This note is an overview of the connection between the philosophy of consciousness and artificial intelligence. She does not pretend to be an original study, but the author hopes for a fruitful discussion and destructive criticism.
Introduction
At present, it is difficult to find a topic that is more relevant and rapidly developing than artificial intelligence. The problems that arise and the results achieved, touching upon aspects that are acute for many, such as man’s monopoly on the mind and consciousness, require philosophical research, for example, the problem of distinguishing between “strong” and “weak” artificial intelligence and, in particular, the problem of the possibility of creating “artificial consciousness” . This note attempts to provide an overview of the current relationships between philosophical theories of consciousness and the current state of artificial intelligence (AI).
Philosophers exist much longer than computers, and try to solve some questions related to AI: how does the mind work? Is it possible for machines to act reasonably like humans, and if so, did they have real, “conscious” minds? What are the ethical implications of intelligent machines (Russel & Norvig, 2016)?
However, it should be noted that it will be incorrect to consider the current level of AI development as something stable, and even more so final. It is possible to find completely, it would seem, reasonable forecasts that completely can not stand the test of time. So in his very popular book “Gödel, Escher, Bach: This Endless Garland” (Hofstadter, 2001), the mathematician and philosopher Douglas Hofstadter writes that “programs can be created that can beat anyone [in chess], but they [... ] will be programs of the general mind [...] and will have character. ” After only a couple of decades, chess programs beat anyone, while, firstly, not being artificial intelligence systems in the full (from the point of view of the current state of computer science) sense, and secondly, without showing, of course,not the slightest sign of consciousness in the intuitive understanding of the term.
:
«» .
, « , » (Samuel, 1756).
«» . «» : , , ( , ) . , — , : , , (Sutherland, 1989). «» , ; , , -, — . . , - , , (Vimal, 2006).
, , , . (Schneider & Velmans, 2008):
- : , , . , . .
- : , .
- : (, ) . — .
- : , , , , , , .
- : , .
.
«»
, , , , .
. , , . , — , . , (Descartes, 2008). , . . «», «». , , (Gennaro, 1999).
, . , - . , . : , , , , - , .
, , «» ( «») « ». (Skirry, 2016): « - , ?».
, . .
, , . , , , - . , , . , , , . , . .
, , , , . « ».
« » — (, 2009) , - . :
, .
- , - , (Jackson, 1982).
, . ( ), ( , , ) ().
, , . , . .
, , , , — . , , , (. « »).
, , , , , .
« » « » (Chalmers, 1996).
, : , , , . , — , . ? « », . , .
, (Salazar, et al., 2019), , : , , , , , — . — ; , . , , , : , , , , .
, , , , , ( ), . (. « ») — , , , , .
, « », (Jackson, 1982). , , - . , , , ( , ). - . , - , — , . , , , , , .
( ), , , , — , . , , , , . -, « » , - . « - ». , , , — , , , , , , . -, - « » . , - , . , , , , , , , — , .
, , , :
« » (Philosophy Index, 2020) , . , — , .
, , — . , «, , » ( – «» «») ( «» «»).
()
- , . . - , , , . -, , , , , ( ) ( ) — , , , .
(, 2000) , . , , , — , . - , , «» . — , «», «», «», «». , , , ( ) ( ) . . , , .
, . , , , . , , . , , , .
() . (Tononi, 2004; Fallon, 2020) 2004 , , , , , ϕ-.
, , - . , , , , , , . , . . , - , . .
, , , . . ϕ- , , , .
Φ — - , . — φ>0, ϕ. , , . , , , , .
(Dennett D., 1991) , . , ϕ-. , . , , , . , , . , , , . , , , .
, , . , , . , .
, « » , , .
«»
, «» .
, : , , . , , -. . — , - , , , . , , .
, .
, , ( ) , ; . , (Gallup, 1970). 50 , . , , , , .
, , .
, , , . , , .
, , (. « »).
, , , . ( . . — « , , » (, 1964) , - , .
, (Searle, 1983) — .
, , , «» (Allen, 2001). , , -, , -. «». «» , . («») , , . «-» , .
. , , . , « » (., , (Churchland, 1986), . , , .
«qualia» 1929 . . . .
, , , . . , , , , . , , . . , , , . (. « »).
, «» , , .
.
1950 (Turing, Computing Machinery and Intelligence, 1950), : " « ?». , , , , « », .
, ( ) . , ; , 30% . , 2000 109 , . — .
, , , . ELIZA -, MGONZ NATACHATA, , - CYBER LOVER - « » (Russel & Norvig, 2016). , 1991 , , « ». . , , .
(McCarthy, 2007).
— , . , , .
«» . , .
«», . , , . , .
« ?» — . , , . , . «».
. , - , , , . , , , . , , , .
, , , . , , , , , . , , . , .
, 2007 , 1970 , «», «». , , , « », . , AlphaZero , (Silver, 2017).
, .
1949 (Jefferson, 1949): « , , , , , , .. , , . ( , ) , , , - , , , ».
, -, « ». , , , , , . , , , . , , , , , , . .
(« — , » (Gardner, 1983).
, , , . , , , .
, , , , , .
. , «» , , «» . , , (Joshi, 2016):
, . . , . , , . . «». . . IBM Deep Blue, 1997 .
— , , . , , . , , , , , .
, , . — , . , , , , . - , , , , «» .
, . , , . , , , . , , , , .
, , « », « » « -».
, , - . , , , .
() — , , . , , .
-
- (), , , , , , . , .
« » «» «» .
: ?
, , , , , , , ( ), .
, — , , , .
— . , , , « ?» « ?» (Russel & Norvig, 2016).
, , (Turing, Computing Machinery and Intelligence, 1950). . (Kurzweil, 2005), — , . , , . - , , , .
, , , , .
: ?
« » , - , -, , , — . .
. , ( , ). , , : « ?». , ? . , : « , , , ».
, , : . , . . , , «» - . , , .
, «» (. . (Holland, 2003) . , , .
, : « «» , ?» . , 10 , . , « » . , « » . (. « »).
, , . , . . , , . , .
.
, , , (. Theory of Mind). .
.
theory of mind ( « ») . .
— , , , , — (Premack & Woodruff, 1978).
, , , .
, (« »).
, — , (). , , , , , , «». — , «» .
, — , , (, , ) — , (Rescorla, 2020).
, . , . , , . , , - . , . , (, , ). , .
:
- . , . , (, ) (, ). , ;
- . . , ;
- : , . - . . . , (Gallistel & King, 2009);
- , , . , . , , (Fodor & Pylyshyn, Connectionism and Cognitive Architecture: A Critical Analysis, 1988);
- : . . . , , .
, «- », .
, .
(Putnam, 1967) « ». . , (, ), (, ) (, ). , . , — . , . , , . — , . , . (. « »).
1980- , . , . , , .
«», (. . -) . :
- . , , - , ;
- . - . - (Graves, Wayne, & Danihelka, 2014).
, « », . , «» , . : , - . , « » (. ).
. . (Scassellati, 2002) , , - (Simon Baron-Cohen) (Alan M. Leslie).
, , .
, , . , ; , . , , , , . , .
- , . , Cog, , - ( , ), , , , , , , .
, , , , , . -, , - . , , . , Cog , 2002 . , .
(Blum, Hafner, & Winfield, 2018).
« », , , ( ), . , , .
« , », — . « [...] — ». , .
, , , , , . , , , , .
, , . , , « ». , , , «, » . , , , , . , , , . « ».
. , , , , — . , , , . , : « », : .
, (Schreiber, 2020), , , «», , , , , . , , . « », , , . , , . , . , , , , — .
, (Allen, 2001). , , ( ) . , , , , , , . (Davidson, 1975) , , , , .
, . : .
, , , . (Zhu, 2009), :
« » (intentional stance).
« » (Dennett D. C., 1987): « : , , ; , , . , , , , , , . , ; , ».
, , , , , , . « » ( 1) — , (Braitenberg, 1984). , , « , , , ». , , , « », « », « ». , , , .
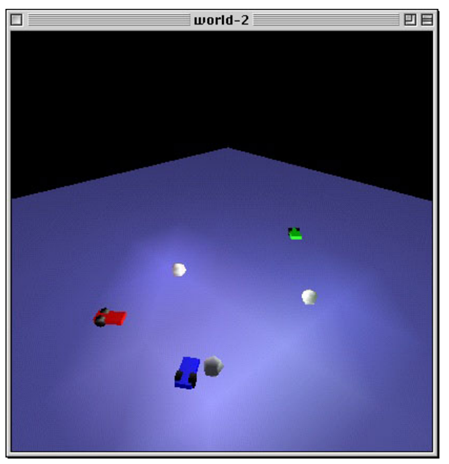
, , . (, Adobe Photoshop) (, Microsoft Clippy). , . , Voyager — , (Lewis, 2000). . , «» -, « ». Voyager’ , «» , .
. , , . , , , , , , .
, , , . , , . , «» . , .
, (Chella & Gaglio, 2009). , ( 2). , . . , , 3D . - . «» «», .
. , - . , . , - . , . , , , , , 2D, , , . 2D , . , , .
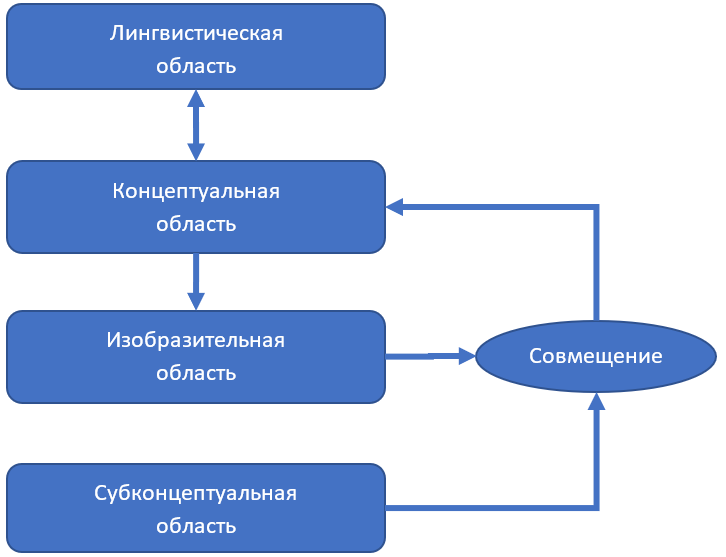
, , . (Gärdenfors, 2000). , , . — , — , , , , . , . , , : , , , . , . , - .
, - . « », , , . .
, Situation (), Action (), Time_Instant ( ) . «» , (, precond (), part_of ().
.
«, — », , (Woods & Schmolze, 1992):
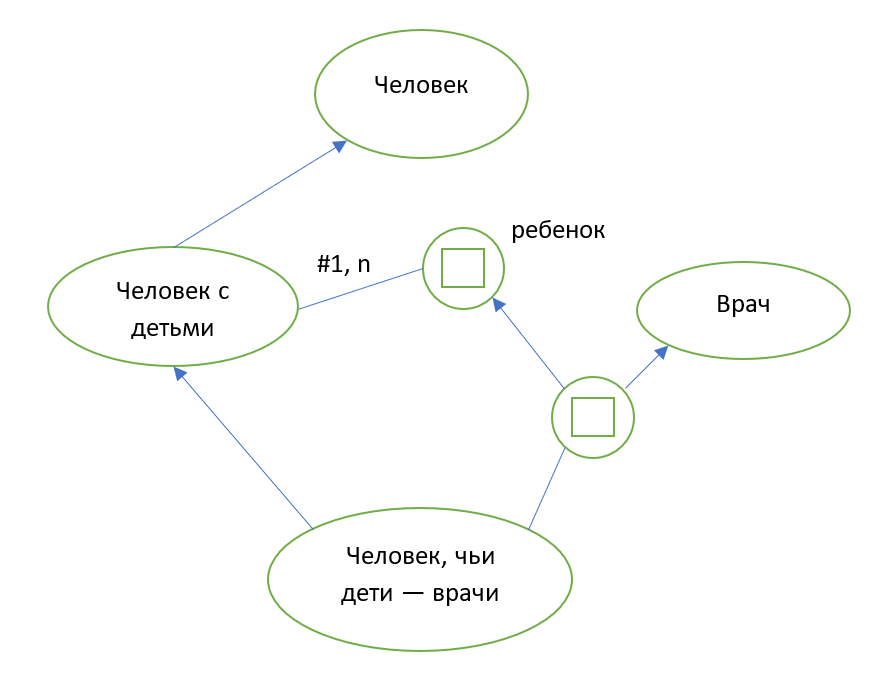
, 2D ( 3D), , .
, (), «» , . . ( 4).

— , , , , , .
, ( 4) «» , , , — , — :
" " . , :
- ;
- ;
- , , .
, , . , , - , :
- — , ;
- , , .
, , , :
- ;
- / ;
- /.
(Bringsjord & Govindarajulu, 2013) R, , :
- R;
- , R;
- , R;
- , .
, , , .
(Yampolskiy, 2017) , , , . . , . , , , , , . «» (, , . .), , , , , , . , . . , , , . .
— , ( 5). , , , : « ? ? ?» , , . , . , : «, , ». , , .
(Koch, 2019), OpenAI GPT-2 (Radford, et al., 2019). GPT-2 — , , : - , . «» . , , , , . . , -, DeepL (Coldeway & Lardinois, 2017) :
, , , .
, .
.
. .
(Fodor & Block, What Psychological States Are Not, 1972). « ». . . , , . , . , , - , . , . -, , .
« ». . , , « », « ». , , . . , . . , . , , . .
(Rescorla, 2020). .
, , . , , , . , , , .
, , « » (, 1989).
, . , , .
? ? , ? , , . , , .
:
- - «» , .
- , (), «» , , .
- , , , -.
- , , .
́
. , (, ). , , , . - , . , , .
, . , « », , . , , , ́, , . , , .
« » , , . , . , , . , , . , .
.
(Graziano, 2016) .
, . — . . ́ , . , .
, , . , , – . , , . , « ».
, . , , , , .
, . . , , . , . . . . , : «, !». .
, , , . . . . . , , . , . , , .
?
— . , . . , .
, - — . . , , , . , , , — , . . — .
-, , , , , , , , .
, - « » — « ?». , , , , ?
:
- , ;
- , , , ;
- " ", , , ;
- .
, , , , ( ) -, , ".
, . , (Fretten, 2017).
, , , , , , , , , . , , , . , , , - , .
«» « » , - , . «» , , - , , - - , , , , , , .
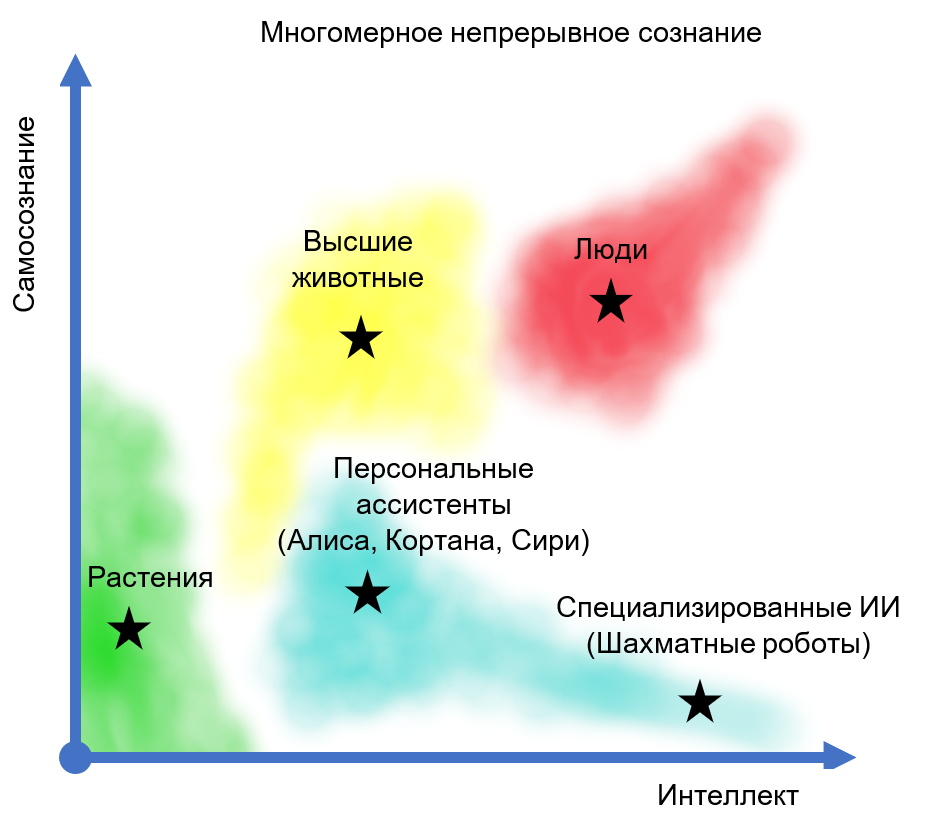
, «» . « ».
« », (Searle, 1983; Hauser, 2020) , , «» «» , . ; «» ( «») , . , , . , , «», «», «»; , « ». «»: .
, , , . , , -.
, , , : « , . , , , , ».
« — » (Kugel, 2004) . « »,
- , ,
- ,
- , «».
, — — (1) (2) «» . , : .
, . , (1) — , — . , (2) — — .
, , , ( ):
- : « «» «», . ?»
- : «.»
- : « , — ?»
- : «.»
, , , , (). , , . , «».
, . « », . , « ».
« » , : , , , . , «, , », , « , ».
, « », , . « », — , — « , , , ».
« » , , .
, . , , « », . . , , , .
, , , . : , , . «» , .
(Holloway, 2019), , . , (Turing, On Computable Numbers, with an Application to the Entscheidungsproblem, 1937). , , , . , , « ». , , .
:
- .
- , , , .
- , , .
:
- , .
- , .
- « », . . , , , , , , .
, ? , , . , , . , , , . , , , .
, , , . — .
, , , - , , . , .
, , .
(Mumford, 2019) , , «, ». , . , , , . , , , , , , , . , , , , . . , , , : « , ». : « , , ». , . , : « , ». — , , , .
, () ( ), . « » , , , . , , , , , , - , .
, , . , , , , . , , - .
(Nguyen, Yosinski, & Clune, 2014) , , , , ImageNet, , 99,6% , . , DNN (. 6).
, , « » , , 35% . , 20% , .
(Manzotti & Chella, 2018) , «» ( — Good Old-Fashioned Artificial Consciousness, GOFAC) .
— , . , , , « ».
GOFAC , . , , , , . , , , , , , . , , , : . « », , , .
, . , , . , . , - — . . « » , — . .
, , « ». -, , , , , , . , - -. , . , . , , , — -, -, / .
Currently, the development of theories of AI and some theories of consciousness goes hand in hand. However, we see that the adoption of the “strong” artificial intelligence hypothesis leads to the incompatibility of many existing theories of consciousness, especially idealistic ones.
Despite the fact that the question of the possibility of “strong” artificial intelligence remains open, the main arguments against it, such as the “Chinese room”, are increasingly inferior under the pressure of new developments in the field of “smart machines”.
Bibliography
References- Allen, C. (2001). Intentionality: Natural and Artificial. Department of History & Philosophy of Science. University of Pittsburgh:
- Blum, C., Hafner, V., & Winfield, A. (2018). Simulation-Based Internal Models for Safer Robots. Front. Robot. AI.
- Braitenberg, V. (1984). Vehicles: Experiments in synthetic psychology. Cambridge: MIT Press.
- Bringsjord, S., & Govindarajulu, N. (2013). Toward a Modern Geography of Minds, Machines, and Math. Philosophy and Theory of Artificial Intelligence, 151-165.
- Chalmers, D. (1996). The Conscious Mind: In Search of a Fundamental Theory. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Chella, A., & Gaglio, S. (2009). In Search of Computational Correlates of Artificial Qualia. Proceedings of the 2nd Conference on Artificial General Intelligence.
- Churchland, P. (1986). Neurophilosophy: toward a unified science of the mind/brain. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- Coldeway, D., & Lardinois, F. (2017). DeepL schools other online translators with clever machine learning. TechCrunch
- Davidson, D. (1975). Thought and talk. Mind and Language, Oxford University Press.
- Dennett, D. (1991). Consciousness Explained. New York: Little, Brown.
- Dennett, D. C. (1987). The Intentional Stance. Cambridge: MIT Press.
- Descartes, R. (2008). Descartes and the Pineal Gland. Stanford University.
- Fallon, F. (2020). Integrated Information Theory of Consciousness. Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy
- Fodor, J., & Block, N. (1972). What Psychological States Are Not. The Philosophical Review, 81, 159–181.
- Fodor, J., & Pylyshyn, Z. (1988). Connectionism and Cognitive Architecture: A Critical Analysis. Cognition, 28, 3–71.
- Fretten, R. (2017). How Artificial Intelligence is Making Us Rethink Consciousness. Medium
- Gallistel, C., & King, A. (2009). Memory and the Computational Brain. Malden: Wiley-Blackwell.
- Gallup, G. G. (1970). Chimpanzees: Self-Recognition. Science, 86–87.
- Gärdenfors, P. (2000). Conceptual Spaces. Cambridge: MIT Press.
- Gardner, M. (1983). The Whys of a Philosophical Scrivener. New York: Quill.
- Gennaro, R. (1999). Leibniz on Consciousness and Self Consciousness”. R. Gennaro, & C. Huenemann, New Essays on the Rationalists. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Graves, A., Wayne, G., & Danihelka, I. (2014). Neural Turing Machines. arXiv
- Graziano, M. (2016). Most Popular Theories of Consciousness Are Worse Than Wrong. The Atlantic
- Hauser, L. (2020). Chinese Room Argument. The Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy
- Holland, O. (2003). Machine Consciousness. New York: Imprint Academic.
- Holloway, E. (2019). Artificial Intellegence Must Be Possible. Mind Matters
- Jackson, F. (1982). Epiphenomenal Qualia. Philosophical Quarterly, 32.
- Jacob, P. (2019). Intentionality. The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy
- Jefferson, G. (1949). The Mind of Mechanical Man. British Medical Journal, i, 1105-1121.
- Joshi, N. (2016). 7 Types Of Artificial Intelligence. ]Forbes Cognitive World
- Koch, C. (2019). Will Machines Ever Become Conscious? Scientific American
- Kugel, P. (2004). The Chinese room is a trick. BEHAVIORAL AND BRAIN SCIENCES 27, 153–168.
- Kurzweil, R. (2005). Long Live AI. Forbes
- Lewis, G. E. (2000). Too many notes: Computers, complexity and culture in voyager. Leonardo Music Journal, vol. 10, 33–39.
- Manzotti, R., & Chella, A. (2018). Good old-fashioned artificial consciousness and the intermediate level fallacy. Frontiers in Robotics and AI.
- McCarthy, J. (12 11 2007 .). What Is Artificial Intelligence:
- Mumford, D. (11 April 2019 .). Can an artificial intelligence machine be conscious? David Mumford. Archive for Reprints, Notes, Talks, and Blog:
- Nguyen, A., Yosinski, J., & Clune, J. (2014). Deep Neural Networks are Easily Fooled: High Confidence Predictions for Unrecognizable Images. arXiv.
- Philosophy Index. (2020). Type Identity Theory.
- Premack, D., & Woodruff, G. (1978). Does the chimpanzee have a theory of mind? Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 1, 515—526.
- Putnam, H. (1967). Psychophysical Predicates. Art, Mind, and Religion.
- Radford, A., Wu, J., Child, R., Luan, D., Amodei, D., & Sutskever, I. (2019). Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners. Computer Science.
- Rescorla, M. (2020). The Computational Theory of Mind. Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy
- Russel, S. J., & Norvig, P. (2016). Artificial Intelligence. A Modern Approach. Third Edition. Harlow: Pearson Education Limited.
- Salazar, H., Hendricks, C., Vintiadis, E., Asoulin, E., Blum, P., Haas, D., Cheng, T. (2019). Introduction to Philosophy: Philosophy of Mind. Rebus Community. Introduction to Philosophy: PPhilosophy of Mind.
- Samuel, J. (1756). A Dictionary of the English language. London.
- Scassellati, B. (2002). Theory of Mind for a Humanoid Robot. Autonomous Robots.
- Schneider, S., & Velmans, M. (2008). The Blackwell Companion to Consciousness.
- Schreiber, A. (2020). AI Theory of Mind. Medium — Artificial Intelligence:
- Searle, J. (1983). Intentionality. An essay in the philosophy of mind. Cambridge.
- Silver, D. e. (2017). Mastering Chess and Shogi by Self-Play with a General Reinforcement Learning Algorithm. arXiv:1712.01815.
- Skirry, J. (2016). Rene Descartes: The Mind-Body Distinction. Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy
- Sutherland, S. (1989). Consciousness. Macmillan Dictionary of Psychology. Macmillan.
- Tononi, G. (2004). An information integration theory of consciousness. BMC Neuroscience, 5: 42.
- Turing, A. M. (1937). On Computable Numbers, with an Application to the Entscheidungsproblem. Proceedings of the London Mathematical Society, Vol. 42, 230–265.
- Turing, A. M. (1950). Computing Machinery and Intelligence. Mind, v.59, pp. 433 — 460.
- Vimal, R. L. (2006). Meanings attributed to the term "consciousness". Journal of Consciousness Studies.
- Woods, W., & Schmolze, J. (1992). The KL-ONE Family. Computers Mathematical Applications, 133-177.
- Yampolskiy, R. V. (2017). Detecting Qualia in Natural and Artificial Agents. arXiv
- Zhu, J. (2009). Intentional Systems and the Artificial Intelligence Hermeneutic Network. Georgia Institute of Technology.
- , . . (2009). . : -.
- , . . (1964). . : .
- , . (1989). The Emperor's New Mind: Concerning Computers, Minds and The Laws of Physics. .
- , . (2000). . : -.
- , . . (2001). , , : . : "-".