Hi Hi! We again prepared for you a selection of interesting questions and tasks from interviews at leading IT companies! Issues will appear every week - stay tuned! The column is supported by the recruitment agency Spice IT .This week we collected tasks from interviews at the American company PayPal. By the way, the answers to the problems from the previous issue have already been published .
Issues will appear every week - stay tuned! The column is supported by the recruitment agency Spice IT .This week we collected tasks from interviews at the American company PayPal. By the way, the answers to the problems from the previous issue have already been published .Questions
1. Prisoner and Policeman PuzzlePoliceman decided to punish the Prisoner and asked him to make a statement. The Prisoner should make such a statement so that he would be alive.
If the statement is held true by Policeman, the Prisoner will be hanged to death and if the statement is held false, the Prisoner will be shot dead.
2. Matchstick PuzzleHow to make 4 equilateral triangles with 6 identical match sticks?
Tasks
1. Intersection of two arraysGiven two arrays A and B respectively of size N and M. The task is to print the count of elements in the intersection (or common elements) of the two arrays.
For this question, intersection of two arrays can be defined as the set containing distinct common elements between the two arrays.
Input:
The first line of input contains an integer T denoting the number of test cases. The first line of each test case is N and M, N is the size of array A and M is size of array B. The second line of each test case contains N input A[i].
The third line of each test case contains M input B[i].
Output:
Print the count of intersecting elements.
Constraints:
1 ≤ T ≤ 100
1 ≤ N, M ≤ 105
1 ≤ A[i], B[i] ≤ 105
Example:
Input: Output: Explanation: Testcase 1: 89 is the only element in the intersection of two arrays. Testcase 2: 3 4 5 and 6 are the elements in the intersection of two arrays. Testcase 3: Non of the elements are common so the output will be -1. Testcase 4: 10 is the only element which is in the intersection of two arrays.
4
5 3
89 24 75 11 23
89 2 4
6 5
1 2 3 4 5 6
3 4 5 6 7
4 4
10 10 10 10
20 20 20 20
3 3
10 10 10
10 10 10
1
4
0
1
TransferA B N M. , ( ) .
, .
:
T, . — N M, N- A, M- B. N A[i].
M B[i].
:
.
:
1 ≤ T ≤ 100
1 ≤ N, M ≤ 105
1 ≤ A[i], B[i] ≤ 105
:
:
4
5 3
89 24 75 11 23
89 2 4
6 5
1 2 3 4 5 6
3 4 5 6 7
4 4
10 10 10 10
20 20 20 20
3 3
10 10 10
10 10 10
:
1
4
0
1
:
1: 89 — .
2: 3 4 5 6 — .
3: , 0.
4: 10 — , .
2. Concatenation of Zig-Zag String in 'n' RowsGiven a string and number of rows 'n'. Print the string formed by concatenating n rows when input string is written in row-wise Zig-Zag fashion.
Examples: Input:
The first line of input consists number of the test cases. The description of T test cases is as follows: The first line of each test case contains the string, and the second line has 'n' the number of rows. Output:
In each separate line print the string after concatenating n rows in a zig zag form. Constraints: Example: Input: Output:
Input:
str = "ABCDEFGH"
n = 2
Output: "ACEGBDFH"
Explanation: Let us write input string in Zig-Zag fashion in 2 rows.
A___C___E___G
__B___D___F___H
Now concatenate the two rows and ignore spaces
in every row. We get "ACEGBDFH"
Input:
str = "SPICEITRECRUITMENT"
n = 3
Output: SEEINPCIRCUTETITRM
Explanation: Let us write input string in Zig-Zag fashion in 3 rows.
S_______E_______E_______I_______N
__P___C___I___R___C___U___T___E___T
____I_______T_______R_______M
Now concatenate the two rows and ignore spaces
in every row. We get "SEEINPCIRCUTETITRM"
1 ≤ T ≤ 70
1 ≤ N ≤ size of string
2
qrrc
3
rfkqyuqfjkxy
2
qrcr
rkyqjxfqufky
Transfer‘n'. , n , .
:
:
str = "ABCDEFGH"
n = 2
: "ACEGBDFH"
: 2 .
A___C___E___G
__B___D___F___H
. "ACEGBDFH"
: SEEINPCIRCUTETITRM
str = "SPICEITRECRUITMENT"
n = 3
:
: 3 .
S_______E_______E_______I_______N
__P___C___I___R___C___U___T___E___T
____I_______T_______R_______M
. "SEEINPCIRCUTETITRM"
:
. t :
, 'n' — .
:
n .
:
1 ≤ T ≤ 70
1 ≤ N ≤
:
:
2
qrrc
3
rfkqyuqfjkxy
2
:
qrcr
rkyqjxfqufky
3. Solve the SudokuGiven an incomplete Sudoku configuration in terms of a 9 x 9 2-D square matrix (mat[][]). The task to print a solved Sudoku. For simplicity you may assume that there will be only one unique solution.
Sample Sudoku for you to get the logic for its solution:
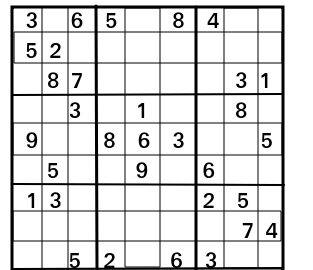
Input:
The first line of input contains an integer T denoting the no of test cases. Then T test cases follow. Each test case contains 9*9 space separated values of the matrix mat[][] representing an incomplete Sudoku state where a 0 represents empty block.
Output:
For each test case, in a new line, print the space separated values of the solution of the the sudoku.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 10
0 <= mat[] <= 9
Example:
Input:
1
3 0 6 5 0 8 4 0 0
5 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 8 7 0 0 0 0 3 1
0 0 3 0 1 0 0 8 0
9 0 0 8 6 3 0 0 5
0 5 0 0 9 0 6 0 0
1 3 0 0 0 0 2 5 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 7 4
0 0 5 2 0 6 3 0 0
Output:
3 1 6 5 7 8 4 9 2 5 2 9 1 3 4 7 6 8 4 8 7 6 2 9 5 3 1 2 6 3 4 1 5 9 8 7 9 7 4 8 6 3 1 2 5 8 5 1 7 9 2 6 4 3 1 3 8 9 4 7 2 5 6 6 9 2 3 5 1 8 7 4 7 4 5 2 8 6 3 1 9
Explanation:
Testcase 1: The solved sudoku is:
3 1 6 5 7 8 4 9 2
5 2 9 1 3 4 7 6 8
4 8 7 6 2 9 5 3 1
2 6 3 4 1 5 9 8 7
9 7 4 8 6 3 1 2 5
8 5 1 7 9 2 6 4 3
1 3 8 9 4 7 2 5 6
6 9 2 3 5 1 8 7 4
7 4 5 2 8 6 3 1 9
9 x 9 2D (mat [] []). . , .
, :
 :
:T, . T . 9 * 9 mat [] [], , 0 .
:.
:1 <= T <= 10
0 <= mat[] <= 9:
:1
3 0 6 5 0 8 4 0 0
5 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 8 7 0 0 0 0 3 1
0 0 3 0 1 0 0 8 0
9 0 0 8 6 3 0 0 5
0 5 0 0 9 0 6 0 0
1 3 0 0 0 0 2 5 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 7 4
0 0 5 2 0 6 3 0 0:3 1 6 5 7 8 4 9 2 5 2 9 1 3 4 7 6 8 4 8 7 6 2 9 5 3 1 2 6 3 4 1 5 9 8 7 9 7 4 8 6 3 1 2 5 8 5 1 7 9 2 6 4 3 1 3 8 9 4 7 2 5 6 6 9 2 3 5 1 8 7 4 7 4 5 2 8 6 3 1 9:1: :
3 1 6 5 7 8 4 9 2
5 2 9 1 3 4 7 6 8
4 8 7 6 2 9 5 3 1
2 6 3 4 1 5 9 8 7
9 7 4 8 6 3 1 2 5
8 5 1 7 9 2 6 4 3
1 3 8 9 4 7 2 5 6
6 9 2 3 5 1 8 7 4
7 4 5 2 8 6 3 1 92.

1t=0
try:
t=int(input().strip())
except:
pass
if __name__ == "__main__":
while t:
t-=1
n, m = map(int, input().strip().split())
a = list(map(int, input().strip().split()))
b = list(map(int, input().strip().split()))
a.sort()
count=0;x=0
for i in a:
if i==x:
pass
else:
if i in b:
count+=1
x=i
print(count)
2#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
string str;
cin>>str;
int row;
cin>>row;
vector<char> v[row];
int flag=1,k=0;
while(1)
{
if(flag==1 && k<str.length())
{
for(int i=0;i<row && k<str.length();i++)
{
v[i].push_back(str[k]);
k++;
}
flag=0;
}
if(flag==0 && k<str.length())
{
for(int i=row-2;i>0 && k<str.length();i--)
{
v[i].push_back(str[k]);
k++;
}
flag=1;
}
if(k==str.length())
break;
}
string res="";
for(int i=0;i<row;i++)
{
for(char ch:v[i])
{
res+=ch;
}
}
cout<<res<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
3#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
int grid[9][9];
int row[9][10];
int col[9][10];
int box[3][3][10];
bool flag;
vector<pair<int,int> >V;
void call(int I)
{
if(V.size()==I)
{
flag=false;
for(int i=0;i<9;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<9;j++)
cout<<grid[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
return;
}
int x=V[I].first,y=V[I].second;
int boxx,boxy;
if(x<3)
boxx=0;
else if(x<6)
boxx=1;
else
boxx=2;
if(y<3)
boxy=0;
else if(y<6)
boxy=1;
else
boxy=2;
for(int i=1;i<=9 && flag;i++)
{
if(row[x][i]==0 && col[y][i]==0 && box[boxx][boxy][i]==0)
{
row[x][i]=1; col[y][i]=1; box[boxx][boxy][i]=1;
grid[x][y]=i;
call(I+1);
row[x][i]=0; col[y][i]=0; box[boxx][boxy][i]=0;
grid[x][y]=0;
}
}
return;
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
for(int i=0;i<9;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<9;j++)
grid[i][j]=0;
}
for(int i=0;i<9;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=9;j++)
{
row[i][j]=0;
col[i][j]=0;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
for(int k=1;k<=9;k++)
box[i][j][k]=0;
}
flag=true;
V.clear();
for(int i=0;i<9;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<9;j++)
{
cin>>grid[i][j];
if(grid[i][j]==0)
{
V.push_back(make_pair(i,j));
continue;
}
row[i][grid[i][j]]=1;
col[j][grid[i][j]]=1;
if(i<3)
{
if(j<3)
{
box[0][0][grid[i][j]]=1;
}
else if(j<6)
{
box[0][1][grid[i][j]]=1;
}
else
{
box[0][2][grid[i][j]]=1;
}
}
else if(i<6)
{
if(j<3)
{
box[1][0][grid[i][j]]=1;
}
else if(j<6)
{
box[1][1][grid[i][j]]=1;
}
else
{
box[1][2][grid[i][j]]=1;
}
}
else
{
if(j<3)
{
box[2][0][grid[i][j]]=1;
}
else if(j<6)
{
box[2][1][grid[i][j]]=1;
}
else
{
box[2][2][grid[i][j]]=1;
}
}
}
}
call(0);
}
return 0;
}