Problema
Uno de los problemas de Java es su verbosidad y la cantidad de código estándar que se necesita. Esto es de conocimiento común.
Veamos una clase simple de Cat en Java. Queremos que cada objeto Cat tenga los siguientes atributos (campos):
- Nombre
- Número de vidas
- Color
Bastante simple, ¿verdad? Ahora veamos el código en Java. Para simplificar, hagamos que nuestra clase sea inmutable (inmutable): sin setters, configuraremos todo en nuestro constructor.
public final class Cat {
private final String name;
private final int numberOfLives;
private final String color;
public Cat(String name, int numberOfLives, String color) {
this.name = name;
this.numberOfLives = numberOfLives;
this.color = color;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getNumberOfLives() {
return numberOfLives;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
}
Ya es bastante largo, ¿no?
. equals() hashCode().
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Cat cat = (Cat) o;
return numberOfLives == cat.numberOfLives &&
Objects.equals(name, cat.name) &&
Objects.equals(color, cat.color);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, numberOfLives, color);
}
? , toString():
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cat{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", numberOfLives=" + numberOfLives +
", color='" + color + '\'' +
'}';
}
. ! ( IDE ) . , (, ) .
, :
private final String name;
private final int numberOfLives;
private final String color;
— , . IDE , , Lombok, .
Java , , Cat. — , , equals(), hashCode() toString(). , , . — , . . , hashCode() equals()?
Records
Java 14 , Record, JEP 359: Records (Preview).
50 , :
public record Cat(String name, int numberOfLives, String color) { }
, ?
, — :
- equals(), hashCode() toString()
, .
public final class Cat extends java.lang.Record {
private final java.lang.String name;
private final int numberOfLives;
private final java.lang.String color;
public Cat(java.lang.String name, int numberOfLives, java.lang.String color) { }
public java.lang.String toString() { }
public final int hashCode() { }
public final boolean equals(java.lang.Object o) { }
public java.lang.String name() { }
public int numberOfLives() { }
public java.lang.String color() { }
}
, Cat. , , — getColor() color().
java.lang.Record.
equals() , . toString() :
Cat[name=Fluffy, numberOfLives=9, color=White]
, , .
, .
, . , , , . :
public record Cat(String name, int numberOfLives, String color) {
public boolean isAlive() {
return numberOfLives >= 0;
}
}
.
(Custom)
, . , Cat :
Cat cat = new Cat("Fluffy", 9, "White");
, — , .
, , 9. , , 9 . , .
public record Cat(String name, int numberOfLives, String color) {
public Cat(String name, String color) {
this(name, 9, color);
}
}
. . , . , , :
public record Cat(String name, int numberOfLives, String color) {
public Cat(String name,int numberOfLives, String color) {
if(numberOfLives < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of lives cannot be less than 0.");
}
if(numberOfLives > 9) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cats cannot have that many lives.");
}
this.name = name;
this.numberOfLives = numberOfLives;
this.color = color;
}
}
, ( ), . , .
public record Cat(String name, int numberOfLives, String color) {
public Cat {
}
}
java.lang.Class , , .
isRecord(). , , - :
Cat cat = new Cat("Fluffy", 9, "White");
if(cat.getClass().isRecord()) {
}
getRecordComponents(). , . java.lang.reflect.RecordComponent. , , :
!
, , Java 14 ( 2/2020).
Preview feature ( )
(Records) Java 14. . ?
VM — Java SE, , , . JDK ; , Java SE.
JDK , , Java SE , , . , ( ), ( ), .
JDK, . . , , , .
, JDK 14.
IntelliJ IDEA
IntelliJ IDEA Preview feature File → Project Structure.
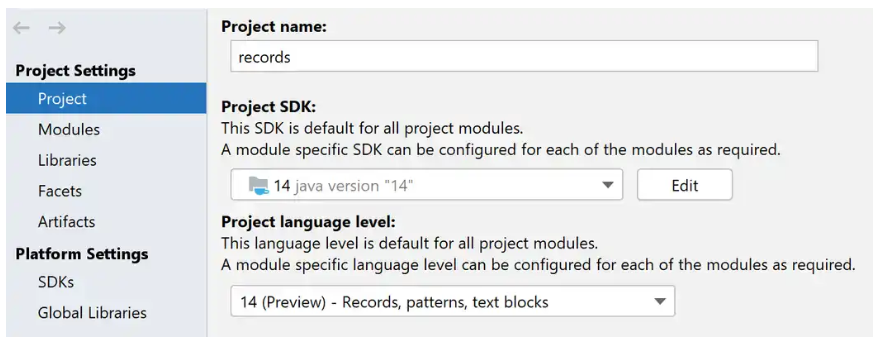
Para usar entradas en IntelliJ IDEA, necesitará la versión 2020.1 y posteriores. A partir del 2/2020, está disponible como una compilación del Programa de acceso temprano . IDEA actualmente tiene soporte básico para grabaciones, pero el soporte completo debería estar disponible en la versión de lanzamiento.
Compilación manual
Una alternativa es ensamblar manualmente el proyecto. Luego debe proporcionar las siguientes opciones para javac:
javac --release 14 --enable-preview ...
Esto es para compilación. En tiempo de ejecución, simplemente proporciona --enable-preview
java --enable-preview ...
Proyectos Maven
Para las compilaciones de Maven, puede usar la siguiente configuración:
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<release>14</release>
<compilerArgs>
--enable-preview
</compilerArgs>
```14</source>
<target>14</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<argLine>--enable-preview</argLine>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-failsafe-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<argLine>--enable-preview</argLine>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>