Hello, Habr!This article describes the process of upgrading a self-propelled platform based on the esp8266 MK with micropython , to a simple robot equipped with a scanning ultrasonic obstacle sensor, a blinking LED, a start / stop button, as well as an integrated web server, as part of a training project.KDPV: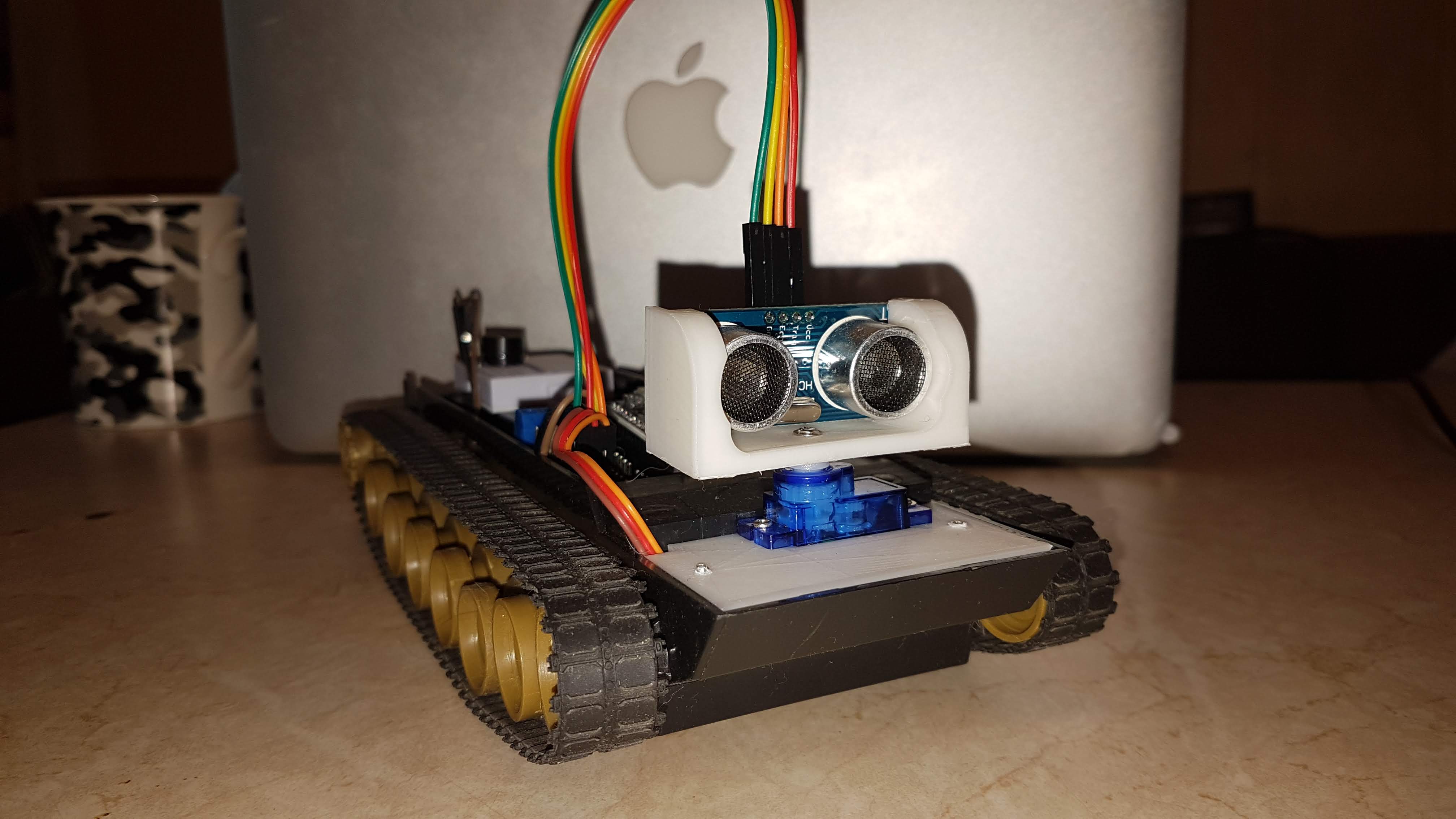 So, the first two parts described the manufacture of a self-propelled platform controlled via a wifi web interface.The task for the current stage is to equip this ultrasound platform with the HC-SR04 sensor, and add the ability to work offline.To begin with - the mechanical part:it is necessary to fix the sensor and the servo in the case, design (I used FreeCAD for this ) and make the missing parts:
So, the first two parts described the manufacture of a self-propelled platform controlled via a wifi web interface.The task for the current stage is to equip this ultrasound platform with the HC-SR04 sensor, and add the ability to work offline.To begin with - the mechanical part:it is necessary to fix the sensor and the servo in the case, design (I used FreeCAD for this ) and make the missing parts: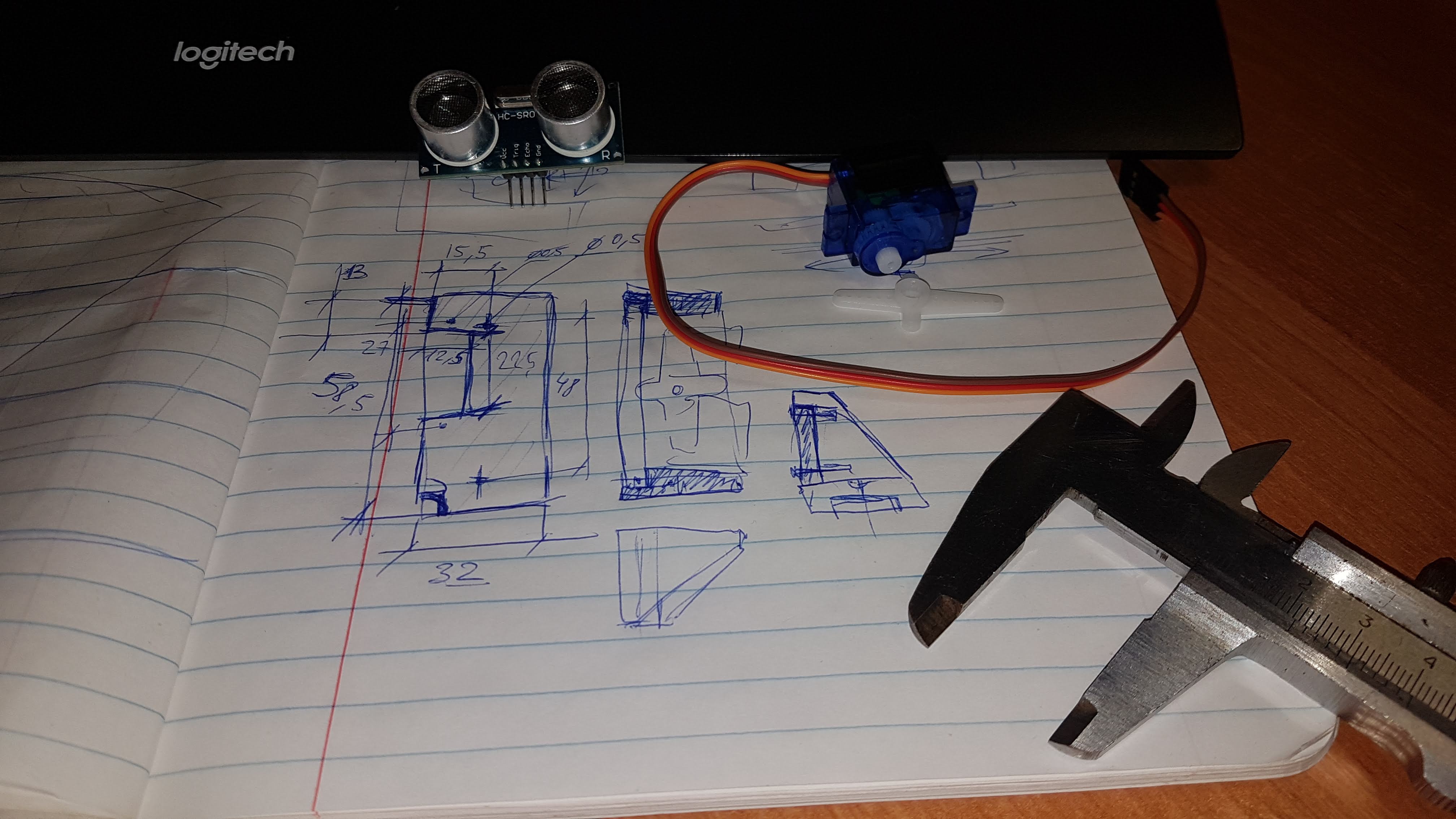
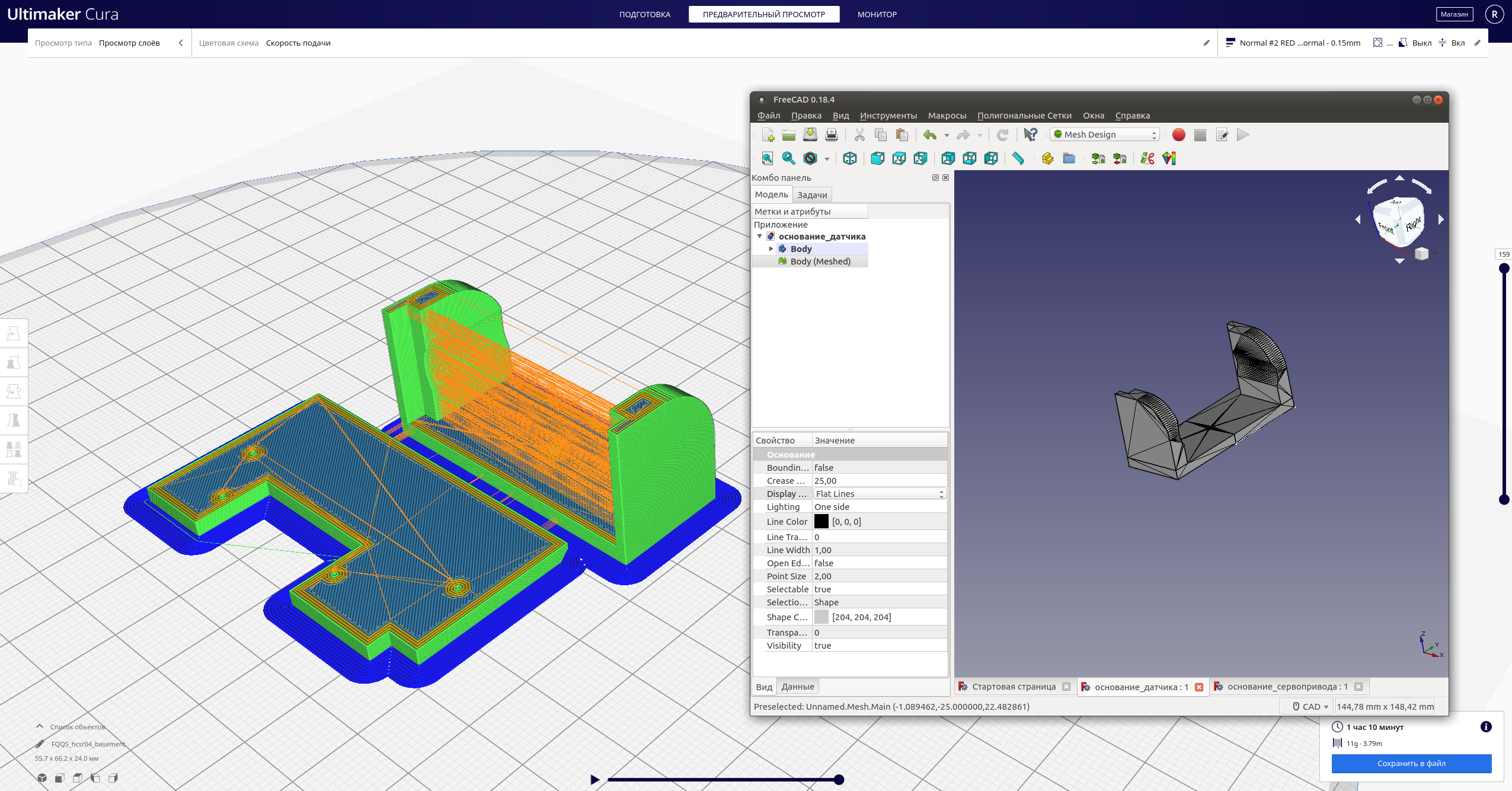 Then - the electric one:draw up the circuit (for example, in Fritzing ) and perform the switching in accordance with it:
Then - the electric one:draw up the circuit (for example, in Fritzing ) and perform the switching in accordance with it: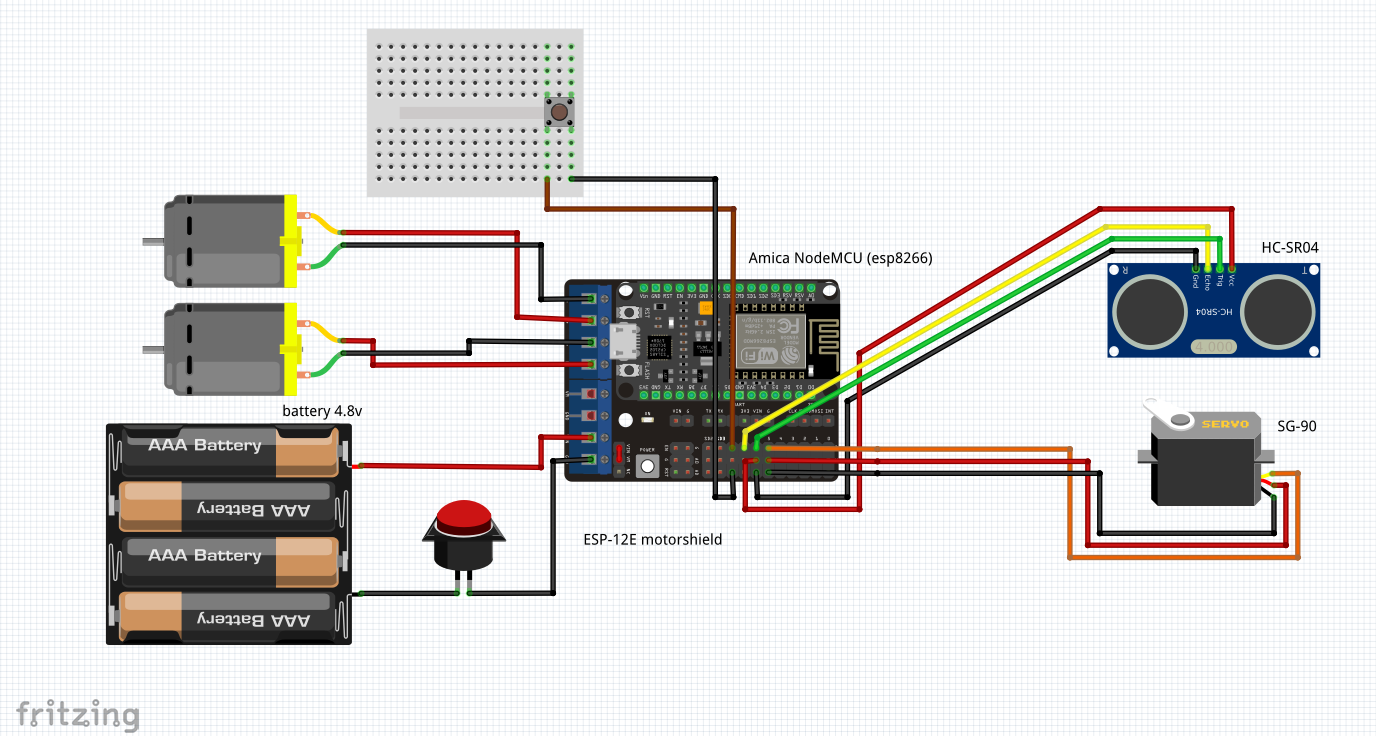 After that, try to make it all fly up ...Since I wanted certain functions of the robot program to be performed in parallel (for example, the process of scanning the distance to obstacles and the motion function), I had to plunge into the capabilities of the asyncio module . More detailed work with asyncio is described in this and this articles.For example, to blink an LED, you can apply such coroutine, which is practically no different from synchronous:
After that, try to make it all fly up ...Since I wanted certain functions of the robot program to be performed in parallel (for example, the process of scanning the distance to obstacles and the motion function), I had to plunge into the capabilities of the asyncio module . More detailed work with asyncio is described in this and this articles.For example, to blink an LED, you can apply such coroutine, which is practically no different from synchronous:import uasyncio as asyncio
from machine import Pin
syst_led = Pin(16, Pin.OUT)
async def blink_led(led, interval_ms):
led_val = True
while True:
led_val = not(led_val)
led_state = led.value(int(led_val))
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.create_task(blink_led(syst_led, interval_ms=250))
loop.run_forever()
The difference is that such coroutines that perform different tasks can be launched several at the same time (the resources will be allocated by the scheduler).Thus, we will write coroutines for measuring distance and scanning the sector, as well as a callback for a hardware interrupt (button) that starts or stops scanning. The transfer of state between coroutines in the simplest case can be done through global variables:Callback for the button:from machine import Pin
run_flag = False
button = Pin(15, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP)
def callback(p):
global run_flag
run_flag = not(run_flag)
print('set run_flag', run_flag, p)
button.irq(trigger=Pin.IRQ_FALLING, handler=callback)
Distance measurement:import uasyncio as asyncio
from utime import sleep, sleep_us
from machine import Pin, time_pulse_us
trig=Pin(12, Pin.OUT)
echo=Pin(13, Pin.IN)
async def async_measure_range():
echo_timeout_us=500*2*30
trig.off()
sleep_us(5)
trig.on()
sleep_us(10)
trig.off()
try:
pulse_time = time_pulse_us(echo, 1, echo_timeout_us)
except:
pass
dist = (pulse_time / 2) / 29.1
return dist
Sector scanning (with calling the distance measurement coroutine):import uasyncio as asyncio
from machine import Pin, PWM
pos_actual = 75
dist_cm = 50
p14 = Pin(14, Pin.OUT)
servo = PWM(p14, freq=50)
async def radar_scan(interval_ms):
pos_list = [45,75,105,75]
global pos_actual
global dist_cm
while True:
if run_flag:
for pos in pos_list:
servo.duty(pos)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
dist_cm = await async_measure_range()
pos_actual = pos
print('pos_actual = %s, dist_cm = %s' % (pos_actual, dist_cm)
elif not run_flag:
await asyncio.sleep(0)
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop(
loop.create_task(radar_scan(interval_ms=250))
loop.run_forever()
In the process of debugging the sensor, from time to time, gave a negative distance value. It turned out - “Electronics is the science of bad contacts” , when the sensor was turned, the cable was pulled and the contact was lost.It remains to fasten the logic of the choice of action based on the scan results:avoid_left = False
avoid_right = False
avoid_backward = False
async def make_decision(interval_ms, avoid_limit_cm):
global avoid_left
global avoid_right
global avoid_backward
while True:
if run_flag:
if pos_actual == 45 and dist_cm < avoid_limit_cm :
avoid_left = True
if debug : print('avoid_left = %s' % avoid_left)
elif pos_actual == 45 and dist_cm >= avoid_limit_cm :
avoid_left = False
if debug : print('avoid_left = %s' % avoid_left)
elif pos_actual == 75 and dist_cm < avoid_limit_cm*1.25 :
avoid_backward = True
if debug : print('avoid_backward = %s' % avoid_backward)
elif pos_actual == 75 and dist_cm >= avoid_limit_cm*1.25 :
avoid_backward = False
if debug : print('avoid_backward = %s' % avoid_backward)
elif pos_actual == 105 and dist_cm < avoid_limit_cm :
avoid_right = True
if debug : print('avoid_right = %s' % avoid_right)
elif pos_actual == 105 and dist_cm >= avoid_limit_cm :
avoid_right = False
if debug : print('avoid_right = %s' % avoid_right)
if debug : print('pos = %s, dist_cm = %s' % (pos_actual,dist_cm))
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
elif not run_flag:
await asyncio.sleep(0)
loop.create_task(make_decision(interval_ms=250, avoid_limit_cm=15))
Motor functions:from random import getrandbits
async def moving(interval_ms):
while True:
if run_flag:
if avoid_backward :
print('avoid_backward = %s' % avoid_backward)
await backward(interval_ms*2)
if bool(getrandbits(1)) :
await right_rotate(interval_ms+getrandbits(3)*100)
await stop_all()
else:
await left_rotate(interval_ms+getrandbits(3)*100)
await stop_all()
elif avoid_left :
print('avoid_left = %s' % avoid_left)
await left_turn(interval_ms)
elif avoid_right :
print('avoid_right = %s' % avoid_right)
await right_turn(interval_ms)
else:
print('move_forward')
await forward(interval_ms)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
elif not run_flag:
await stop_all()
await asyncio.sleep(0)
loop.create_task(moving(interval_ms=1000))
And motor control
p5 = Pin(5, Pin.OUT)
p4 = Pin(4, Pin.OUT)
revrs_L = Pin(0, Pin.OUT, value=0)
revrs_R = Pin(2, Pin.OUT, value=0)
motor_L = PWM(p5, freq=1000, duty=0)
motor_R = PWM(p4, freq=1000, duty=0)
speed = 1023
async def stop_all():
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(0)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(0)
async def forward(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def backward(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(1)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(1)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def right_rotate(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(1)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def left_rotate(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(1)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def right_turn(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(0)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def left_turn(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(0)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
As well as a blinking LED to control that the program is working:async def blink_led(led, interval_ms):
led_val = True
while True:
if run_flag:
led_val = not(led_val)
led_state = led.value(int(led_val))
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
elif not run_flag:
await asyncio.sleep(0)
loop.create_task(blink_led(syst_led, interval_ms=250))
After which, it remains only to collect all thisin one pieceimport gc
import uasyncio as asyncio
from utime import sleep, sleep_us
from machine import Pin, PWM, time_pulse_us
from random import getrandbits
p5 = Pin(5, Pin.OUT)
p4 = Pin(4, Pin.OUT)
revrs_L = Pin(0, Pin.OUT, value=0)
revrs_R = Pin(2, Pin.OUT, value=0)
motor_L = PWM(p5, freq=1000, duty=0)
motor_R = PWM(p4, freq=1000, duty=0)
speed = 1023
p14 = Pin(14, Pin.OUT)
servo = PWM(p14, freq=50)
button = Pin(15, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP)
syst_led = Pin(16, Pin.OUT)
trig=Pin(12, Pin.OUT)
echo=Pin(13, Pin.IN)
run_flag = False
avoid_left = False
avoid_right = False
avoid_backward = False
pos_actual = 75
dist_cm = 50
debug = False
def callback(p):
global run_flag
run_flag = not(run_flag)
print('set run_flag', run_flag, p)
def stop_all_sync():
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(0)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(0)
async def stop_all():
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(0)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(0)
async def forward(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def backward(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(1)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(1)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def right_rotate(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(1)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def left_rotate(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(1)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def right_turn(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(0)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def left_turn(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(0)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def moving(interval_ms):
while True:
if run_flag:
if avoid_backward :
print('avoid_backward = %s' % avoid_backward)
await backward(interval_ms*2)
if bool(getrandbits(1)) :
await right_rotate(interval_ms+getrandbits(3)*100)
await stop_all()
else:
await left_rotate(interval_ms+getrandbits(3)*100)
await stop_all()
elif avoid_left :
print('avoid_left = %s' % avoid_left)
await left_turn(interval_ms)
elif avoid_right :
print('avoid_right = %s' % avoid_right)
await right_turn(interval_ms)
else:
print('move_forward')
await forward(interval_ms)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
elif not run_flag:
await stop_all()
await asyncio.sleep(0)
async def blink_led(led, interval_ms):
led_val = True
while True:
if run_flag:
led_val = not(led_val)
led_state = led.value(int(led_val))
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
elif not run_flag:
await asyncio.sleep(0)
async def async_measure_range():
echo_timeout_us=500*2*30
trig.off()
sleep_us(5)
trig.on()
sleep_us(10)
trig.off()
try:
pulse_time = time_pulse_us(echo, 1, echo_timeout_us)
except:
pass
dist = (pulse_time / 2) / 29.1
return dist
async def make_decision(interval_ms, avoid_limit_cm):
global avoid_left
global avoid_right
global avoid_backward
while True:
if run_flag:
if pos_actual == 45 and dist_cm < avoid_limit_cm :
avoid_left = True
if debug : print('avoid_left = %s' % avoid_left)
elif pos_actual == 45 and dist_cm >= avoid_limit_cm :
avoid_left = False
if debug : print('avoid_left = %s' % avoid_left)
elif pos_actual == 75 and dist_cm < avoid_limit_cm*1.25 :
avoid_backward = True
if debug : print('avoid_backward = %s' % avoid_backward)
elif pos_actual == 75 and dist_cm >= avoid_limit_cm*1.25 :
avoid_backward = False
if debug : print('avoid_backward = %s' % avoid_backward)
elif pos_actual == 105 and dist_cm < avoid_limit_cm :
avoid_right = True
if debug : print('avoid_right = %s' % avoid_right)
elif pos_actual == 105 and dist_cm >= avoid_limit_cm :
avoid_right = False
if debug : print('avoid_right = %s' % avoid_right)
if debug : print('pos = %s, dist_cm = %s' % (pos_actual,dist_cm))
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
elif not run_flag:
await asyncio.sleep(0)
async def radar_scan(interval_ms):
pos_list = [45,75,105,75]
global pos_actual
global dist_cm
while True:
if run_flag:
for pos in pos_list:
servo.duty(pos)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
dist_cm = await async_measure_range()
pos_actual = pos
elif not run_flag:
await asyncio.sleep(0)
stop_all_sync()
print('Move sensor to initial position...')
servo.duty(75)
sleep(1)
print('Waiting for start button...')
gc.enable()
button.irq(trigger=Pin.IRQ_FALLING, handler=callback)
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.create_task(blink_led(syst_led, interval_ms=250))
loop.create_task(radar_scan(interval_ms=250))
loop.create_task(make_decision(interval_ms=250, avoid_limit_cm=15))
loop.create_task(moving(interval_ms=1000))
loop.run_forever()
and check in work:However, I would like to keep the possibility of manual control via the web page ...For this, in a separate coroutine, add a simple web server:async def web_page(request):
global auto_run_flag
motor_state="Stopped"
if request.find('GET /?forward') > 0:
motor_state="Going Forward"
auto_run_flag = False
forward_sync()
elif request.find('GET /?left_rotate') > 0:
motor_state="Rotate Left"
auto_run_flag = False
left_rotate_sync()
elif request.find('GET /?right_rotate') > 0:
motor_state="Rotate Right"
auto_run_flag = False
right_rotate_sync()
elif request.find('GET /?left_turn') > 0:
motor_state="Turn Left"
auto_run_flag = False
left_turn_sync()
elif request.find('GET /?right_turn') > 0:
motor_state="Turn Right"
auto_run_flag = False
right_turn_sync()
elif request.find('GET /?backward') > 0:
motor_state="Going Backward"
auto_run_flag = False
backward_sync()
elif request.find('GET /?stop') > 0:
motor_state="Stopped"
auto_run_flag = False
stop_all_sync()
elif request.find('GET /?auto') > 0:
auto_run_flag = not auto_run_flag
if auto_run_flag :
motor_state="Autopilot"
elif not auto_run_flag :
motor_state="Stopped"
stop_all_sync()
html = """<html><head><title>RoboTank WEB</title>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<link rel="icon" href="data:,"> <style>
html{font-family: Helvetica; display:inline-block; margin: 0px auto; text-align: center;}
h1{color: #0F3376; padding: 2vh;}p{font-size: 1.5rem;}
.button{display: inline-block; background-color: #33c080; border: none;
border-radius: 4px; color: white; text-decoration: none; font-size: 30px; width:100%}
.button2{background-color: #4286f4; width:30%}
.button3{background-color: #eb2b10; width:35%}
.button4{background-color: #8386f4; width:44%}
</style></head>
<body> <h1>RoboTank WEB</h1>
<p>Status : <strong>""" + motor_state + """</strong></p>
<p><a href='/?forward'><button class="button">Forward</button></a></p>
<p><a href='/?left_turn'><button class="button button2">LEFT</button></a>
<a href='/?stop'><button class="button button3">STOP</button></a>
<a href='/?right_turn'><button class="button button2">RIGHT</button></a>
<p><a href='/?backward'><button class="button">Backward</button></a></p>
<p><a href='/?left_rotate'><button class="button button4">L-rotate</button></a>
<a href='/?right_rotate'><button class="button button4">R-rotate</button></a></p>
<p><a href='/?auto'><button class="button button3">AUTO</button></a></p>
</body></html>"""
return html
async def web_handler(reader, writer):
try:
request = str(await reader.read(1024))
header = """HTTP/1.1 200 OK\nContent-Type: text/html\nConnection: close\n\n"""
response = await web_page(request)
await writer.awrite(header)
await writer.awrite(response)
await writer.aclose()
print("Finished processing request")
except Exception as e:
print(e)
async def tcp_server(host, port):
server = await asyncio.start_server(web_handler, host, port)
loop.create_task(tcp_server('0.0.0.0', 80))
And synchronous motion functions for manual control.def stop_all_sync():
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(0)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(0)
def backward_sync():
revrs_L.value(1)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(1)
motor_R.duty(speed)
def forward_sync():
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(speed)
def right_rotate_sync():
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(1)
motor_R.duty(speed)
def left_rotate_sync():
revrs_L.value(1)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(speed)
def right_turn_sync():
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(0)
def left_turn_sync():
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(0)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(speed)
Interface appearance: Tests of the final version:Sources are available here.Sources of inspiration:docs.micropython.org/en/latest/library/uasyncio.htmlhabr.com/en/post/484446habr.com/en/post/337420habr.com/en/post/484472github.com/peterhinch /micropython-async/blob/master/TUTORIAL.mdgithub.com/rsc1975/micropython-hcsr04medium.com/@pgjones/an-asyncio-socket-tutorial-5e6f3308b8b0
Tests of the final version:Sources are available here.Sources of inspiration:docs.micropython.org/en/latest/library/uasyncio.htmlhabr.com/en/post/484446habr.com/en/post/337420habr.com/en/post/484472github.com/peterhinch /micropython-async/blob/master/TUTORIAL.mdgithub.com/rsc1975/micropython-hcsr04medium.com/@pgjones/an-asyncio-socket-tutorial-5e6f3308b8b0