Hallo Habr!Dieser Artikel beschreibt den Prozess des Upgrades einer selbstfahrenden Plattform auf Basis des esp8266 MK mit Mikropython auf einen einfachen Roboter, der im Rahmen eines Schulungsprojekts mit einem Ultraschall-Hindernissensor, einer blinkenden LED, einer Start / Stopp-Taste sowie einem integrierten Webserver ausgestattet ist.KDPV: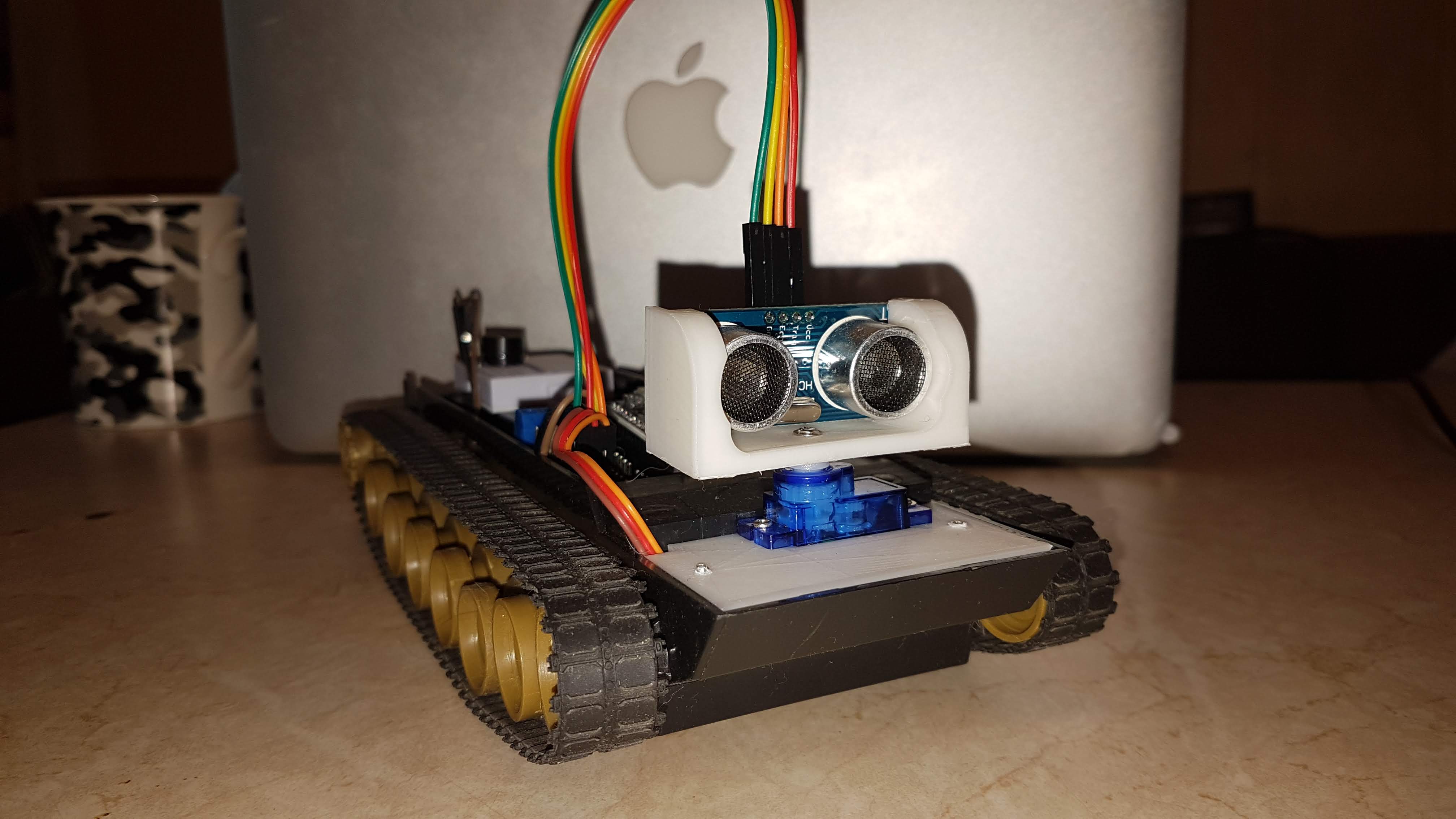 In den ersten beiden Teilen wurde die Herstellung einer selbstfahrenden Plattform beschrieben, die über eine WLAN-Webschnittstelle gesteuert wird.Die Aufgabe für die aktuelle Phase besteht darin, diese Ultraschallplattform mit dem HC-SR04-Sensor auszustatten und die Möglichkeit hinzuzufügen, offline zu arbeiten.Zunächst - das mechanische Teil:Es ist notwendig, den Sensor und das Servo im Gehäuse zu befestigen, das Design zu entwerfen (ich habe dafür FreeCAD verwendet ) und die fehlenden Teile herzustellen:
In den ersten beiden Teilen wurde die Herstellung einer selbstfahrenden Plattform beschrieben, die über eine WLAN-Webschnittstelle gesteuert wird.Die Aufgabe für die aktuelle Phase besteht darin, diese Ultraschallplattform mit dem HC-SR04-Sensor auszustatten und die Möglichkeit hinzuzufügen, offline zu arbeiten.Zunächst - das mechanische Teil:Es ist notwendig, den Sensor und das Servo im Gehäuse zu befestigen, das Design zu entwerfen (ich habe dafür FreeCAD verwendet ) und die fehlenden Teile herzustellen: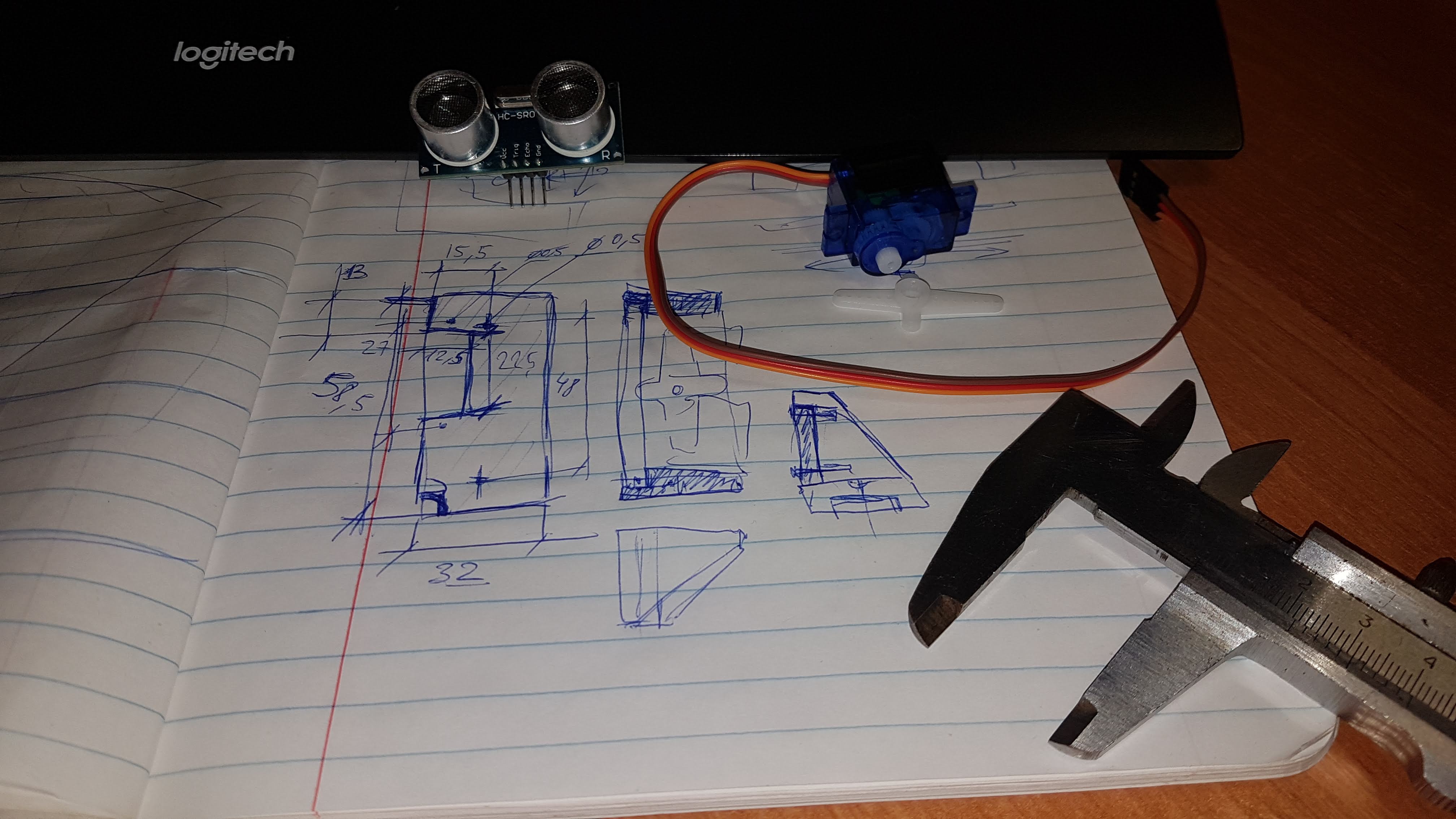
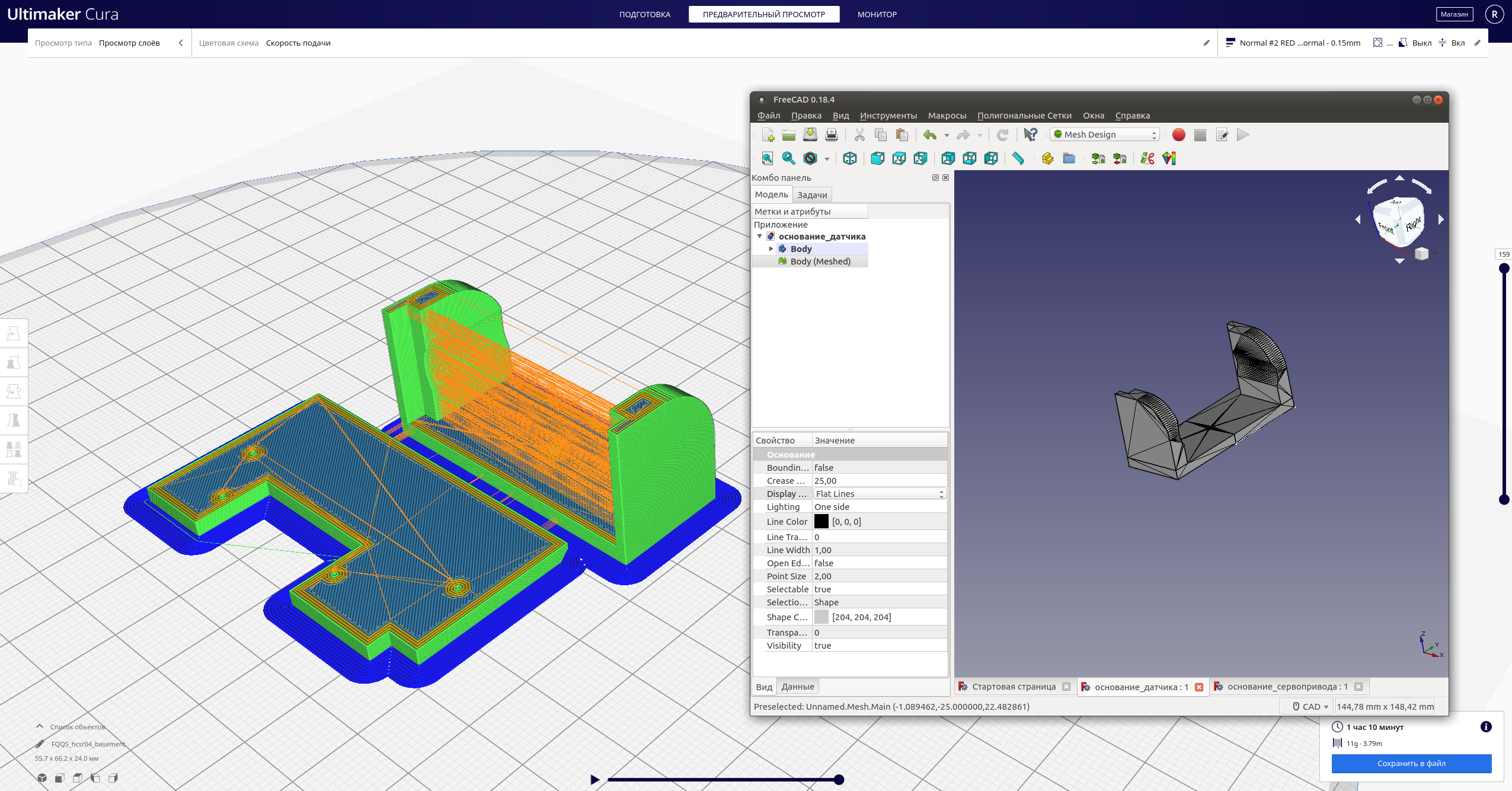 Dann - das elektrische:Zeichnen Sie den Stromkreis (zum Beispiel in Fritzing ) und führen Sie die Umschaltung entsprechend durch:
Dann - das elektrische:Zeichnen Sie den Stromkreis (zum Beispiel in Fritzing ) und führen Sie die Umschaltung entsprechend durch: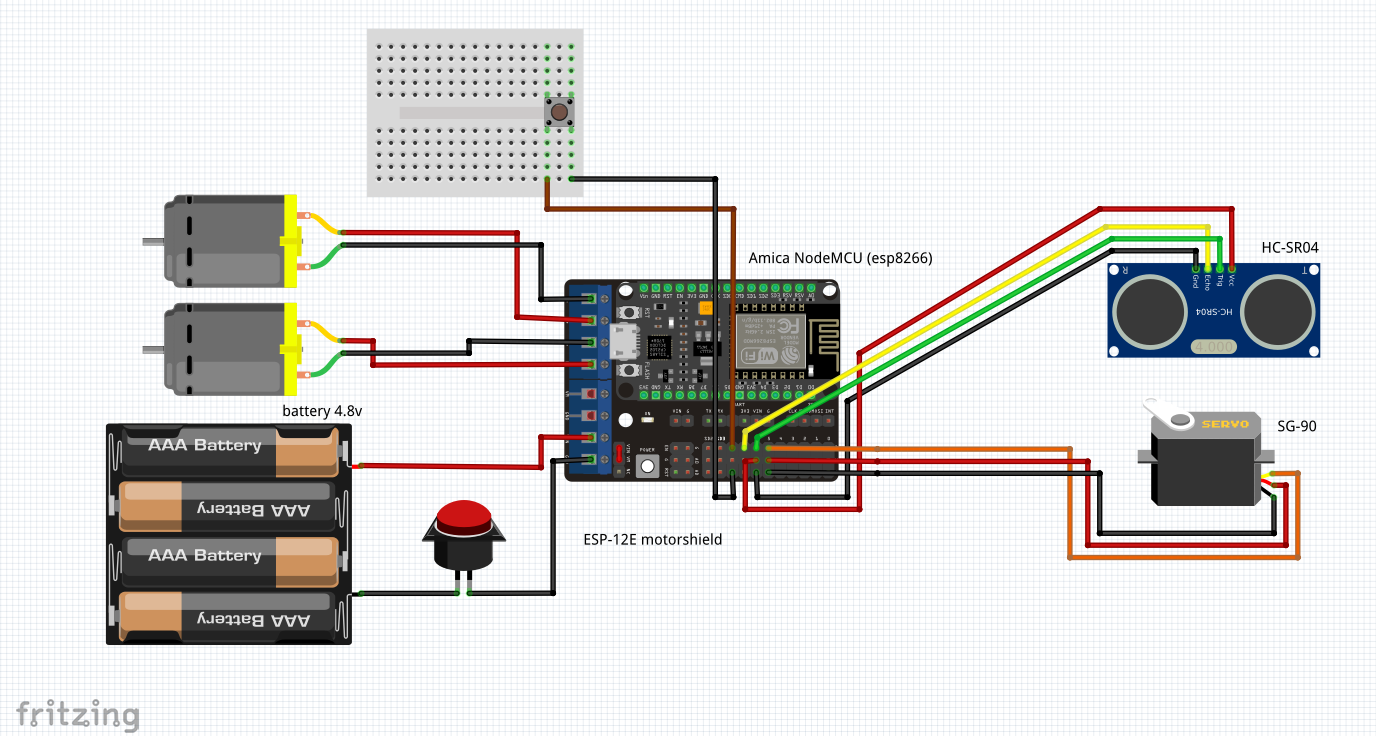 Danach: versuche alles zum Fliegen zu bringen ...Da ich wollte, dass bestimmte Funktionen des Roboterprogramms parallel ausgeführt werden (z. B. das Scannen der Entfernung zu Hindernissen und die Bewegungsfunktion), musste ich in die Funktionen des Asyncio- Moduls eintauchen . Ausführlichere Arbeiten mit Asyncio werden in diesem und diesem Artikel beschrieben.Um beispielsweise eine LED zu blinken, können Sie eine solche Coroutine anwenden, die sich praktisch nicht von synchron unterscheidet:
Danach: versuche alles zum Fliegen zu bringen ...Da ich wollte, dass bestimmte Funktionen des Roboterprogramms parallel ausgeführt werden (z. B. das Scannen der Entfernung zu Hindernissen und die Bewegungsfunktion), musste ich in die Funktionen des Asyncio- Moduls eintauchen . Ausführlichere Arbeiten mit Asyncio werden in diesem und diesem Artikel beschrieben.Um beispielsweise eine LED zu blinken, können Sie eine solche Coroutine anwenden, die sich praktisch nicht von synchron unterscheidet:import uasyncio as asyncio
from machine import Pin
syst_led = Pin(16, Pin.OUT)
async def blink_led(led, interval_ms):
led_val = True
while True:
led_val = not(led_val)
led_state = led.value(int(led_val))
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.create_task(blink_led(syst_led, interval_ms=250))
loop.run_forever()
Der Unterschied besteht darin, dass solche Coroutinen, die unterschiedliche Aufgaben ausführen, mehrere gleichzeitig gestartet werden können (die Ressourcen werden vom Scheduler zugewiesen).Daher schreiben wir Coroutinen zum Messen der Entfernung und zum Scannen eines Sektors sowie einen Rückruf für einen Hardware-Interrupt (Schaltfläche), der das Scannen startet oder stoppt. Die Übertragung des Zustands zwischen Coroutinen kann im einfachsten Fall über globale Variablen erfolgen:Rückruf für die Schaltfläche:from machine import Pin
run_flag = False
button = Pin(15, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP)
def callback(p):
global run_flag
run_flag = not(run_flag)
print('set run_flag', run_flag, p)
button.irq(trigger=Pin.IRQ_FALLING, handler=callback)
Entfernungsmessung:import uasyncio as asyncio
from utime import sleep, sleep_us
from machine import Pin, time_pulse_us
trig=Pin(12, Pin.OUT)
echo=Pin(13, Pin.IN)
async def async_measure_range():
echo_timeout_us=500*2*30
trig.off()
sleep_us(5)
trig.on()
sleep_us(10)
trig.off()
try:
pulse_time = time_pulse_us(echo, 1, echo_timeout_us)
except:
pass
dist = (pulse_time / 2) / 29.1
return dist
Sektor-Scannen (mit Aufrufen der Entfernungsmessungs-Coroutine):import uasyncio as asyncio
from machine import Pin, PWM
pos_actual = 75
dist_cm = 50
p14 = Pin(14, Pin.OUT)
servo = PWM(p14, freq=50)
async def radar_scan(interval_ms):
pos_list = [45,75,105,75]
global pos_actual
global dist_cm
while True:
if run_flag:
for pos in pos_list:
servo.duty(pos)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
dist_cm = await async_measure_range()
pos_actual = pos
print('pos_actual = %s, dist_cm = %s' % (pos_actual, dist_cm)
elif not run_flag:
await asyncio.sleep(0)
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop(
loop.create_task(radar_scan(interval_ms=250))
loop.run_forever()
Beim Debuggen ergab der Sensor von Zeit zu Zeit einen negativen Abstandswert. Es stellte sich heraus - "Elektronik ist die Wissenschaft von schlechten Kontakten" , als der Sensor gedreht wurde, das Kabel gezogen wurde und der Kontakt verloren ging.Es bleibt die Logik der Wahl der Aktion basierend auf den Scanergebnissen zu festigen:avoid_left = False
avoid_right = False
avoid_backward = False
async def make_decision(interval_ms, avoid_limit_cm):
global avoid_left
global avoid_right
global avoid_backward
while True:
if run_flag:
if pos_actual == 45 and dist_cm < avoid_limit_cm :
avoid_left = True
if debug : print('avoid_left = %s' % avoid_left)
elif pos_actual == 45 and dist_cm >= avoid_limit_cm :
avoid_left = False
if debug : print('avoid_left = %s' % avoid_left)
elif pos_actual == 75 and dist_cm < avoid_limit_cm*1.25 :
avoid_backward = True
if debug : print('avoid_backward = %s' % avoid_backward)
elif pos_actual == 75 and dist_cm >= avoid_limit_cm*1.25 :
avoid_backward = False
if debug : print('avoid_backward = %s' % avoid_backward)
elif pos_actual == 105 and dist_cm < avoid_limit_cm :
avoid_right = True
if debug : print('avoid_right = %s' % avoid_right)
elif pos_actual == 105 and dist_cm >= avoid_limit_cm :
avoid_right = False
if debug : print('avoid_right = %s' % avoid_right)
if debug : print('pos = %s, dist_cm = %s' % (pos_actual,dist_cm))
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
elif not run_flag:
await asyncio.sleep(0)
loop.create_task(make_decision(interval_ms=250, avoid_limit_cm=15))
Motorfunktionen:from random import getrandbits
async def moving(interval_ms):
while True:
if run_flag:
if avoid_backward :
print('avoid_backward = %s' % avoid_backward)
await backward(interval_ms*2)
if bool(getrandbits(1)) :
await right_rotate(interval_ms+getrandbits(3)*100)
await stop_all()
else:
await left_rotate(interval_ms+getrandbits(3)*100)
await stop_all()
elif avoid_left :
print('avoid_left = %s' % avoid_left)
await left_turn(interval_ms)
elif avoid_right :
print('avoid_right = %s' % avoid_right)
await right_turn(interval_ms)
else:
print('move_forward')
await forward(interval_ms)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
elif not run_flag:
await stop_all()
await asyncio.sleep(0)
loop.create_task(moving(interval_ms=1000))
Und Motorsteuerung
p5 = Pin(5, Pin.OUT)
p4 = Pin(4, Pin.OUT)
revrs_L = Pin(0, Pin.OUT, value=0)
revrs_R = Pin(2, Pin.OUT, value=0)
motor_L = PWM(p5, freq=1000, duty=0)
motor_R = PWM(p4, freq=1000, duty=0)
speed = 1023
async def stop_all():
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(0)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(0)
async def forward(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def backward(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(1)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(1)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def right_rotate(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(1)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def left_rotate(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(1)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def right_turn(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(0)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def left_turn(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(0)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
Sowie eine blinkende LED, um zu steuern, dass das Programm funktioniert:async def blink_led(led, interval_ms):
led_val = True
while True:
if run_flag:
led_val = not(led_val)
led_state = led.value(int(led_val))
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
elif not run_flag:
await asyncio.sleep(0)
loop.create_task(blink_led(syst_led, interval_ms=250))
Danach bleibt nur noch alles zu sammelnan einem Stückimport gc
import uasyncio as asyncio
from utime import sleep, sleep_us
from machine import Pin, PWM, time_pulse_us
from random import getrandbits
p5 = Pin(5, Pin.OUT)
p4 = Pin(4, Pin.OUT)
revrs_L = Pin(0, Pin.OUT, value=0)
revrs_R = Pin(2, Pin.OUT, value=0)
motor_L = PWM(p5, freq=1000, duty=0)
motor_R = PWM(p4, freq=1000, duty=0)
speed = 1023
p14 = Pin(14, Pin.OUT)
servo = PWM(p14, freq=50)
button = Pin(15, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP)
syst_led = Pin(16, Pin.OUT)
trig=Pin(12, Pin.OUT)
echo=Pin(13, Pin.IN)
run_flag = False
avoid_left = False
avoid_right = False
avoid_backward = False
pos_actual = 75
dist_cm = 50
debug = False
def callback(p):
global run_flag
run_flag = not(run_flag)
print('set run_flag', run_flag, p)
def stop_all_sync():
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(0)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(0)
async def stop_all():
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(0)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(0)
async def forward(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def backward(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(1)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(1)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def right_rotate(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(1)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def left_rotate(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(1)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def right_turn(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(0)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def left_turn(interval_ms):
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(0)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(speed)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
async def moving(interval_ms):
while True:
if run_flag:
if avoid_backward :
print('avoid_backward = %s' % avoid_backward)
await backward(interval_ms*2)
if bool(getrandbits(1)) :
await right_rotate(interval_ms+getrandbits(3)*100)
await stop_all()
else:
await left_rotate(interval_ms+getrandbits(3)*100)
await stop_all()
elif avoid_left :
print('avoid_left = %s' % avoid_left)
await left_turn(interval_ms)
elif avoid_right :
print('avoid_right = %s' % avoid_right)
await right_turn(interval_ms)
else:
print('move_forward')
await forward(interval_ms)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
elif not run_flag:
await stop_all()
await asyncio.sleep(0)
async def blink_led(led, interval_ms):
led_val = True
while True:
if run_flag:
led_val = not(led_val)
led_state = led.value(int(led_val))
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
elif not run_flag:
await asyncio.sleep(0)
async def async_measure_range():
echo_timeout_us=500*2*30
trig.off()
sleep_us(5)
trig.on()
sleep_us(10)
trig.off()
try:
pulse_time = time_pulse_us(echo, 1, echo_timeout_us)
except:
pass
dist = (pulse_time / 2) / 29.1
return dist
async def make_decision(interval_ms, avoid_limit_cm):
global avoid_left
global avoid_right
global avoid_backward
while True:
if run_flag:
if pos_actual == 45 and dist_cm < avoid_limit_cm :
avoid_left = True
if debug : print('avoid_left = %s' % avoid_left)
elif pos_actual == 45 and dist_cm >= avoid_limit_cm :
avoid_left = False
if debug : print('avoid_left = %s' % avoid_left)
elif pos_actual == 75 and dist_cm < avoid_limit_cm*1.25 :
avoid_backward = True
if debug : print('avoid_backward = %s' % avoid_backward)
elif pos_actual == 75 and dist_cm >= avoid_limit_cm*1.25 :
avoid_backward = False
if debug : print('avoid_backward = %s' % avoid_backward)
elif pos_actual == 105 and dist_cm < avoid_limit_cm :
avoid_right = True
if debug : print('avoid_right = %s' % avoid_right)
elif pos_actual == 105 and dist_cm >= avoid_limit_cm :
avoid_right = False
if debug : print('avoid_right = %s' % avoid_right)
if debug : print('pos = %s, dist_cm = %s' % (pos_actual,dist_cm))
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
elif not run_flag:
await asyncio.sleep(0)
async def radar_scan(interval_ms):
pos_list = [45,75,105,75]
global pos_actual
global dist_cm
while True:
if run_flag:
for pos in pos_list:
servo.duty(pos)
await asyncio.sleep_ms(interval_ms)
dist_cm = await async_measure_range()
pos_actual = pos
elif not run_flag:
await asyncio.sleep(0)
stop_all_sync()
print('Move sensor to initial position...')
servo.duty(75)
sleep(1)
print('Waiting for start button...')
gc.enable()
button.irq(trigger=Pin.IRQ_FALLING, handler=callback)
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.create_task(blink_led(syst_led, interval_ms=250))
loop.create_task(radar_scan(interval_ms=250))
loop.create_task(make_decision(interval_ms=250, avoid_limit_cm=15))
loop.create_task(moving(interval_ms=1000))
loop.run_forever()
und Check-in Arbeit:Ich möchte jedoch die Möglichkeit der manuellen Steuerung über die Webseite beibehalten ...Fügen Sie dazu in einer separaten Coroutine einen einfachen Webserver hinzu:async def web_page(request):
global auto_run_flag
motor_state="Stopped"
if request.find('GET /?forward') > 0:
motor_state="Going Forward"
auto_run_flag = False
forward_sync()
elif request.find('GET /?left_rotate') > 0:
motor_state="Rotate Left"
auto_run_flag = False
left_rotate_sync()
elif request.find('GET /?right_rotate') > 0:
motor_state="Rotate Right"
auto_run_flag = False
right_rotate_sync()
elif request.find('GET /?left_turn') > 0:
motor_state="Turn Left"
auto_run_flag = False
left_turn_sync()
elif request.find('GET /?right_turn') > 0:
motor_state="Turn Right"
auto_run_flag = False
right_turn_sync()
elif request.find('GET /?backward') > 0:
motor_state="Going Backward"
auto_run_flag = False
backward_sync()
elif request.find('GET /?stop') > 0:
motor_state="Stopped"
auto_run_flag = False
stop_all_sync()
elif request.find('GET /?auto') > 0:
auto_run_flag = not auto_run_flag
if auto_run_flag :
motor_state="Autopilot"
elif not auto_run_flag :
motor_state="Stopped"
stop_all_sync()
html = """<html><head><title>RoboTank WEB</title>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<link rel="icon" href="data:,"> <style>
html{font-family: Helvetica; display:inline-block; margin: 0px auto; text-align: center;}
h1{color: #0F3376; padding: 2vh;}p{font-size: 1.5rem;}
.button{display: inline-block; background-color: #33c080; border: none;
border-radius: 4px; color: white; text-decoration: none; font-size: 30px; width:100%}
.button2{background-color: #4286f4; width:30%}
.button3{background-color: #eb2b10; width:35%}
.button4{background-color: #8386f4; width:44%}
</style></head>
<body> <h1>RoboTank WEB</h1>
<p>Status : <strong>""" + motor_state + """</strong></p>
<p><a href='/?forward'><button class="button">Forward</button></a></p>
<p><a href='/?left_turn'><button class="button button2">LEFT</button></a>
<a href='/?stop'><button class="button button3">STOP</button></a>
<a href='/?right_turn'><button class="button button2">RIGHT</button></a>
<p><a href='/?backward'><button class="button">Backward</button></a></p>
<p><a href='/?left_rotate'><button class="button button4">L-rotate</button></a>
<a href='/?right_rotate'><button class="button button4">R-rotate</button></a></p>
<p><a href='/?auto'><button class="button button3">AUTO</button></a></p>
</body></html>"""
return html
async def web_handler(reader, writer):
try:
request = str(await reader.read(1024))
header = """HTTP/1.1 200 OK\nContent-Type: text/html\nConnection: close\n\n"""
response = await web_page(request)
await writer.awrite(header)
await writer.awrite(response)
await writer.aclose()
print("Finished processing request")
except Exception as e:
print(e)
async def tcp_server(host, port):
server = await asyncio.start_server(web_handler, host, port)
loop.create_task(tcp_server('0.0.0.0', 80))
Und Synchronbewegungsfunktionen zur manuellen Steuerung.def stop_all_sync():
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(0)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(0)
def backward_sync():
revrs_L.value(1)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(1)
motor_R.duty(speed)
def forward_sync():
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(speed)
def right_rotate_sync():
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(1)
motor_R.duty(speed)
def left_rotate_sync():
revrs_L.value(1)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(speed)
def right_turn_sync():
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(speed)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(0)
def left_turn_sync():
revrs_L.value(0)
motor_L.duty(0)
revrs_R.value(0)
motor_R.duty(speed)
Erscheinungsbild der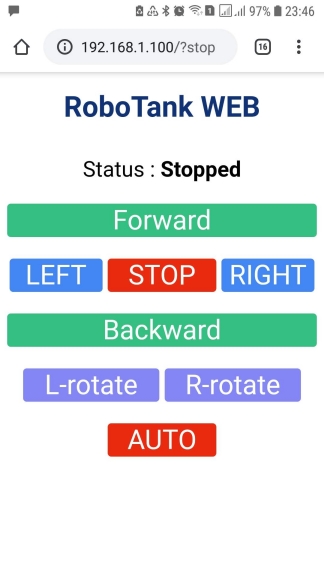 Benutzeroberfläche : Tests der endgültigen Version:Quellen finden Sie hier.Inspirationsquellen:docs.micropython.org/en/latest/library/uasyncio.htmlhabr.com/en/post/484446habr.com/en/post/337420habr.com/en/post/484472github.com/peterhinch /micropython-async/blob/master/TUTORIAL.mdgithub.com/rsc1975/micropython-hcsr04medium.com/@pgjones/an-asyncio-socket-tutorial-5e6f3308b8b0
Benutzeroberfläche : Tests der endgültigen Version:Quellen finden Sie hier.Inspirationsquellen:docs.micropython.org/en/latest/library/uasyncio.htmlhabr.com/en/post/484446habr.com/en/post/337420habr.com/en/post/484472github.com/peterhinch /micropython-async/blob/master/TUTORIAL.mdgithub.com/rsc1975/micropython-hcsr04medium.com/@pgjones/an-asyncio-socket-tutorial-5e6f3308b8b0