CoLab notepad with examples.
It is possible to make a rolling window (rolling window, sliding window , moving window) over NumPy arrays in the Python programming language without explicit loops . This article discusses the creation of one-, two-, three-, and N-dimensional sliding windows over NumPy arrays. As a result, the data processing speed increases by several thousand times and is comparable in speed with the C programming language .
A sliding window is used in: image processing, artificial neural networks, Internet Protocol TCP, processing of genomic data, forecasting time series, etc.
Disclaimer : There may be errors in the source code! If you see a mistake, please write to me.
Introduction
This article is a continuation of my answer on the StackOverflow website. My first experiments with a sliding window here and here .
The practical implementation of a sliding two-dimensional window on a two-dimensional image array is in the function of rollthe logic_tools.pyproject file Manual marking of images using polygons .
Algorithms for a one-dimensional sliding window are already implemented here , here and here .
, , (strides, ).
- Pandas, Pandas, , . , . , Cython, - , NumPy.
1. 1D ND Numpy

:
def roll(a,
b,
dx=1):
shape = a.shape[:-1] + (int((a.shape[-1] - b.shape[-1]) / dx) + 1,) + b.shape
strides = a.strides[:-1] + (a.strides[-1] * dx,) + a.strides[-1:]
return np.lib.stride_tricks.as_strided(a, shape=shape, strides=strides)
numpy.lib.stride_tricks.as_strided (view) (shape) (strides).
(shape) , , . (strides) .
(shape) :
a.shape[:-1] — ND-, N > 1. N == 1, t == (), N == 1.(int((a.shape[-1] - b.shape[-1]) / dx) + 1,) — [-1] . dx : 1, 2, 3 ..b.shape — .
(strides) :
a.strides[:-1] — ND-, N > 1. N == 1, t == (), N == 1.(a.strides[-1] * dx,) — . , int 4 , dx == 2 4 * 2 = 8 .a.strides[-1:] — . , int 4 , (4,).
2. 2D ND Numpy

2D 2D :
, 2D - . , , , , .. , , .
def roll(a,
b,
dx=1,
dy=1):
shape = a.shape[:-2] + \
((a.shape[-2] - b.shape[-2]) // dy + 1,) + \
((a.shape[-1] - b.shape[-1]) // dx + 1,) + \
b.shape
strides = a.strides[:-2] + \
(a.strides[-2] * dy,) + \
(a.strides[-1] * dx,) + \
a.strides[-2:]
return np.lib.stride_tricks.as_strided(a, shape=shape, strides=strides)
: , , — ((a.shape[-2] - b.shape[-2]) // dy + 1,). :
(int((a.shape[-1] - b.shape[-1]) / dx) + 1,)
((a.shape[-1] - b.shape[-1]) // dx + 1,)
.
() , (a.strides[-2] * dy,) 2D .
counts, coords :
def show_results(a, b, dx=1, dy=1):
n = a.ndim
bool_array = np.all(roll(a, b, dx, dy) == b, axis=(n, n+1))
counts = np.count_nonzero(bool_array)
coords = np.transpose(np.nonzero(bool_array)) * [dy, dx]
print("Found {counts} elements with coordinates:\n{coords}".format(
counts=counts, coords=coords))
np.all 2D 4D . coords [dy, dx] .
3. 3D ND Numpy
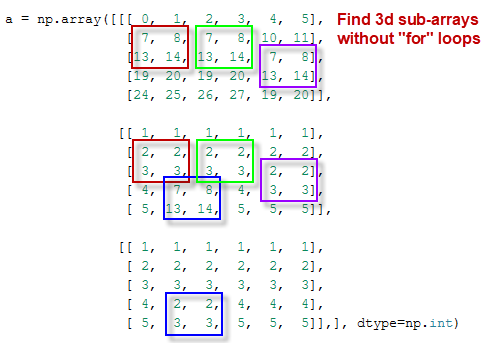
() - . , 3D ND- .
3D 3D — ( ) . CoLab 3D - , (, , ..).
def roll(a,
b,
dx=1,
dy=1,
dz=1):
shape = a.shape[:-3] + \
((a.shape[-3] - b.shape[-3]) // dz + 1,) + \
((a.shape[-2] - b.shape[-2]) // dy + 1,) + \
((a.shape[-1] - b.shape[-1]) // dx + 1,) + \
b.shape
strides = a.strides[:-3] + \
(a.strides[-3] * dz,) + \
(a.strides[-2] * dy,) + \
(a.strides[-1] * dx,) + \
a.strides[-3:]
return np.lib.stride_tricks.as_strided(a, shape=shape, strides=strides)
counts coords :
def show_results(a, b, dx=1, dy=1, dz=1):
n = a.ndim
bool_array = np.all(roll(a, b, dx, dy, dz) == b, axis=(n, n+1, n+2))
counts = np.count_nonzero(bool_array)
coords = np.transpose(np.nonzero(bool_array)) * [dz, dy, dx]
print("Found {counts} elements with coordinates:\n{coords}".format(
counts=counts, coords=coords))
4. MD ND , M ≤ N
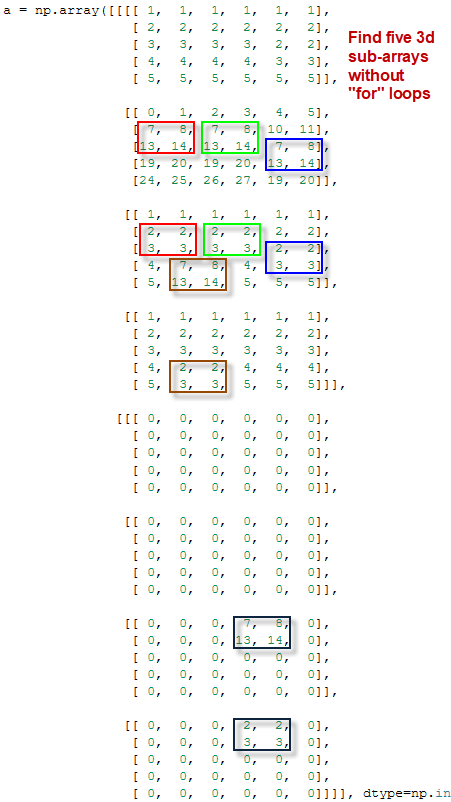
roll show_results MD ND , M N : M ≤ N.
def roll(a,
b,
d=None):
n = a.ndim
m = b.ndim
if m > n:
print("Error: rolling window dimensions is larger than the array dims")
return None
if d is None:
d = np.ones(m, dtype=np.uint32)
elif d.ndim != 1 and d.size != m:
print("Error: steps number must be equal to rolling window dimensions")
return None
elif not np.issubdtype(d.dtype, np.integer) or \
not (d > 0).all():
print("Error: steps must be integer and > 0")
return None
s = np.flip(d)
sub = np.subtract(a.shape[-m:], b.shape[-m:])
steps = tuple(np.divide(sub, s).astype(np.uint32) + 1)
shape = a.shape[:-m] + steps + b.shape
section = tuple(np.multiply(a.strides[-m:], s))
strides = a.strides[:-m] + section + a.strides[-m:]
return np.lib.stride_tricks.as_strided(a, shape=shape, strides=strides)
roll . :
steps = tuple(np.divide(sub, s).astype(np.uint32) + 1) — .section = tuple(np.multiply(a.strides[-m:], s)) — () « ».- « »
section ND-: strides = a.strides[:-m] + section + a.strides[-m:].
counts coords :
def show_results(a, b, d=None):
n = a.ndim
m = b.ndim
if d is None:
d = np.ones(m, dtype=np.uint32)
bool_array = roll(a, b, d) == b
bool_array = np.all(bool_array, axis=tuple(range(n, n + m)))
counts = np.count_nonzero(bool_array)
s = np.concatenate((np.ones(n-m, dtype=int), np.flip(d)))
coords = np.transpose(np.nonzero(bool_array)) * s
print("Found {counts} elements with coordinates:\n{coords}".format(
counts=counts, coords=coords))
show_results :
- ()
bool_array . numpy.all m , True. , bool_array — (N+M)D , np.all m MD :
bool_array = roll(a, b, d) == b
bool_array = np.all(bool_array, axis=tuple(range(n, n + m)))
5. MD ND M N
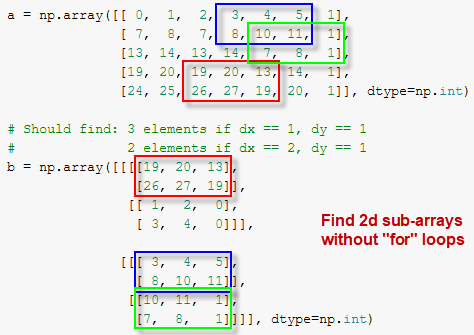
MD ND , M > N? , ! ND , MD M > N.
MD ND . MD ND M N. roll show_results.
def get_results(a, b, d=None):
n = a.ndim
m = b.ndim
if d is None:
d = np.ones(m, dtype=np.uint32)
bool_array = roll(a, b, d) == b
bool_array = np.all(bool_array, axis=tuple(range(n, n + m)))
counts = np.count_nonzero(bool_array)
s = np.concatenate((np.ones(n-m, dtype=int), np.flip(d)))
coords = np.transpose(np.nonzero(bool_array)) * s
return (counts, coords)
def show_intersections(a, b, d=None):
d_tmp = d
n = a.ndim
m = b.ndim
if d_tmp is None:
d_tmp = np.ones(m, dtype=np.uint32)
elif m > n and d_tmp.size == n:
d_tmp = np.concatenate((np.ones(m-n, dtype=int), d_tmp))
counts = 0
coords = None
if m <= n:
results = get_results(a, b, d_tmp)
counts = results[0]
coords = results[1]
else:
t = m - n
layers = np.prod(b.shape[:t])
temp = b.reshape((layers,) + b.shape[t:])
for i in range(layers):
results = get_results(a, temp[i], d_tmp[t:])
counts += results[0]
if coords is None:
coords = results[1]
else:
coords = np.concatenate((coords, results[1]))
print("Found {counts} elements with coordinates:\n{coords}".format(
counts=counts, coords=coords))
get_results , show_results .
show_intersections . M <= N, show_intersections get_results, . M > N, b a.
t = m - n MD b ND a. b a: layers = np.prod(b.shape[:t]). ( , reshape) b MD (N+1)D :
temp = b.reshape((layers,) + b.shape[t:])
: (N+1)D ND, (N+1) layers:
for i in range(layers):
results = get_results(a, temp[i], d_tmp[t:])
Combine the number of matches countsand the found coordinates of these matches coordsfor each layer:
for i in range(layers):
results = get_results(a, temp[i], d_tmp[t:])
counts += results[0]
if coords is None:
coords = results[1]
else:
coords = np.concatenate((coords, results[1]))
All examples are in CoLab notepad .
Thank you for the attention!