Ketogenic diet: from the treatment of epilepsy to an unhealthy fashion
 Each era of humanity is filled with its idols. People who somehow stand out from the crowd often become role models, inheritance, and copying. It has always been this way and it is happening now. Today, social networks, access to which can be obtained from every second device, dominate in matters of public opinion. In some situations, it’s even good if a person to whom the attention of thousands or millions of his subscribers is riveted shares useful and accurate information. However, most often we observe a situation when someone “famous” said something not quite smart, and the crowd supported him, because the principle works “well, this is“ Name ”, he won’t say nothing.” A similar situation has developed around the ketogenic diet used earlier in sports and in the treatment of epilepsy. Keto dietbased on high fat and low carbohydrate foods, it has become popular with some celebrities (excuse me for Englishism). But is it so good, and most importantly, is such a diet good for the human body? As scientists from Yale University found out, the harm from it is much more than good. What processes occur in the body during keto-diet, what are its consequences and is it worth it to go on a diet? We learn about this from the report of the research group. Go.what are its consequences and is it worth it to go on a diet? We learn about this from the report of the research group. Go.what are its consequences and is it worth it to go on a diet? We learn about this from the report of the research group. Go.
Each era of humanity is filled with its idols. People who somehow stand out from the crowd often become role models, inheritance, and copying. It has always been this way and it is happening now. Today, social networks, access to which can be obtained from every second device, dominate in matters of public opinion. In some situations, it’s even good if a person to whom the attention of thousands or millions of his subscribers is riveted shares useful and accurate information. However, most often we observe a situation when someone “famous” said something not quite smart, and the crowd supported him, because the principle works “well, this is“ Name ”, he won’t say nothing.” A similar situation has developed around the ketogenic diet used earlier in sports and in the treatment of epilepsy. Keto dietbased on high fat and low carbohydrate foods, it has become popular with some celebrities (excuse me for Englishism). But is it so good, and most importantly, is such a diet good for the human body? As scientists from Yale University found out, the harm from it is much more than good. What processes occur in the body during keto-diet, what are its consequences and is it worth it to go on a diet? We learn about this from the report of the research group. Go.what are its consequences and is it worth it to go on a diet? We learn about this from the report of the research group. Go.what are its consequences and is it worth it to go on a diet? We learn about this from the report of the research group. Go.Study basis
In the 1920s, a special diet was developed to prevent attacks in children with epilepsy. Its essence is a significant reduction in carbohydrates and an increase in fat in the patient’s food. When a person’s body does not receive enough carbohydrates, the level of glucose necessary for the nutrition and functioning of the brain decreases. In attempts to somehow adapt to such circumstances, the body begins to burn fats, processing them into fatty acids and ketone bodies (acetone, acetoacetic acid and beta-hydroxybutyric acid). Ketone bodies enter the brain and become a replacement for glucose, i.e. a new source of energy. This condition is called ketosis, and it leads to a decrease in the frequency of epilepsy attacks.Classical ketodiet implies a certain ratio of consumed fats and carbohydrates, or rather 4 to 1. In this case, the child's body will receive enough carbohydrates to continue the development of the body and to maintain a normal weight. If the goal of the diet is to lose weight, then the ratio may outweigh more towards fats, sometimes completely eliminating carbohydrates from the diet. Alfred HauptmannBut diet was not the only method to combat epilepsy and its manifestations. Pharmaceuticals did not stand still, because from the 19th century various anticonvulsant drugs were used. In 1912, Alfred Hauptmann discovered that phenobarbital has anticonvulsant properties. These substances were more effective than the bromides that were previously used, but did not completely cure epilepsy. Nevertheless, the expansion of the spectrum of anticonvulsants has led to the fact that the keto diet has practically ceased to be used.Currently, there are a number of studies claiming that keto-diet has a positive effect on patients with cancer and type 2 diabetes. However, there is very little clinical data to draw any conclusive conclusions.Considering that the keto diet literally makes the human body burn fats instead of carbohydrates, it is not surprising that this has attracted the attention of those who want to lose weight. In addition to the aesthetic effect, there is also a positive effect on health. And it is true, due to keto-diet in laboratory mice, blood sugar levels decreased and inhibition of inflammatory processes began. So far, everything sounds very beautiful, but the catch of the keto diet is that it does not demonstrate all its shortcomings immediately, but after a while.Scientists recall that visceral adipose tissue * contains a unique compartment of resident leukocytes, which help maintain energy homeostasis, but can also cause inflammation in chronic excess calories.
Alfred HauptmannBut diet was not the only method to combat epilepsy and its manifestations. Pharmaceuticals did not stand still, because from the 19th century various anticonvulsant drugs were used. In 1912, Alfred Hauptmann discovered that phenobarbital has anticonvulsant properties. These substances were more effective than the bromides that were previously used, but did not completely cure epilepsy. Nevertheless, the expansion of the spectrum of anticonvulsants has led to the fact that the keto diet has practically ceased to be used.Currently, there are a number of studies claiming that keto-diet has a positive effect on patients with cancer and type 2 diabetes. However, there is very little clinical data to draw any conclusive conclusions.Considering that the keto diet literally makes the human body burn fats instead of carbohydrates, it is not surprising that this has attracted the attention of those who want to lose weight. In addition to the aesthetic effect, there is also a positive effect on health. And it is true, due to keto-diet in laboratory mice, blood sugar levels decreased and inhibition of inflammatory processes began. So far, everything sounds very beautiful, but the catch of the keto diet is that it does not demonstrate all its shortcomings immediately, but after a while.Scientists recall that visceral adipose tissue * contains a unique compartment of resident leukocytes, which help maintain energy homeostasis, but can also cause inflammation in chronic excess calories.Visceral adipose tissue * (abdominal fat) - located inside the abdominal cavity, located between the organs (stomach, liver, intestines, kidneys, etc.).
It is noteworthy that with obesity, the composition of the immune cells of adipose tissue deviates towards increasing proportions of pro-inflammatory (involved in the inflammatory response) tissue types. The influx of pro-inflammatory cells suppresses resident cells present in adipose tissue in lean animals, which usually support tissue homeostasis. Such an accumulation of pro-inflammatory leukocytes contributes to systemic inflammation, leading to a violation of metabolic homeostasis.Previously, scientists have already identified a key factor in inflammation and diseases associated with obesity - this is inflammasome * NLRP3.Inflammasoma * is a multi-protein oligomeric complex responsible for the activation of the inflammatory response.
Inflammasoma NLRP3 is a regulated cytosolic natural immune sensor expressed in immune cells that provides the basis for caspase 1 * activation , allowing cleavage and secretion of IL-1β (interleukin 1, beta) and IL-18 (interleukin 18).Caspase 1 * is a proteolytic enzyme, i.e. an enzyme that breaks down the peptide bond between amino acids in proteins. Caspase 1 plays an important role in the immune system, being an activator of the inflammatory response.
Increased NLRP3-dependent activation of caspase 1 can be detected in the visceral white adipose tissue of obese mice. Meanwhile, NLRP3 - / - mice (“ - / - " means complete shutdown, ie in this case mice without NLRP3) are fully protected from obesity-induced inflammatory diseases, including glucose intolerance and liver steatosis (fatty hepatosis).These observations suggest that the NLRP3 inflammasome is a critical aspect of adipose tissue inflammation in obesity.Ketone body Β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) inhibits the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome, which binds natural immunity and metabolism. As we already know, ketogenesis (an increase in the level of ketogen bodies) occurs initially in the liver when glucose levels drop sharply. Hepatocytes (liver epithelial cells) lack the necessary enzyme for ketolysis, namely 3-oxoacid coenzyme A transferase 1, which allows ketone bodies to be transported in the blood to other important tissues (brain, heart and skeletal muscles) for oxidation and generation of adenosine triphosphate ( ATP, an energy source for biological processes in the body).In previous studies, it was found that keto diet increases the life expectancy of laboratory mice, and also improves cognitive function in older individuals. However, a detailed study of the influence of keto-diets on various processes associated with fatty tissues, the immune system, and metabolism has not been carried out, which is why there is little data for complete conclusions about its benefits or harms. That is why scientists decided to study in more detail how keto-diet affects inflammation of visceral adipose tissue.Research results
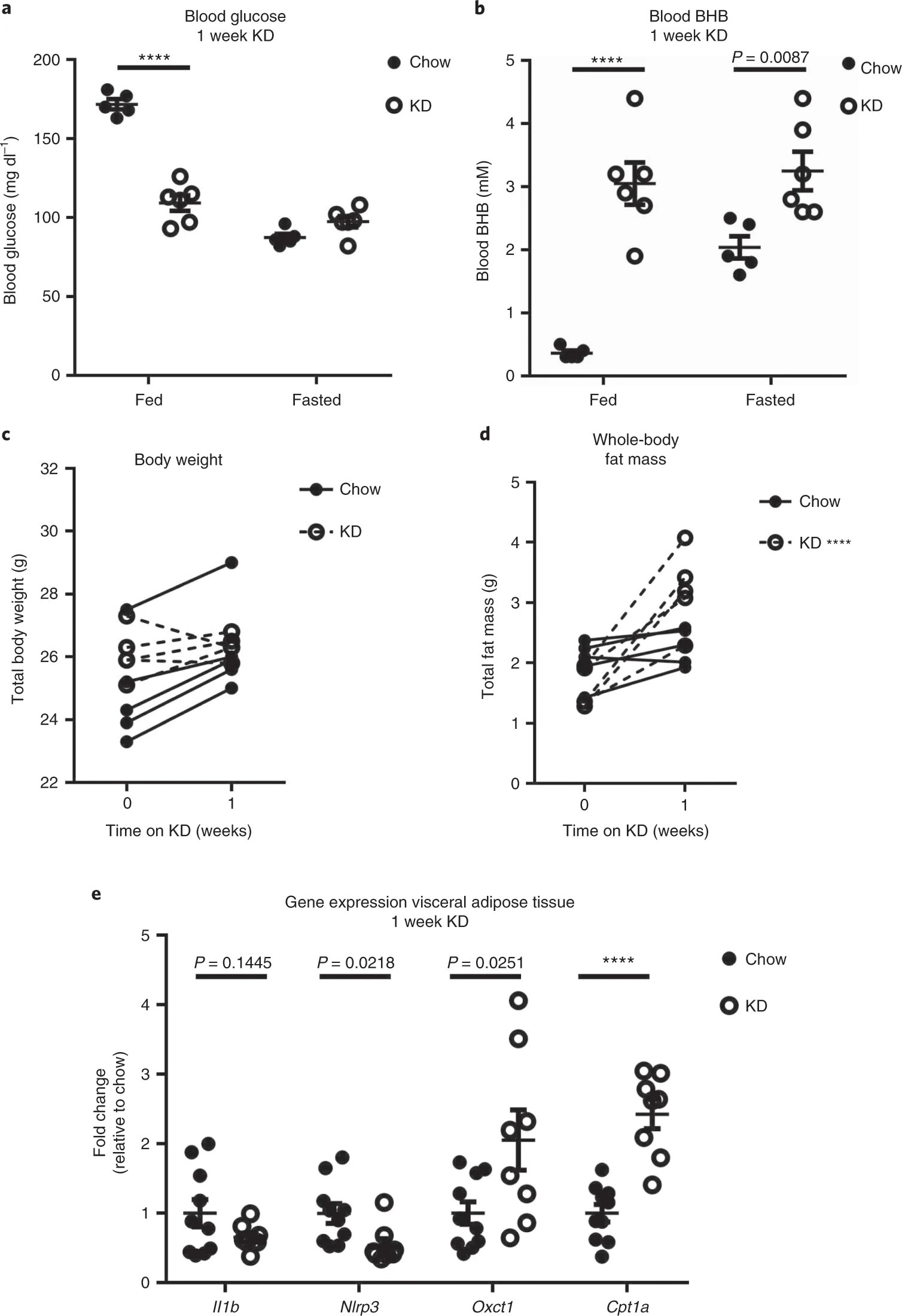 Image No. 1The first stage of observations was to assess the physiological response of experimental mice to short-term keto-diet (1 week). As was already established in previous studies, the keto-diet led to a decrease in the level of glucose in the blood of non-starving subjects to the level of glucose in the blood of starving individuals ( 1a ). The diet also increased the level of circulating BHB, with no additional effect on BHB during keto diet + starvation ( 1b ). Despite the absence of a net change in body weight ( 1c ), a slight but constant increase in fat mass was observed after 1 week of diet ( 1d ).A week of diet significantly reduced the expression of the Nlrp3 gene in epididymal fat (Efat ), and the expression of Il1b (interleukin 1, beta) in Efat in diet mice was lower than that of normally feeding mice ( 1e ).Ketodiet is an example of a metabolic paradox, because it is very rich in fats, but it also contributes to the oxidation of fatty acids with the formation of ATP. It has been found that the ketogenic diet increases expression Oxct1 - ketoliza enzyme rate-limiting and Cpt1a - mitochondrial membrane enzyme which allows delivery of long chain fatty acids into the mitochondria for oxidation ( 1d ).The induction of fatty acid metabolism genes is usually associated with improved metabolic homeostasis, despite an increase in body fat mass. The totality of these data suggests that 1 week diet improves glycemia (glucose in the blood) and increases the expression of genes associated with the oxidation of fatty acids and ketones in Efat.At the next stage of the study, the task was to find out exactly how the keto-diet affects the fatty immune compartment. For this, RNA sequencing of exclusively resident hemocytoblast cells (blood cell precursors) in Efat was performed after 1 week of normal feeding or keto-diet.Before sequencing, resident cells were identified to exclude all circulating cells by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) ( 2a ).
Image No. 1The first stage of observations was to assess the physiological response of experimental mice to short-term keto-diet (1 week). As was already established in previous studies, the keto-diet led to a decrease in the level of glucose in the blood of non-starving subjects to the level of glucose in the blood of starving individuals ( 1a ). The diet also increased the level of circulating BHB, with no additional effect on BHB during keto diet + starvation ( 1b ). Despite the absence of a net change in body weight ( 1c ), a slight but constant increase in fat mass was observed after 1 week of diet ( 1d ).A week of diet significantly reduced the expression of the Nlrp3 gene in epididymal fat (Efat ), and the expression of Il1b (interleukin 1, beta) in Efat in diet mice was lower than that of normally feeding mice ( 1e ).Ketodiet is an example of a metabolic paradox, because it is very rich in fats, but it also contributes to the oxidation of fatty acids with the formation of ATP. It has been found that the ketogenic diet increases expression Oxct1 - ketoliza enzyme rate-limiting and Cpt1a - mitochondrial membrane enzyme which allows delivery of long chain fatty acids into the mitochondria for oxidation ( 1d ).The induction of fatty acid metabolism genes is usually associated with improved metabolic homeostasis, despite an increase in body fat mass. The totality of these data suggests that 1 week diet improves glycemia (glucose in the blood) and increases the expression of genes associated with the oxidation of fatty acids and ketones in Efat.At the next stage of the study, the task was to find out exactly how the keto-diet affects the fatty immune compartment. For this, RNA sequencing of exclusively resident hemocytoblast cells (blood cell precursors) in Efat was performed after 1 week of normal feeding or keto-diet.Before sequencing, resident cells were identified to exclude all circulating cells by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) ( 2a ).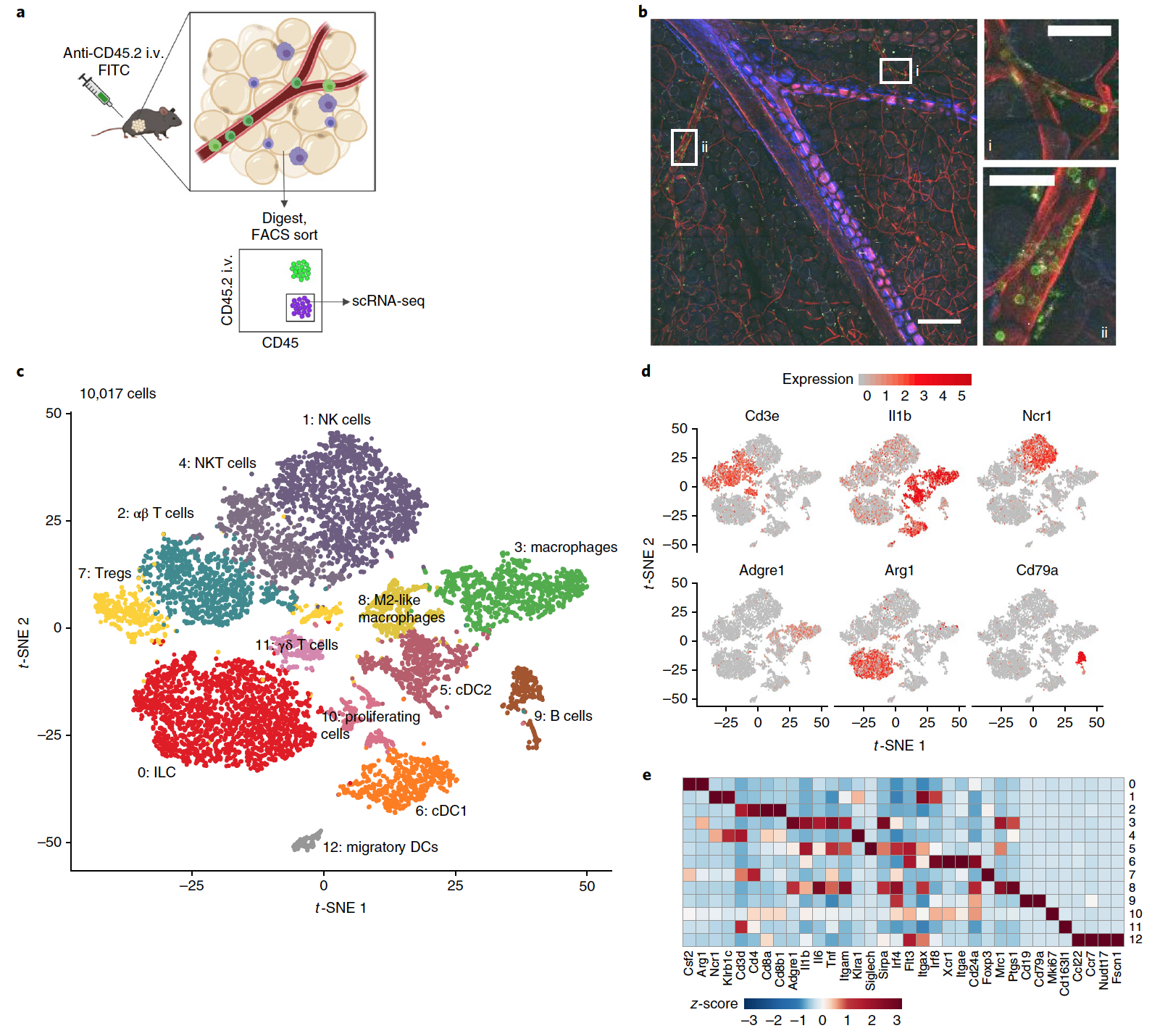 Image No. 2Using two-photon microscopy, it was possible to visually confirm that marking is found even in the microvasculature of visceral adipose tissue. This increases the confidence that the analysis widely covers all CD45 + cells actually located in the studied tissues ( 2b ).Sequencing provided data on 4458 cells of experimental subjects who ate normally, and 5559 cells of those fed on keto-diet. The data of both groups were combined to identify subpopulations of cells; as a result, 13 clusters were found (2c ).Labeling cells by type revealed that among these clusters were: macrophages * (cluster 3 and 8), T cells * (cluster 2, 7 and 11), NK cells * (cluster 1), NKT cells * (cluster 4), B cells * (cluster 9), lymphoid cells * (cluster 0), fat-resident dendritic cells * (cluster 5 and 6) and migrating dendritic cells (cluster 12).
Image No. 2Using two-photon microscopy, it was possible to visually confirm that marking is found even in the microvasculature of visceral adipose tissue. This increases the confidence that the analysis widely covers all CD45 + cells actually located in the studied tissues ( 2b ).Sequencing provided data on 4458 cells of experimental subjects who ate normally, and 5559 cells of those fed on keto-diet. The data of both groups were combined to identify subpopulations of cells; as a result, 13 clusters were found (2c ).Labeling cells by type revealed that among these clusters were: macrophages * (cluster 3 and 8), T cells * (cluster 2, 7 and 11), NK cells * (cluster 1), NKT cells * (cluster 4), B cells * (cluster 9), lymphoid cells * (cluster 0), fat-resident dendritic cells * (cluster 5 and 6) and migrating dendritic cells (cluster 12).Macrophages * - cells capable of capturing and digesting foreign or toxic particles (bacteria, dead cells, etc.).
T-cells (T-lymphocytes) * - participate in the formation of acquired immunity, allowing you to recognize and destroy cells with a foreign antigen.
NK- ( )* — , , .
NKT- ( -)* — -, -, NK-.
- (-)* — , ( , ). - , .
()* — , , .
* — -, .. -.
Images 2d and 2e show expression patterns of these cell clusters.A comparative analysis of samples from the conventional nutrition group and keto-diets showed striking differences. Significant changes in the overall cellular composition and transcriptional states of individual cell subtypes ( 3a and 3b ) were detected .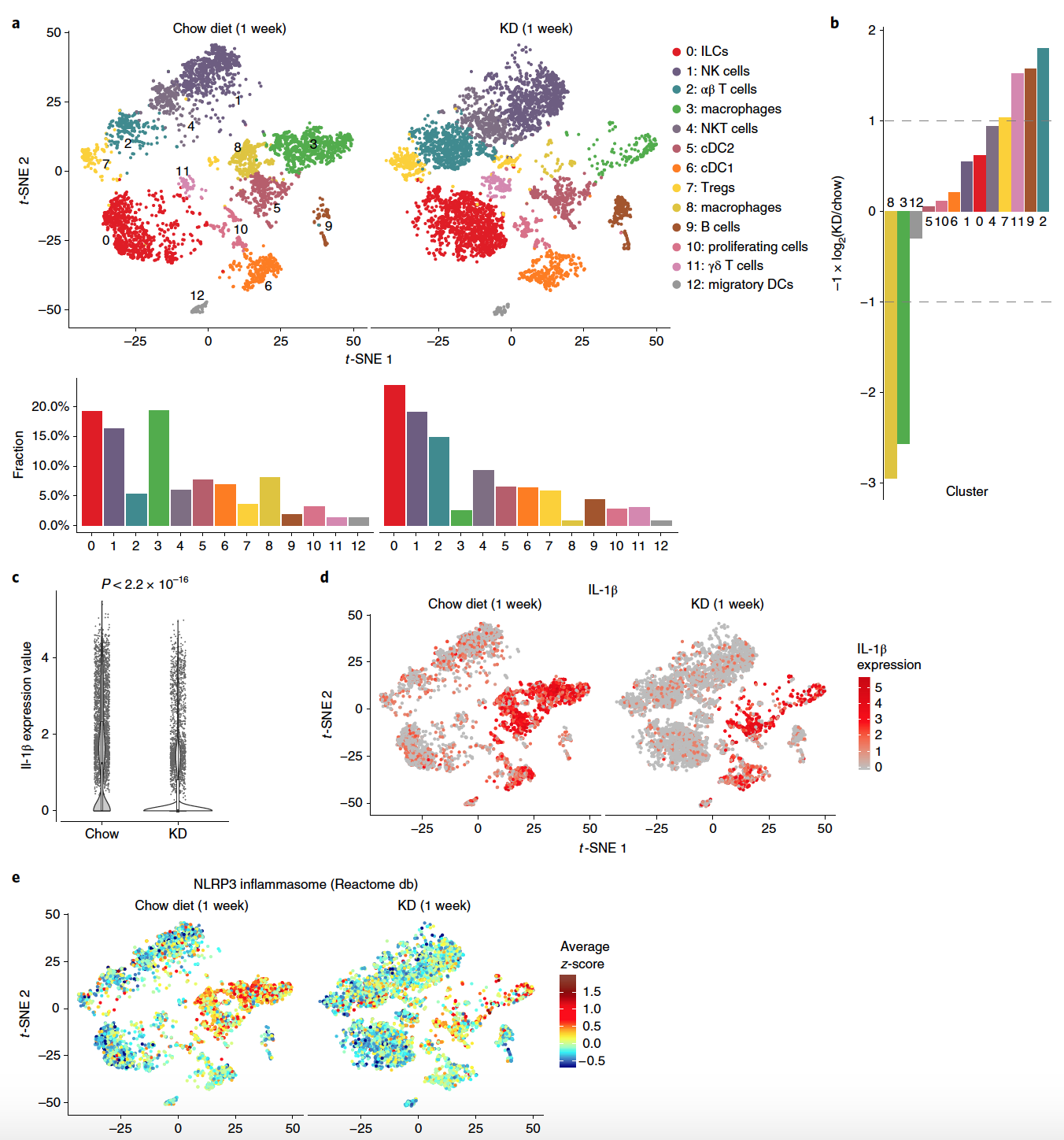 Image No. 3Previously, scientists have already established that VNV inhibits pro-inflammatory macrophages. Moreover, a pronounced decrease in the number of these cells was observed in diet mice ( 3b ). The loss of macrophages ( 3d ) resulted in reduced expression of Il1b ( 3c ).A decrease in the expression of the Nlrp3 gene after one week of ketodiet ( 1d ) can also be associated with a decrease in the number of macrophages, as clusters 3 and 8 show the NLRP3 signature of the inflammasome ( 3e ).Both natural killer cells and lymphoid cells showed significant transcriptional changes ( 3a ). However, the most obvious change occurred with fat-resident T-cells and B-cells (cluster 9, 2 and 11), the number of which increased about 2 times after a week of diet ( 3b ).The researchers focused on γδ T cells (gamma-delta T cells).
Image No. 3Previously, scientists have already established that VNV inhibits pro-inflammatory macrophages. Moreover, a pronounced decrease in the number of these cells was observed in diet mice ( 3b ). The loss of macrophages ( 3d ) resulted in reduced expression of Il1b ( 3c ).A decrease in the expression of the Nlrp3 gene after one week of ketodiet ( 1d ) can also be associated with a decrease in the number of macrophages, as clusters 3 and 8 show the NLRP3 signature of the inflammasome ( 3e ).Both natural killer cells and lymphoid cells showed significant transcriptional changes ( 3a ). However, the most obvious change occurred with fat-resident T-cells and B-cells (cluster 9, 2 and 11), the number of which increased about 2 times after a week of diet ( 3b ).The researchers focused on γδ T cells (gamma-delta T cells).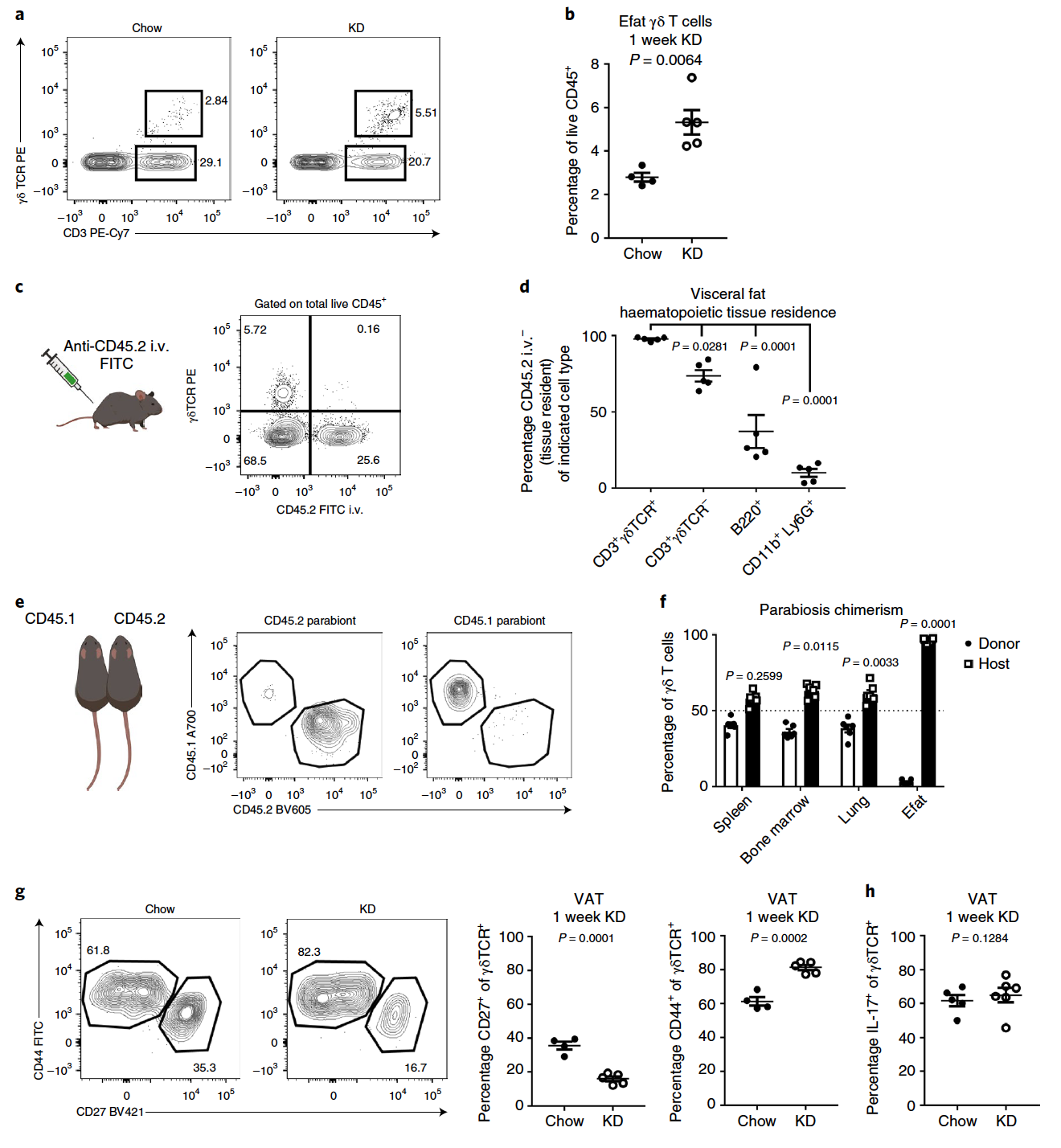 Image No. 4By flow cytometry of adipose tissue, the expansion (multiplication) of γδ T cells observed in the sequencing data ( 4a and 4b ) was confirmed . This technique once again confirmed the loss of macrophages and additionally showed the loss of eosinophils (a subspecies of granular leukocytes), which was difficult to see in previous tests.Cell labeling showed that almost 100% of γδ T cells were tissue dependent (i.e., these cells were almost completely located in adipose tissue), which was noticeable in comparison with other CD3 + cells and B cells ( 4c and 4d ). Labeling also showed that neutrophils are also present in healthy adipose tissue (a subspecies of granular leukocytes, CD11b + Ly6G+ ), but they are not resident ( 4d ).Next, experiments were conducted with parabiosis (when the cell is in a state between life and death). The results showed that γδ T cells in adipose tissues, in contrast to the spleen, brain and lungs, are actually uniquely resident with almost zero chimerism ( 4e and 4f ).The combination of the above data confirms the unique location of γδ T cells in visceral adipose tissue.A complete transcriptome analysis of γδ T cells from Efat mice of both groups showed that fatty γδ T cells are initially ready for the process of remodeling adipose tissue, and their activation can enhance the physiological effect of keto-diet on the body. In other words, γδ T cells are capable of altering the structure of adipose tissue, but under normal conditions they do not. In the case of a prolonged ketodiet, which causes changes at the cellular level, the process of tissue restructuring begins, initiated precisely by γδ T cells.If a short (up to 1 week) diet within the framework of a keto diet has some positive effects on the body, then a long one leads to serious problems.
Image No. 4By flow cytometry of adipose tissue, the expansion (multiplication) of γδ T cells observed in the sequencing data ( 4a and 4b ) was confirmed . This technique once again confirmed the loss of macrophages and additionally showed the loss of eosinophils (a subspecies of granular leukocytes), which was difficult to see in previous tests.Cell labeling showed that almost 100% of γδ T cells were tissue dependent (i.e., these cells were almost completely located in adipose tissue), which was noticeable in comparison with other CD3 + cells and B cells ( 4c and 4d ). Labeling also showed that neutrophils are also present in healthy adipose tissue (a subspecies of granular leukocytes, CD11b + Ly6G+ ), but they are not resident ( 4d ).Next, experiments were conducted with parabiosis (when the cell is in a state between life and death). The results showed that γδ T cells in adipose tissues, in contrast to the spleen, brain and lungs, are actually uniquely resident with almost zero chimerism ( 4e and 4f ).The combination of the above data confirms the unique location of γδ T cells in visceral adipose tissue.A complete transcriptome analysis of γδ T cells from Efat mice of both groups showed that fatty γδ T cells are initially ready for the process of remodeling adipose tissue, and their activation can enhance the physiological effect of keto-diet on the body. In other words, γδ T cells are capable of altering the structure of adipose tissue, but under normal conditions they do not. In the case of a prolonged ketodiet, which causes changes at the cellular level, the process of tissue restructuring begins, initiated precisely by γδ T cells.If a short (up to 1 week) diet within the framework of a keto diet has some positive effects on the body, then a long one leads to serious problems.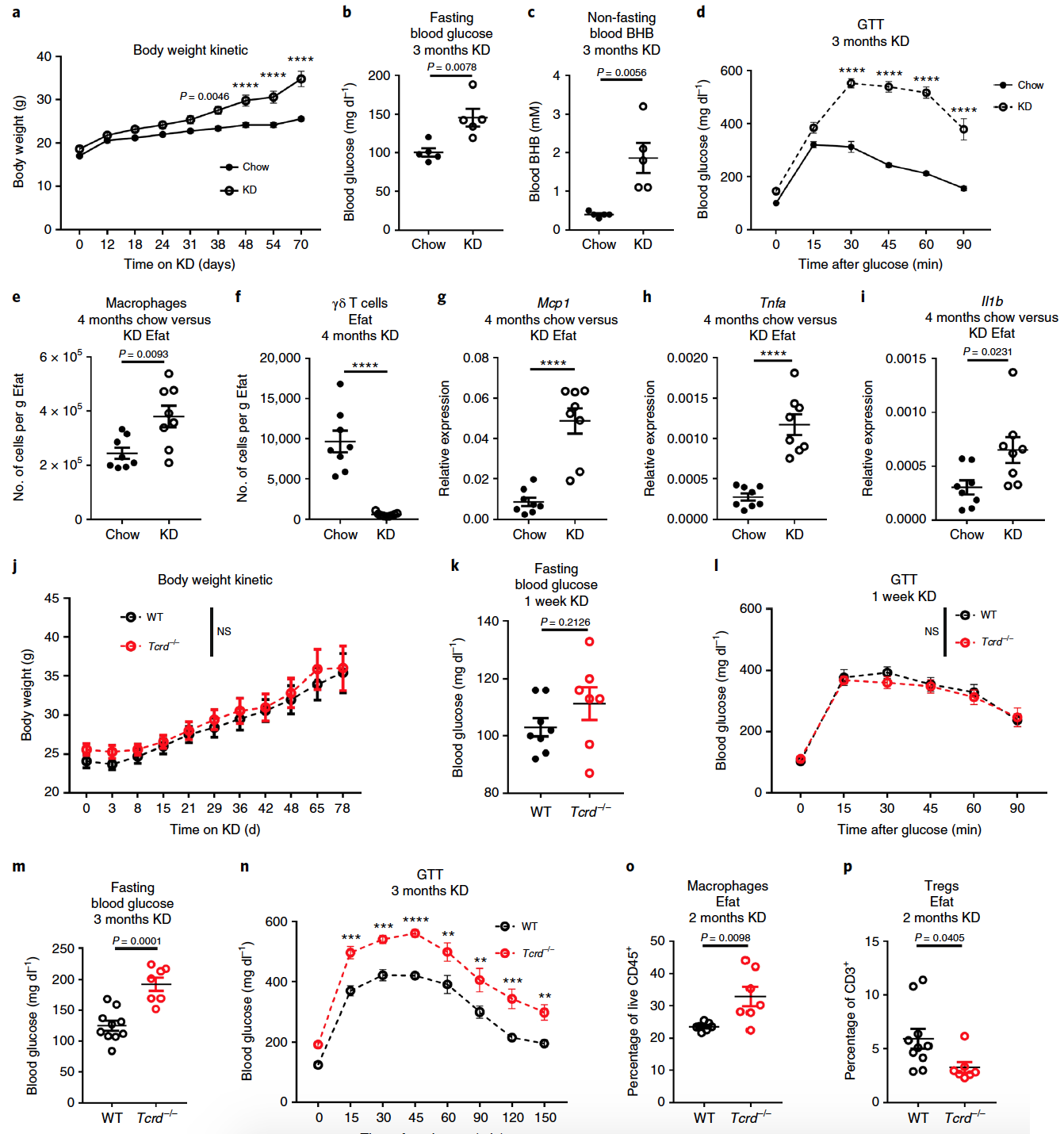 Observed changes due to prolonged keto-diet compared to normal nutrition.After 2-3 months, on a keto-diet, the mice gained significantly more weight (graph a in the image above) in comparison with individuals from the control group (normal nutrition). In addition, they have high blood sugar ( b ). The increase in body weight was mainly due to the accumulation of fat in the body, including in the liver. Such observations are closely related to impaired glucose tolerance ( d ). Cellular analysis of adipose tissue of mice on a long-term diet showed an increase in the number of macrophages ( e ) and a decrease in the number of γδ T cells ( f ). An increased expression of the pro-inflammatory genes Mcp1, Tnfa and Il1b ( g - i ) was also detected .It was also found that in mice whose γδ T cells were inactive, the same processes occur. From these observations, it follows that prolonged keto-diet leads to obesity and loss of control over glycemia (glucose level).For a more detailed acquaintance with the nuances of the study, I recommend that you look into the report of scientists and additional materials to it.
Observed changes due to prolonged keto-diet compared to normal nutrition.After 2-3 months, on a keto-diet, the mice gained significantly more weight (graph a in the image above) in comparison with individuals from the control group (normal nutrition). In addition, they have high blood sugar ( b ). The increase in body weight was mainly due to the accumulation of fat in the body, including in the liver. Such observations are closely related to impaired glucose tolerance ( d ). Cellular analysis of adipose tissue of mice on a long-term diet showed an increase in the number of macrophages ( e ) and a decrease in the number of γδ T cells ( f ). An increased expression of the pro-inflammatory genes Mcp1, Tnfa and Il1b ( g - i ) was also detected .It was also found that in mice whose γδ T cells were inactive, the same processes occur. From these observations, it follows that prolonged keto-diet leads to obesity and loss of control over glycemia (glucose level).For a more detailed acquaintance with the nuances of the study, I recommend that you look into the report of scientists and additional materials to it.Epilogue
In this work, scientists conducted a series of experiments and observations that demonstrated the effect of keto-diet on the body. During the first week of a diet with a high fat content and a low carbohydrate content, it has a number of positive effects, including a decrease in blood sugar and a decrease in the volume of fatty tissues. However, with a longer diet, its flaws begin to appear. The lack of carbohydrates in the body and the need to burn fats for energy leads to impaired glucose tolerance, i.e. to increase blood sugar. In addition, the body does not trivially cope with the large amount of fat obtained, which leads to their accumulation, including in vital organs (in the liver).Popular people often form the opinions and tastes of those around them. This can happen both consciously and unconsciously. However, in any case, such a social effect is associated with a number of serious consequences that do not always have a positive color. The popularization of love for nature, a positive outlook on life, respect for each other - these are rather moral and ethical advice, which rarely have any significant impact on the human body, which will follow these tips. But the advice that directly affects human health should be at least tested and not on themselves, but scientifically, because one is good, the other is poison.Whatever the case, when questions relate to human health, and diet directly affects health, you cannot fully trust the advice of those who, you see, have a million followers, a beautiful profile picture or something like that. For the number of subscribers is not an indicator of competence in a particular issue.Thank you for your attention, stay curious and have a great weekend everyone, guys! :)A bit of advertising :)
Thank you for staying with us. Do you like our articles? Want to see more interesting materials? Support us by placing an order or recommending to your friends, cloud VPS for developers from $ 4.99 , a unique analog of entry-level servers that was invented by us for you: The whole truth about VPS (KVM) E5-2697 v3 (6 Cores) 10GB DDR4 480GB SSD 1Gbps from $ 19 or how to divide the server? (options are available with RAID1 and RAID10, up to 24 cores and up to 40GB DDR4).Dell R730xd 2 times cheaper at the Equinix Tier IV data center in Amsterdam? Only we have 2 x Intel TetraDeca-Core Xeon 2x E5-2697v3 2.6GHz 14C 64GB DDR4 4x960GB SSD 1Gbps 100 TV from $ 199 in the Netherlands!Dell R420 - 2x E5-2430 2.2Ghz 6C 128GB DDR3 2x960GB SSD 1Gbps 100TB - from $ 99! Read about How to Build Infrastructure class c using Dell R730xd E5-2650 v4 servers costing 9,000 euros for a penny?Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/undefined/
All Articles