3 ..b.shape — .
(strides) :
a.strides[:-1] — ND-, N > 1. N == 1, t == (), N == 1.(a.strides[-1] * dx,) — . , int 4 , dx == 2 4 * 2 = 8 .a.strides[-1:] — . , int 4 , (4,).
2. 2D ND Numpy

2D 2D :
, 2D - . , , , , .. , , .
def roll(a,
b,
dx=1,
dy=1):
shape = a.shape[:-2] + \
((a.shape[-2] - b.shape[-2]) // dy + 1,) + \
((a.shape[-1] - b.shape[-1]) // dx + 1,) + \
b.shape
strides = a.strides[:-2] + \
(a.strides[-2] * dy,) + \
(a.strides[-1] * dx,) + \
a.strides[-2:]
return np.lib.stride_tricks.as_strided(a, shape=shape, strides=strides)
: , , — ((a.shape[-2] - b.shape[-2]) // dy + 1,). :
(int((a.shape[-1] - b.shape[-1]) / dx) + 1,)
((a.shape[-1] - b.shape[-1]) // dx + 1,)
.
() , (a.strides[-2] * dy,) 2D .
counts, coords :
def show_results(a, b, dx=1, dy=1):
n = a.ndim
bool_array = np.all(roll(a, b, dx, dy) == b, axis=(n, n+1))
counts = np.count_nonzero(bool_array)
coords = np.transpose(np.nonzero(bool_array)) * [dy, dx]
print("Found {counts} elements with coordinates:\n{coords}".format(
counts=counts, coords=coords))
np.all 2D 4D . coords [dy, dx] .
3. 3D ND Numpy
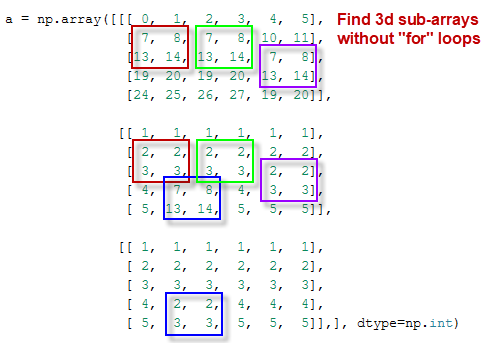
() - . , 3D ND- .
3D 3D — ( ) . CoLab 3D - , (, , ..).
def roll(a,
b,
dx=1,
dy=1,
dz=1):
shape = a.shape[:-3] + \
((a.shape[-3] - b.shape[-3]) // dz + 1,) + \
((a.shape[-2] - b.shape[-2]) // dy + 1,) + \
((a.shape[-1] - b.shape[-1]) // dx + 1,) + \
b.shape
strides = a.strides[:-3] + \
(a.strides[-3] * dz,) + \
(a.strides[-2] * dy,) + \
(a.strides[-1] * dx,) + \
a.strides[-3:]
return np.lib.stride_tricks.as_strided(a, shape=shape, strides=strides)
counts coords :
def show_results(a, b, dx=1, dy=1, dz=1):
n = a.ndim
bool_array = np.all(roll(a, b, dx, dy, dz) == b, axis=(n, n+1, n+2))
counts = np.count_nonzero(bool_array)
coords = np.transpose(np.nonzero(bool_array)) * [dz, dy, dx]
print("Found {counts} elements with coordinates:\n{coords}".format(
counts=counts, coords=coords))
4. MD ND , M ≤ N
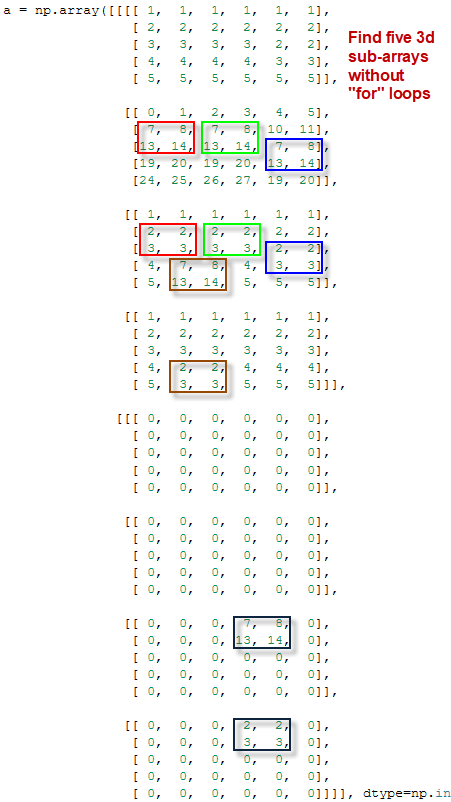
roll show_results MD ND , M N : M ≤ N.
def roll(a,
b,
d=None):
n = a.ndim
m = b.ndim
if m > n:
print("Error: rolling window dimensions is larger than the array dims")
return None
if d is None:
d = np.ones(m, dtype=np.uint32)
elif d.ndim != 1 and d.size != m:
print("Error: steps number must be equal to rolling window dimensions")
return None
elif not np.issubdtype(d.dtype, np.integer) or \
not (d > 0).all():
print("Error: steps must be integer and > 0")
return None
s = np.flip(d)
sub = np.subtract(a.shape[-m:], b.shape[-m:])
steps = tuple(np.divide(sub, s).astype(np.uint32) + 1)
shape = a.shape[:-m] + steps + b.shape
section = tuple(np.multiply(a.strides[-m:], s))
strides = a.strides[:-m] + section + a.strides[-m:]
return np.lib.stride_tricks.as_strided(a, shape=shape, strides=strides)
roll . :
steps = tuple(np.divide(sub, s).astype(np.uint32) + 1) — .section = tuple(np.multiply(a.strides[-m:], s)) — () « ».- « »
section ND-: strides = a.strides[:-m] + section + a.strides[-m:].
counts coords :
def show_results(a, b, d=None):
n = a.ndim
m = b.ndim
if d is None:
d = np.ones(m, dtype=np.uint32)
bool_array = roll(a, b, d) == b
bool_array = np.all(bool_array, axis=tuple(range(n, n + m)))
counts = np.count_nonzero(bool_array)
s = np.concatenate((np.ones(n-m, dtype=int), np.flip(d)))
coords = np.transpose(np.nonzero(bool_array)) * s
print("Found {counts} elements with coordinates:\n{coords}".format(
counts=counts, coords=coords))
show_results :
- ()
bool_array . numpy.all m , True. , bool_array — (N+M)D , np.all m MD :
bool_array = roll(a, b, d) == b
bool_array = np.all(bool_array, axis=tuple(range(n, n + m)))
5. MD ND M N
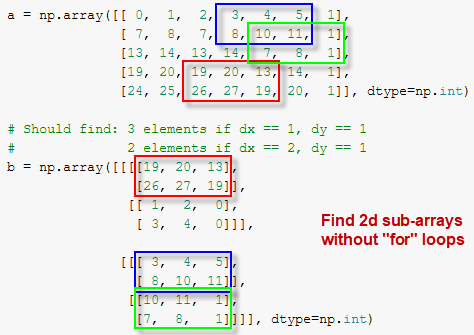
MD ND , M > N? , ! ND , MD M > N.
MD ND . MD ND M N. roll show_results.
def get_results(a, b, d=None):
n = a.ndim
m = b.ndim
if d is None:
d = np.ones(m, dtype=np.uint32)
bool_array = roll(a, b, d) == b
bool_array = np.all(bool_array, axis=tuple(range(n, n + m)))
counts = np.count_nonzero(bool_array)
s = np.concatenate((np.ones(n-m, dtype=int), np.flip(d)))
coords = np.transpose(np.nonzero(bool_array)) * s
return (counts, coords)
def show_intersections(a, b, d=None):
d_tmp = d
n = a.ndim
m = b.ndim
if d_tmp is None:
d_tmp = np.ones(m, dtype=np.uint32)
elif m > n and d_tmp.size == n:
d_tmp = np.concatenate((np.ones(m-n, dtype=int), d_tmp))
counts = 0
coords = None
if m <= n:
results = get_results(a, b, d_tmp)
counts = results[0]
coords = results[1]
else:
t = m - n
layers = np.prod(b.shape[:t])
temp = b.reshape((layers,) + b.shape[t:])
for i in range(layers):
results = get_results(a, temp[i], d_tmp[t:])
counts += results[0]
if coords is None:
coords = results[1]
else:
coords = np.concatenate((coords, results[1]))
print("Found {counts} elements with coordinates:\n{coords}".format(
counts=counts, coords=coords))
get_results , show_results .
show_intersections . M <= N, show_intersections get_results, . M > N, b a.
t = m - n MD b ND a. b a: layers = np.prod(b.shape[:t]). ( , reshape) b MD (N+1)D :
temp = b.reshape((layers,) + b.shape[t:])
: (N+1)D ND, (N+1) layers:
for i in range(layers):
results = get_results(a, temp[i], d_tmp[t:])
Combine el número de coincidencias countsy las coordenadas encontradas de estas coincidencias coordspara cada capa:
for i in range(layers):
results = get_results(a, temp[i], d_tmp[t:])
counts += results[0]
if coords is None:
coords = results[1]
else:
coords = np.concatenate((coords, results[1]))
Todos los ejemplos están en el bloc de notas CoLab .
¡Gracias por la atención!