Hello, Habr!This is my first experience with microcontrollers in general, and ESP8266 (in the form of Nodemcu v2) in particular. Perhaps for someone this experience will be useful.Why exactly micropython? The answer is simple - my modest programming experience is limited to Pascal at the university, and writing configuration scripts for Procera in Python, so it turned out to be the closest. The examples will be for Linux (ubuntu 18.04), but, I believe, there will not be any fundamental difference in other Linux distributions.Training:
We put python3, pip and picocom, if they are not already installed:sudo apt install python3 python3-pip picocom
Checking the python version:python --version
Python 3.6.9
If python version 2.7, change to 3:sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python python /usr/bin/python3 10
update-alternatives: using /usr/bin/python3 to provide /usr/bin/python (python) in auto mode
We update pip and check the version:sudo pip3 install --upgrade pip
pip --version
pip 20.0.2 from /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/pip (python 3.6)
pip3 --version
pip 20.0.2 from /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/pip (python 3.6)
We install a more recent version of esptool 2.8 from pip (since version 2.1 from the ubuntu repository gives the error "A fatal error occurred: ESP8266 ROM does not support function erase_flash." During firmware):pip3 install esptool
Download the firmware here . I used stable build 1.12 .Two options are possible:1. Sunrise manually (using terminal and REPL):
We clear flash on ESP8266:
esptool.py --port /dev/ttyUSB0 erase_flash
Command output:
esptool.py v2.8
Serial port /dev/ttyUSB0
Connecting....
Detecting chip type... ESP8266
Chip is ESP8266EX
Features: WiFi
Crystal is 26MHz
MAC: c8:2b:96:00:63:35
Uploading stub...
Running stub...
Stub running...
Erasing flash (this may take a while)...
Chip erase completed successfully in 9.5s
Hard resetting via RTS pin...
Fill the firmware:
esptool.py --port /dev/ttyUSB0 --baud 460800 write_flash --flash_size=detect 0 Downloads/esp8266-20191220-v1.12.bin
Command output:
esptool.py v2.8
Serial port /dev/ttyUSB0
Connecting....
Detecting chip type... ESP8266
Chip is ESP8266EX
Features: WiFi
Crystal is 26MHz
MAC: c8:2b:96:00:63:35
Uploading stub...
Running stub...
Stub running...
Changing baud rate to 460800
Changed.
Configuring flash size...
Auto-detected Flash size: 4MB
Flash params set to 0x0040
Compressed 619828 bytes to 404070...
Wrote 619828 bytes (404070 compressed) at 0x00000000 in 9.1 seconds (effective 543.8 kbit/s)...
Hash of data verified.
Leaving...
Hard resetting via RTS pin...
And, if desired, check the correctness of the checksum:
esptool.py --port /dev/ttyUSB0 --baud 460800 verify_flash --flash_size=detect 0 Downloads/esp8266-20191220-v1.12.bin
After that, we try to connect to MK and see the REPL console :
picocom /dev/ttyUSB0 -b115200
picocom v2.2
port is : /dev/ttyUSB0
flowcontrol : none
baudrate is : 115200
parity is : none
databits are : 8
stopbits are : 1
escape is : C-a
local echo is : no
noinit is : no
noreset is : no
nolock is : no
send_cmd is : sz -vv
receive_cmd is : rz -vv -E
imap is :
omap is :
emap is : crcrlf,delbs,
Type [C-a] [C-h] to see available commands
Terminal ready
>>> help()
Welcome to MicroPython!
For online docs please visit http://docs.micropython.org/en/latest/esp8266/ .
For diagnostic information to include in bug reports execute 'import port_diag'.
Basic WiFi configuration:
import network
sta_if = network.WLAN(network.STA_IF); sta_if.active(True)
sta_if.scan()
sta_if.connect("<AP_name>", "<password>")
sta_if.isconnected()
ap_if = network.WLAN(network.AP_IF)
ap_if.config(essid="<AP_NAME>", authmode=network.AUTH_WPA_WPA2_PSK, password="<password>")
Control commands:
CTRL-A -- on a blank line, enter raw REPL mode
CTRL-B -- on a blank line, enter normal REPL mode
CTRL-C -- interrupt a running program
CTRL-D -- on a blank line, do a soft reset of the board
CTRL-E -- on a blank line, enter paste mode
For further help on a specific object, type help(obj)
>>>
PS: to exit picocom use Ctrl + a and immediately Ctrl + x2. Using the IDE
Although the first option is quite functional (at least you can also blink an LED in it), with the IDE it is still much more convenient. I tried a couple of options, eventually settled on Thonny .
Installation:
We put python3-tk from the repositories, and actually Thonny via pip:
sudo apt install python3-tk
sudo pip3 install thonny
You can upload firmware to MK directly through Thonny:
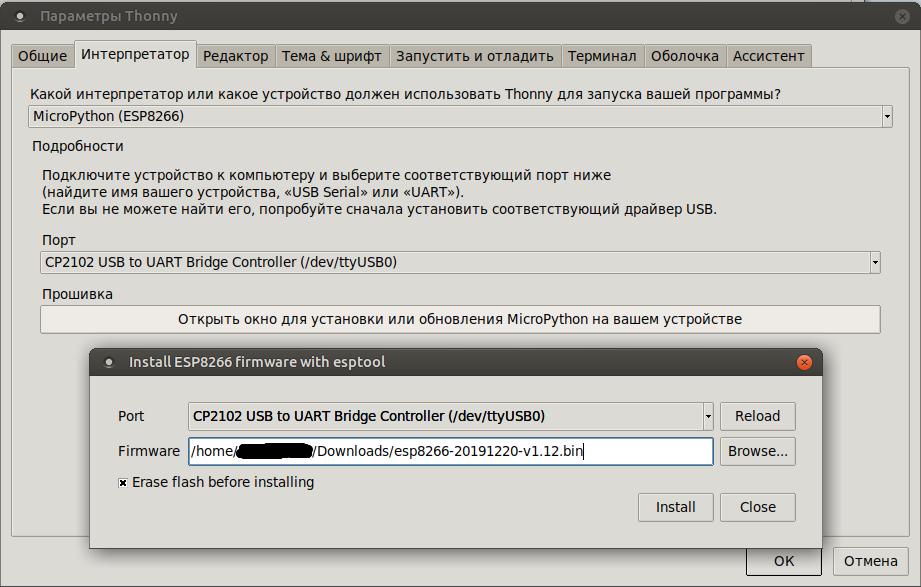
After which, blinking the LED becomes much more convenient:

Total
At the output, we have an esp8266 MK with micropython stitched, and an easy-to-use IDE to work with it.PS: the second part (Self-propelled platform on MK esp8266 with micropyhon)