I present the translation of the article "Masks Don't Work: A review of science relevant to COVID-19 social policy" by Denis Rancourt .
annotation
Masks and respirators are useless.
Extensive randomized controlled trials and a meta-analysis of such trials indicate that masks and respirators do not affect the spread of influenza-like acute respiratory infections (ARIs), which are thought to be transmitted through droplets and aerosol particles.
Moreover, the corresponding physical and biological foundations are such that masks and respirators should not work, given what is known about ARI: the main transmission route is aerosol particles (less than 2.5 micrometers), too small to be blocked and the minimum infectious dose is less than one aerosol particle.
This masked article illustrates the level at which governments, the media, and institutional advocates can act in a scientific vacuum, or by choosing only the scientific data that serves their interests. Such recklessness certainly takes place in true global quarantine, when more than a billion people participate in an experiment unprecedented in the history of medicine and politics.
From a translator, very briefly and popularly. Probably everyone saw dust flying in the air. Viruses are even smaller, they are not hindered by any partitions or distances (except for kilometers, but this is not accurate - see below). Studies and discussions about the benefits of masks are as significant as arguments about reducing the dose of poison from 10 to 2-3 grams when the lethal dose is 1 gram.
Overview of Medical Publications
Many scientific publications prove that surgical masks and respirators (for example, type N95) do not reduce the risk of infection and disease. A review of this literature can be started with the following articles:
- Jacobs, J. L. et al. (2009) “Use of surgical face masks to reduce the incidence of the common cold among health care workers in Japan: A randomized controlled trial” (« : »), American Journal of Infection Control, Volume 37, Issue 5, 417-419, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19216002: « N95 . ».
- Cowling, B. et al. (2010) “Face masks to prevent transmission of influenza virus: A systematic review” (« : »), Epidemiology and Infection, 138(4), 449-456, https://doi.org/10.1017/S0950268809991658: « , . . 1 2».
- bin-Reza et al. (2012) “The use of masks and respirators to prevent transmission of influenza: a systematic review of the scientific evidence” (« : »), Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses 6(4), 257–267, https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1111/j.1750-2659.2011.00307.x: « 17 / ».
- Smith, J. D. et al. (2016) “Effectiveness of N95 respirators versus surgical masks in protecting health care workers from acute respiratory infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis” (« N95 : »), CMAJ Mar 2016, cmaj.150835, https://www.cmaj.ca/content/188/8/567: « 6 N95 : , , ».
- Offeddu, V. et al. (2017) “Effectiveness of Masks and Respirators Against Respiratory Infections in Healthcare Workers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis” (« »), Clinical Infectious Diseases, Volume 65, Issue 11, 1 December 2017, Pages 1934–1942, https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/cix681: « . ».
- Radonovich, L.J. et al. (2019) “N95 Respirators vs Medical Masks for Preventing Influenza Among Health Care Personnel: A Randomized Clinical Trial” (« N95 : »), JAMA. 2019; 322(9): 824–833, https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2749214: « 2862 , 2371 5180 - (). N95 ».
- Long, Y. et al. (2020) “Effectiveness of N95 respirators versus surgical masks against influenza: A systematic review and meta‐analysis” (« N95 : »), J Evid Based Med. 2020, 1-9, https://doi.org/10.1111/jebm.12381: « 9171 . N95 , , , . N95 ».
. . .
( ).
, - , , .
.
« »
, , , , . « ».
-
, , , , , - , .
, , , . . Paules, C. and Subbarao, S. (2017) “Influenza” («»), Lancet, Seminar| Volume 390, ISSUE 10095, P697-708, August 12, 2017, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30129-0. , .
Viboud, C. et al. (2010) “Preliminary Estimates of Mortality and Years of Life Lost Associated with the 2009 A/H1N1 Pandemic in the US and Comparison with Past Influenza Seasons” (« 2009 »), PLoS currents vol. 2 RRN1153. 20 Mar. 2010, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2843747/. . 122 . :
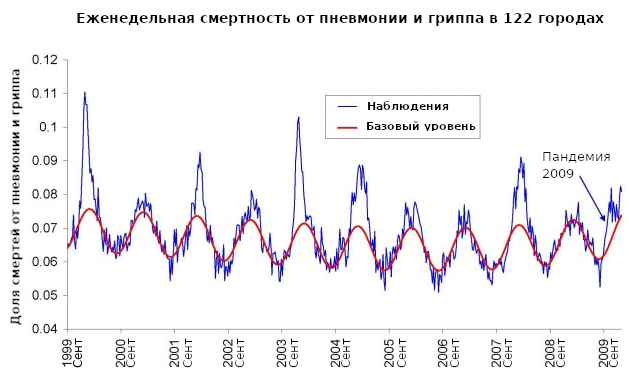
. ( ) , (: - , - ). . Dowell, S. F. (2001) “Seasonal variation in host susceptibility and cycles of certain infectious diseases” (« »), Emerg Infect Dis. 2001; 7(3): 369–374, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2631809/.
Shaman, J. et al. (2010) “Absolute Humidity and the Seasonal Onset of Influenza in the Continental United States” (« »), PLoS Biol 8(2): e1000316, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1000316, .
Lowen, A. C. et al. (2007) “Influenza Virus Transmission Is Dependent on Relative Humidity and Temperature” (« »), PLoS Pathog 3(10): e151, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.0030151 , , .
, . Harper G. J. (1961) “Airborne micro-organisms: survival tests with four viruses” (« : »), The Journal of hygiene, 59(4), 479–486, https://doi.org/10.1017/s0022172400039176. , («»), , (« »): « , , , ».
« » , «» . , . «» .
, [Shaman, J. et al. (2010)] «» , «» «» ( ). , , .
, (R0) , ( - , , ).
, , (, ). 1,28 ( 1,19 1,37). . Biggerstaff, M. et al. (2014) “Estimates of the reproduction number for seasonal, pandemic, and zoonotic influenza: a systematic review of the literature” (« , : »), BMC Infect Dis 14, 480 (2014), https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2334-14-480.
, [Shaman, J. et al. (2010)] , R0 , (, . 2). , , , , , - .
, ( ), R0, . . Coburn, B. J. et al. (2009) “Modeling influenza epidemics and pandemics: insights into the future of swine flu (H1N1)” (« : »), BMC Med 7, 30, https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-7-30 Tracht, S. M. et al. (2010) “Mathematical Modeling of the Effectiveness of Facemasks in Reducing the Spread of Novel Influenza A (H1N1)” (« A(H1N1)»), PLoS ONE 5(2): e9018, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0009018.
, « » . , « » - — , .
« » , , , .
: Despres, V. R. et al. (2012) “Primary biological aerosol particles in the atmosphere: a review” (« : »), Tellus B: Chemical and Physical Meteorology, 64:1, 15598, https://doi.org/10.3402/tellusb.v64i0.15598. , : Hammond, G. W. et al. (1989) “Impact of Atmospheric Dispersion and Transport of Viral Aerosols on the Epidemiology of Influenza” (« »), Reviews of Infectious Diseases, Volume 11, Issue 3, May 1989, Pages 494–497, https://doi.org/10.1093/clinids/11.3.494.
, , ( , ) 2,5 . Yang, W. et al. (2011) “Concentrations and size distributions of airborne influenza A viruses measured indoors at a health centre, a day-care centre and on aeroplanes” (« , »), Journal of the Royal Society, Interface. 2011 Aug;8(61):1176-1184, https://royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/10.1098/rsif.2010.0686:
« 16 , 5800 37000 . , 64% 2,5 , . 40 280 , , 13±5 , . 12 48 ( ), . , »
( 2,5 ) , ( ). , ( ) . , N95 ( 0,3 0,5 ) , : Balazy et al. (2006) “Do N95 respirators provide 95% protection level against airborne viruses, and how adequate are surgical masks?” (« N95 95% , ?»), American Journal of Infection Control, Volume 34, Issue 2, March 2006, Pages 51-57, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2005.08.018.
, , . , , .
, , .
Yezli, S., Otter, J. A. (2011) “Minimum Infective Dose of the Major Human Respiratory and Enteric Viruses Transmitted Through Food and the Environment” (« »), Food Environ Virol 3, 1–30, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-011-9056-7 :
- , , .
- , , .
- 100 1000 .
- 1 10 .
, :
- «-» Haas, C. N. et al. (1993) “Risk Assessment of Virus in Drinking Water” (« »), Risk Analysis, 13: 545-552, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1539-6924.1993.tb00013.x.
- Zwart, M. P. et al. (2009) “An experimental test of the independent action hypothesis in virus-insect pathosystems” (« - »), Proc. R. Soc. B. 2762233–2242, http://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2009.0064 , .
- Baccam, P. et al. (2006) “Kinetics of Influenza A Virus Infection in Humans” (« »), Journal of Virology Jul 2006, 80 (15) 7590-7599, https://jvi.asm.org/content/80/15/7590 , : 6 5 ; 11 ; 3 ; 22 ( R0 22).
- Brooke, C. B. et al. (2013) “Most Influenza A Virions Fail To Express at Least One Essential Viral Protein” (« »), Journal of Virology, Feb 2013, 87 (6), 3155-3162, https://jvi.asm.org/content/87/6/3155 , , , 90% .
, - ( - , ), . . , .
, , , , . :
- Leung, N. H. L. et al. (2020) “Respiratory virus shedding in exhaled breath and efficacy of face masks” (« »), Nature Medicine (2020), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-0843-2.
- Davies, A. et al. (2013) “Testing the Efficacy of Homemade Masks: Would They Protect in an Influenza Pandemic?” (« : ?»), Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness, http://journals.cambridge.org/abstract_S1935789313000438.
- Lai, A. C. K. et al. (2012) “Effectiveness of facemasks to reduce exposure hazards for airborne infections among general populations” (« »), J. R. Soc. Interface, 9938–948, http://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2011.0537.
- Sande, van der, M. et al. (2008) “Professional and Home-Made Face Masks Reduce Exposure to Respiratory Infections among the General Population” (« »), PLoS ONE 3(7): e2618, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0002618.
, , , . , :
- , . , .
- .
- () . . Wada, K. et al. (2012) “Wearing face masks in public during the influenza season may reflect other positive hygiene practices in Japan” (« »), BMC Public Health 12, 1065 (2012), https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-12-1065.
- - .
- , .
- .
- (, ) , , .
- , , .
- ( ), , . .
:
- ?
- , ?
- , , ? , ?
- ?
- ?
- - (, )?
- ?
- , , ?
- ?
- , ?
, « ».
, . , .
, , , , , .
, ?
, , , , . , , , .