In this post, we will briefly review the ECMAScript proposal “Record & Tuple” by Robin Rickard and Rick Button. This sentence adds two kinds of compound primitive values to JavaScript:
- records (records) - the version of simple objects, unchanged and compared by value;
- tuples - the version of arrays that is immutable and compared by value.
1. Comparison by value
Now JavaScript compares only primitive data types by value (i.e., by looking at the contents), for example, strings:
> 'abc' === 'abc'
true
( ).
> {x: 1, y: 4} === {x: 1, y: 4}
false
> ['a', 'b'] === ['a', 'b']
false
«Record & Tuple» , .
, (#), — , :
> #{x: 1, y: 4} === #{x: 1, y: 4}
true
# , — , :
> #['a', 'b'] === #['a', 'b']
true
, , .
1.1. —
, , typeof:
> typeof #{x: 1, y: 4}
'record'
> typeof #['a', 'b']
'tuple'
1.2.
:
:
1.3.
> Record({x: 1, y: 4})
#{x: 1, y: 4}
> Tuple.from(['a', 'b'])
#['a', 'b']
: — (shallow). - ( ) , Record() Tuple.from() .
1.4.
> Object(#{x: 1, y: 4})
{x: 1, y: 4}
> Array.from(#['a', 'b'])
['a', 'b']
: — (shallow).
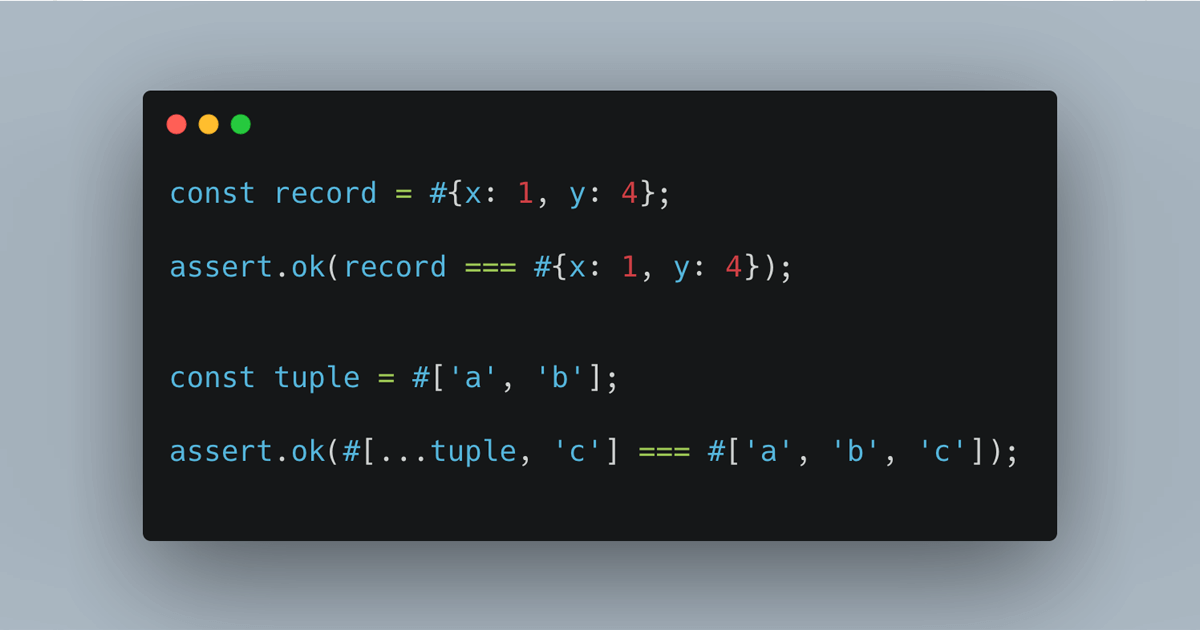
1.5.
const record = #{x: 1, y: 4};
assert.equal(record.y, 4);
const {x} = record;
assert.equal(x, 1);
assert.ok(#{...record, x: 3, z: 9} === #{x: 3, y: 4, z: 9});
1.6.
const tuple = #['a', 'b'];
assert.equal(tuple[1], 'b');
const [a] = tuple;
assert.equal(a, 'a');
assert.ok(#[...tuple, 'c'] === #['a', 'b', 'c']);
assert.ok(tuple.with(0, 'x') === #['x', 'b']);
1.7. , , JavaScript — ?
, - (hash maps) (search trees), , . , . JavaScript , , :
1.8.
:
- , ,
===. - : - , , . .
- : , ( ).
- Map Set, , , Map Set.
.
2. : Set Map
2.1. Set
, , :
> [...new Set([#[3,4], #[3,4], #[5,-1], #[5,-1]])]
[#[3,4], #[5,-1]]
:
> [...new Set([[3,4], [3,4], [5,-1], [5,-1]])]
[[3,4], [3,4], [5,-1], [5,-1]]
2.2. Map
, Map ( WeakMap).
const m = new Map();
m.set({x: 1, y: 4}, 1);
m.set({x: 1, y: 4}, 2);
assert.equal(m.size, 2);
, : Map A .
const persons = [
#{
name: 'Eddie',
address: #{
street: '1313 Mockingbird Lane',
city: 'Mockingbird Heights',
},
},
#{
name: 'Dawn',
address: #{
street: '1630 Revello Drive',
city: 'Sunnydale',
},
},
#{
name: 'Herman',
address: #{
street: '1313 Mockingbird Lane',
city: 'Mockingbird Heights',
},
},
#{
name: 'Joyce',
address: #{
street: '1630 Revello Drive',
city: 'Sunnydale',
},
},
];
const addressToNames = new Map();
for (const person of persons) {
if (!addressToNames.has(person.address)) {
addressToNames.set(person.address, new Set());
}
addressToNames.get(person.address).add(person.name);
}
assert.deepEqual(
[...addressToNames],
[
[
#{
street: '1313 Mockingbird Lane',
city: 'Mockingbird Heights',
},
new Set(['Eddie', 'Herman']),
],
[
#{
street: '1630 Revello Drive',
city: 'Sunnydale',
},
new Set(['Dawn', 'Joyce']),
],
]);
3. :
3.1. ,
Array.filter() ( B), , A.
const persons = [
#{
name: 'Eddie',
address: #{
street: '1313 Mockingbird Lane',
city: 'Mockingbird Heights',
},
},
#{
name: 'Dawn',
address: #{
street: '1630 Revello Drive',
city: 'Sunnydale',
},
},
#{
name: 'Herman',
address: #{
street: '1313 Mockingbird Lane',
city: 'Mockingbird Heights',
},
},
#{
name: 'Joyce',
address: #{
street: '1630 Revello Drive',
city: 'Sunnydale',
},
},
];
const address = #{
street: '1630 Revello Drive',
city: 'Sunnydale',
};
assert.deepEqual(
persons.filter(p => p.address === address),
[
#{
name: 'Dawn',
address: #{
street: '1630 Revello Drive',
city: 'Sunnydale',
},
},
#{
name: 'Joyce',
address: #{
street: '1630 Revello Drive',
city: 'Sunnydale',
},
},
]);
3.2. ?
, (, previousData ), , -.
let previousData;
function displayData(data) {
if (data === previousData) return;
}
displayData(#['Hello', 'world']);
displayData(#['Hello', 'world']);
3.3.
, . , Node.js assert deepEqual(). :
function invert(color) {
return #{
red: 255 - color.red,
green: 255 - color.green,
blue: 255 - color.blue,
};
}
assert.ok(invert(#{red: 255, green: 153, blue: 51}) === #{red: 0, green: 102, blue: 204});
: , , , ( ).
4.
, # ( ) , , . :
const della = #{
name: 'Della',
children: #[
#{
name: 'Huey',
},
#{
name: 'Dewey',
},
#{
name: 'Louie',
},
],
};
, . , , . , — , .
:
const della = Record({
name: 'Della',
children: Tuple([
Record({
name: 'Huey',
}),
Record({
name: 'Dewey',
}),
Record({
name: 'Louie',
}),
]),
});
, JavaScript Tagged Collection- ( , ):
const della = Record!{
name: 'Della',
children: Tuple![
Record!{
name: 'Huey',
},
Record!{
name: 'Dewey',
},
Record!{
name: 'Louie',
},
],
};
, , :
const R = Record;
const T = Tuple;
const della = R!{
name: 'Della',
children: T![
R!{
name: 'Huey',
},
R!{
name: 'Dewey',
},
R!{
name: 'Louie',
},
],
};
5. JSON
JSON.stringify() ().JSON.parseImmutable() JSON.parse(), ().
6. : , ?
. , , .
, , , .
7.
8.