What is a symmetric and asymmetric connection scheme for protection against DDoS attacks? What are the advantages and disadvantages of each of them? Which protection is best for your project? You will find the answers to these questions under the cut.
Along the way, we'll talk about symmetry in telecommunication networks in general. You will find out how asymmetric the Internet is, where this asymmetry comes from, and in general it is good or bad. As a bonus - quick fix for the two most common problems when connecting network protection. And after reading, you can definitely understand what I tried to portray on the KDPV.
What is symmetry?
Everyone understands what is “symmetrical” at the level of “sensations,” but they cannot just immediately articulate what this means. Let's try. If something is called symmetrical, they mean that it does not change under the influence of certain transformations - symmetry transformations. The most obvious example is geometric symmetry.
90 , . : " 90 ". — . — "", . . .
— . . — . : . , , . , , — .

, . , Facebook Facebook . ? : , , , ..
— . . " " . . , . . — , . 1891 — . XX () ( ). , , "" . .
(), .
, .

, , 27 , 1% . , .
— , .
IP- (IP / ID ). . UDP — , . TCP , - , .
, . . ( ) , .
. . , .

:
- .
, .
, , , .
, " " — RFC — :
- Forward direction — , .
- Reverse direction — — , .
- Upstream link — , — downstream links.
. hot-potato routing. , , , . hot-potato — — "" .
?
, . "Observing routing asymmetry in Internet traffic". Tier-2, Tier-1, .
, "". (Flow) — IP , IP , , ID . , .
- .
- .
- , , .. , UDP.
, :
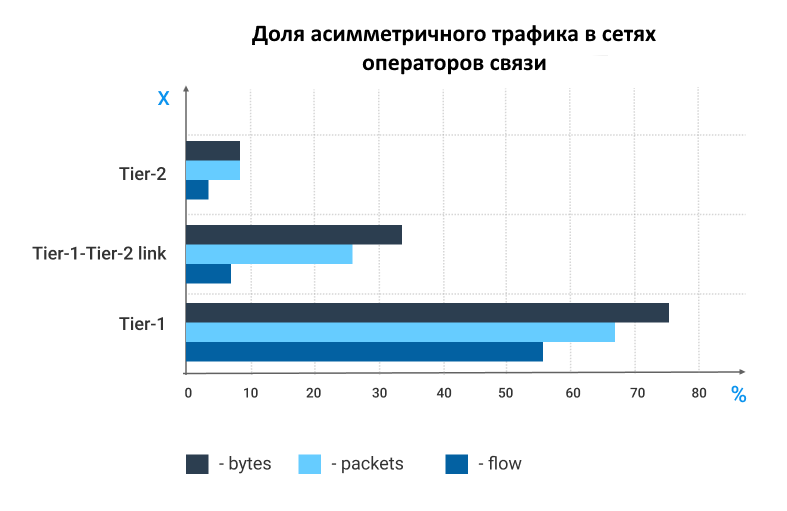
- — flows — / * 100
- — packets — (1-|Nab-Nba|/|Nab+Nba|)*100%, Nab — , Nba — .
- — bytes — (1-|Nab-Nba|/|Nab+Nba|)*100%, Nab — , Nba — .
, , . edge-.
.
"How Asymmetric Is the Internet?" , ( — IP- ).
- 4000 RIPE Atlas. — , . .
- Traceroute . Traceroute , .. , . .

- , 12.6% ( , 5 — 10%).
- , . , :
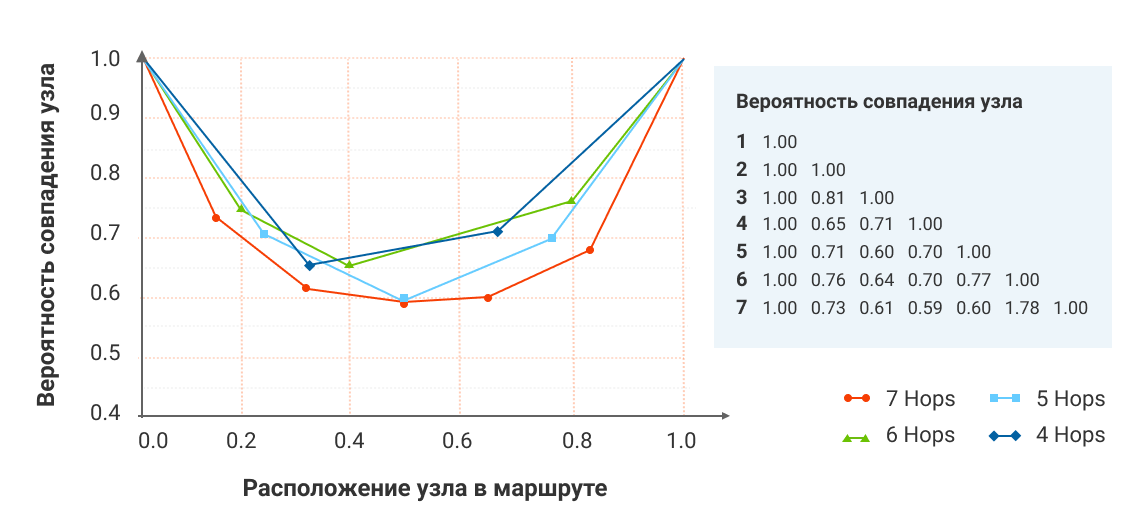
y — , ( ) A --> --> . x — . , — 1. , . — .
, ?
. DDoS.
DDoS- , , , : . - , , . , — , .
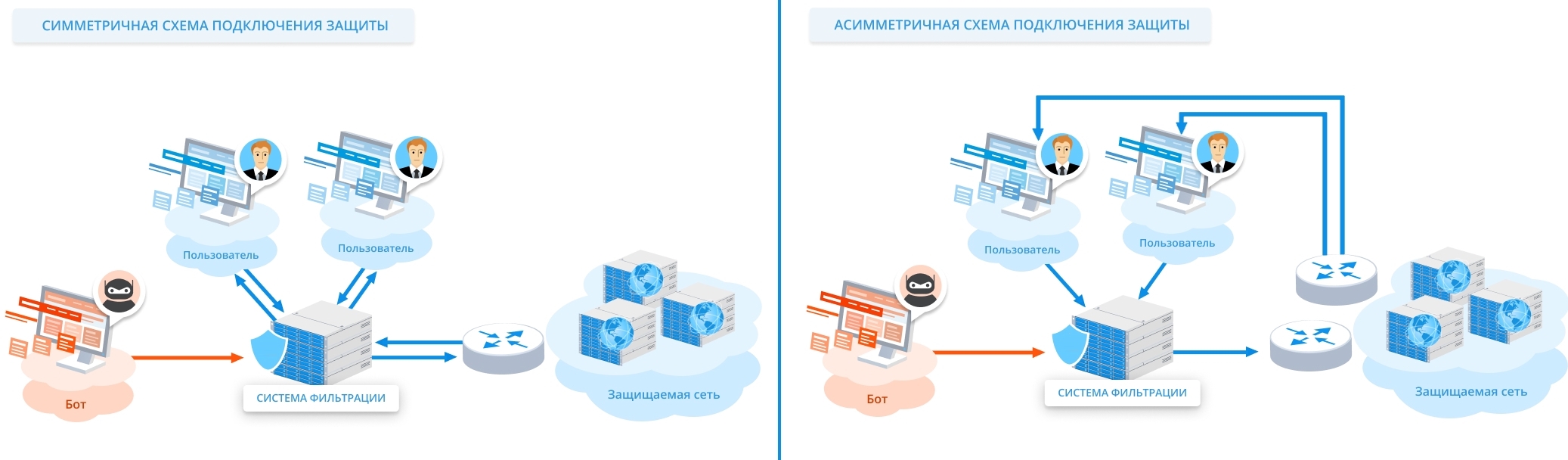
, . . ? .
, .
: , , , ?
:…
: ?
:…
: !
: ...
- . , , , " " .
: , , , ?
: . . .
: ?
: , , .
: !
: .
, , , , . DDoS-.
: SYN flood
, TCP. , (3-way handshake).
- SYN , .
- , SYN-ACK . SYN , A+1, B, .
- ACK B+1, TCP .
, ( ).
SYN flood — DDoS-, — . SYN (spoofed) IP . SYN-ACK ACK', … . TCP .

? , — SYN cookie SYN proxy.
SYN cookie . , SYN (IP , TCP ..), , B SYN-ACK . SYN-ACK TCP cookie. (3 3-way handshake), B+1, ACK . .
ookie . , ACK . , . , , ACK cookie, SYN cookie. . , .

spoofing spoofing'o. , . — , , .
(UDP, QUIC, ICMP) TCP. . IP , .
, .
, , .
edge-, " " . , . : ( ).
, edge-, . :
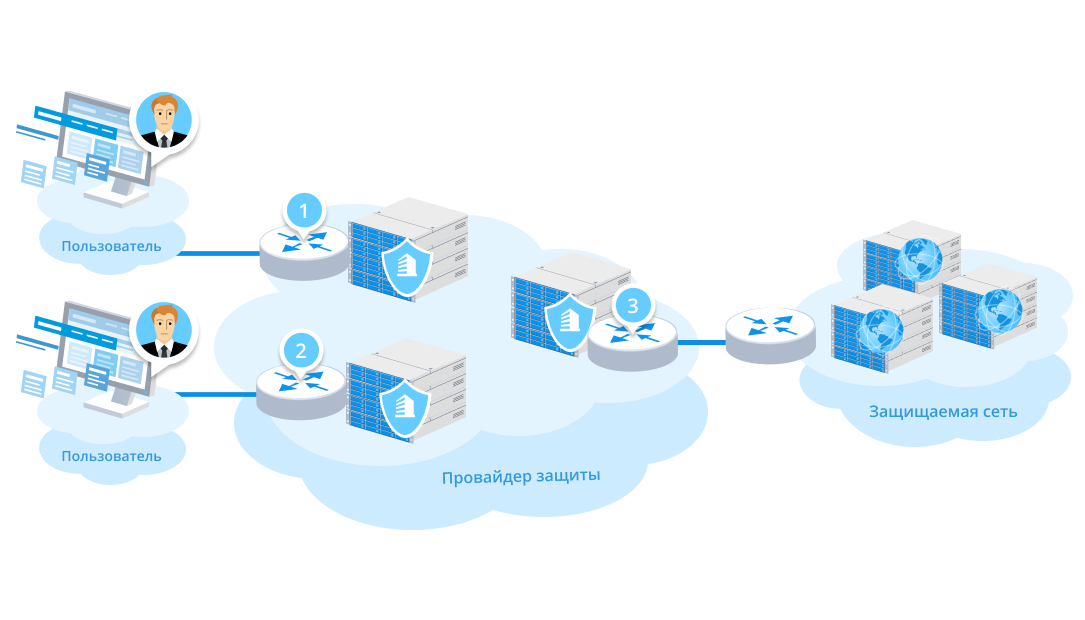
, . , . edge ? — "", , ! .
, ? , 3. , . — . , .. 3 . 1 2 .
, , , — . , . , , 1, 2. . , , , , . , , " ".
DDoS
DDoS, , — . BGP, . . . , — . , , .
- — BGP. peering' .
- . , , , , . , , , troubleshooting' c . , " ". , .
- , , , .. , . , TCP. RTT (. Round Trip Time). .
- . - . , , 100% . .
2-4 , DDoS .
, . DDoS 100% . mitigation — , — . , - . " " , .
?
95% , , DDoS , . , . ( DDoS ) — , . , , , .
. , BGP.

DDoS-GUARD , , . .
BONUS: ,
, - uRPF strict loose. ? uRPF (Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding) . , , , source IP.
uRPF IP- . strict , c , IP, . spoof' IP . , , . loose IP- , .
/ GRE / IPIP-
MTU . :
- Maximal Transmission Unit (MTU) — Protocol Data Unit (PDU).
- PDU — + payload.
- Maximal Segment Size (MSS) — payload.
() PDU payload PDU . , MTU , payload.
MTU 1476, MSS – 1436 ( 1400) ( Don't fragment). - .
. MSS , . MSS : Juniper, Cisco, Mikrotik.