Jupyter Notebook ist eine beliebte Werkzeugumgebung für Datenwissenschaftler, Analysten, Ingenieure, Mathematiker, Studenten und sogar für uns - die gewöhnlichsten Wissenschaftler der experimentellen Physik.
Dieses Tool wurde entwickelt, um mit interpretierten Sprachen und einer bequemen grafischen Darstellung von Daten zu arbeiten. Lange Zeit haben wir nur mit Python- und Mathematikbibliotheken (Numpy, SciPy, Matplot usw.) darauf gerechnet. Es stellt sich jedoch heraus, dass diese Umgebung nicht so einfach ist und ein viel größeres Potenzial hat. Sehr unerwartet, aber Jupyter macht es einfach, elektronische Geräte auf Mikrocontrollern zu manipulieren. Es kann als eine Art REPL-Umgebung für MK nur ohne schwaches MicroPython und beeindruckende Unterstützung für die Peripherie des Chips dienen, was fast sofort einsatzbereit ist.
Ein kleines Intro.
Eines Tages kam ein Messgerät von einem brüderlichen Forschungsinstitut zu uns, obwohl das Gerät laut gesagt eher ein primitiver Sensor ist, dessen Daten noch verarbeitet werden müssen. Der Algorithmus ist einfach, Sie müssen nur die Anstiegszeit der Signalfront messen. Etwas wie das:
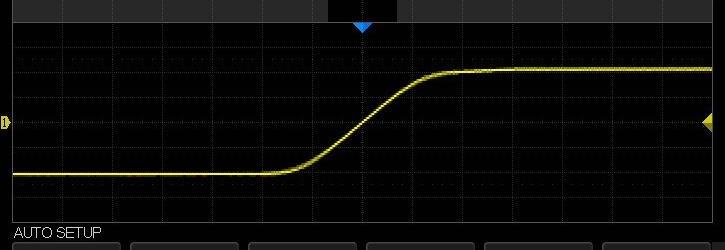
, , , .
, , .
. - USB Ethernet , , . Python.
: sample rate — 10,000 times a second , 8,000 times a second. 40,000 -50,000 times a second.
, . ( ) , . , , , x , computer vision rocket science. .
, , . , , . .
, . . Jupyter Notebook. Jupyter REPL , MicroPython. MicroPython , COM-.

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5LbgyDmRu9s
Jupyter . Jupyter Notebook , . STM32 STM8, — STMicroelectronics. Standard Peripheral Library
: STM8 - .
uint16_t ADC_GetConversionValue(ADC_TypeDef* ADCx);
. Jupyter:

ADC_GetConversionValue /++ -, Jupyter?! xeus-cling, Jupyter ++. , Windows . , Microsoft, c Ubuntu. MacOS, MacBook ...
xeus-cling /++ , - Jupyter NoteBook REMCU. , API, Standard Peripheral Library .. (header) Standard Peripheral Library, STM8LDiscovery :
#include "stm8l15x.h"
, , . .
, Jupyter , . , , :
GPIOC->DDR |= 0x80;
GPIOC->CR1 |= 0x80;
GPIOC->CR2 |= 0x80;
WavesGenerator
Jupyter . Standard Peripheral Library .
. :
- ( ) Ubuntu MacOS Anaconda, Jupyter Notebook xeus-cling xplots( )
- STM8LDiscovery — , . , c STM32.
- REMCU STM8LDiscovery, . .
STM8LDiscovery STM8L152C6 MCU name:, StdPeriph_Driver 1.4.0
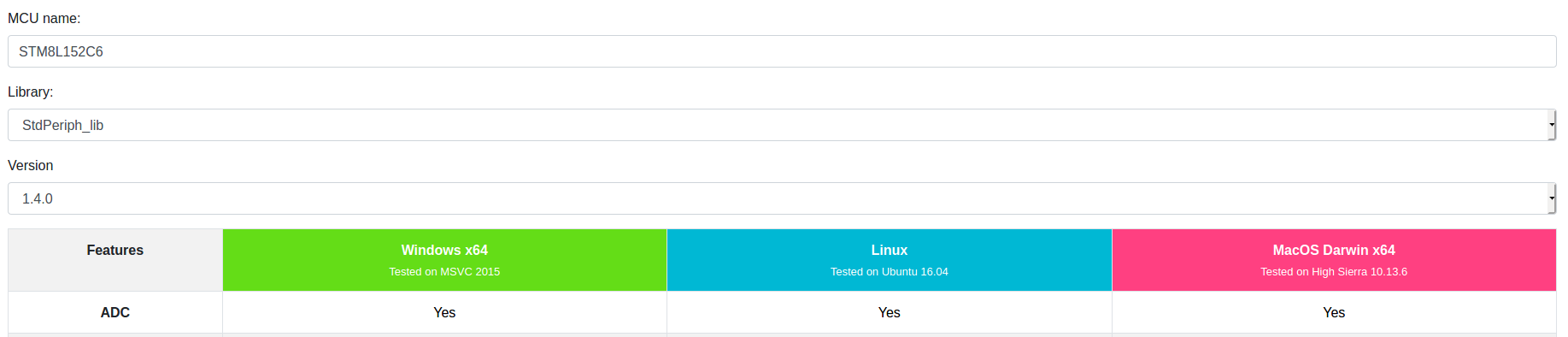
.

- OpenOCD , REMCU. , OpenOCD, Ubuntu apt install STM8LDiscovery.
- ST-Link stick — STM8LDiscovery, . STM8LDiscovery , OpenOCD.
UPD. ST-Link
ST-Link STM8LDiscovery .
OpenOCD :
./openocd -f interface/stlink-v2.cfg -f target/stm8l.cfg
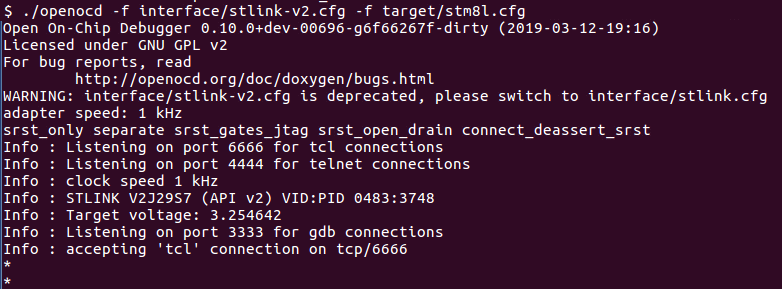
Jupyter STM8LDiscovery. Standard Peripheral Library Arduino. , - , . - , .
GPIO_Toggle — . c REMCU , GitHub REMCU. notebook:
:STM8L-Discovery GPIO example
Load REMCU shared libray
.L libremcu.so
Add path with header files
.I remcu_include
Including necessary header files. The “remcu.h” header must be always included before any MCU header files.
#include "remcu.h"
#include "stm8l15x.h"
remcu_connect2OpenOCD(debug_server_ip, default_openocd_port, timeout_sec)
remcu_resetRemoteUnit(__HALT)
Setting up microcontroller peripherals:
GPIO_Init(GPIOE, GPIO_Pin_7, GPIO_Mode_Out_PP_High_Fast)
GPIO_Init(GPIOC, GPIO_Pin_7, GPIO_Mode_Out_PP_High_Fast)
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOE, GPIO_Pin_7);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC, GPIO_Pin_7);
notebook Jupyter.
6 c REMCU. Standard Peripheral Library . STM8L-Discovery, -:
void GPIO_Init(GPIO_TypeDef* GPIOx, uint8_t GPIO_Pin, GPIO_Mode_TypeDef GPIO_Mode);
void GPIO_ResetBits(GPIO_TypeDef* GPIOx, uint8_t GPIO_Pin);
SDK, . STM8L15X_EVAL. :
GPIO_Init(GPIOE, GPIO_Pin_7, GPIO_Mode_Out_PP_High_Fast);
GPIO_Init(GPIOC, GPIO_Pin_7, GPIO_Mode_Out_PP_High_Fast);
, REMCU notebook .

OpenOCD .
notebook, - GPIO_Init :

- GPIO_ResetBits,
Arduino. :
ADC code
CLK_PeripheralClockConfig(CLK_Peripheral_ADC1, ENABLE);
ADC_Init(ADC1, ADC_ConversionMode_Continuous, ADC_Resolution_12Bit, ADC_Prescaler_2);
ADC_SamplingTimeConfig(ADC1, ADC_Group_SlowChannels, ADC_SamplingTime_384Cycles);
ADC_Cmd(ADC1, ENABLE);
ADC_SoftwareStartConv(ADC1);
ADCData = ADC_GetConversionValue(ADC1);
- STM8 40,000 sample rate . , STM8L DMA — , ( ) . Jupyter Notebook — . .
, , . , , .
DMA ADC_DMA, notebook
Xplots . PC7 STM8LDiscovery.
( ):
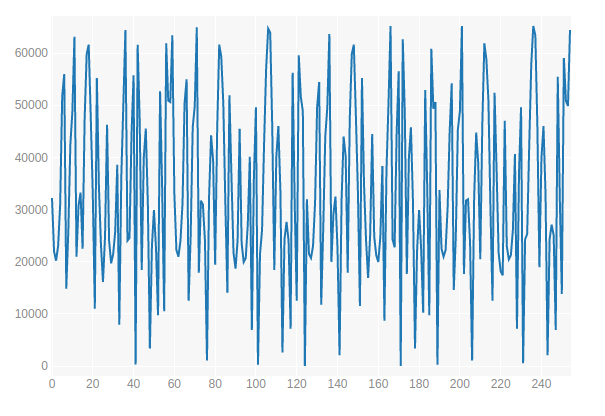
. , - , little-endian big-endian. , little-endian, STM8LDiscovery, big-endian! , . , .
#include <netinet/in.h>
for(int i = 0; i < 0xFF; i++){
uint16_t temp = adc_data[i];
temp = htons(temp);
adc_data[i] = temp;
}
line.y = adc_data;
fig
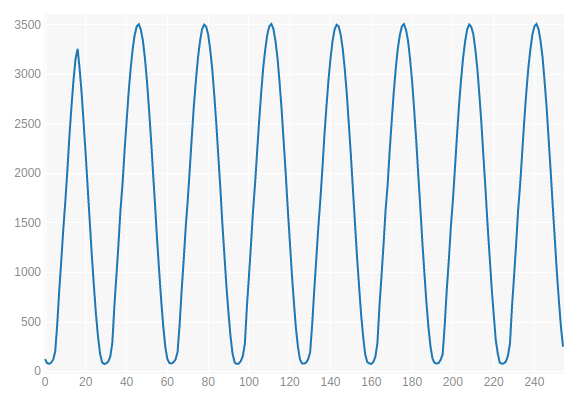
, .

- . - STM8LDiscovery . , , . , .
, , .
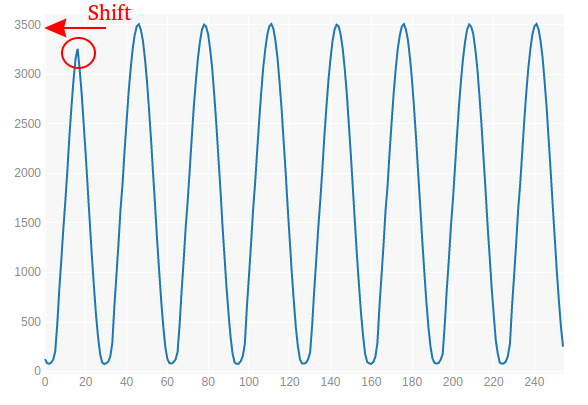
. :
int osc_data[ADC_BUFFER_SIZE] = {0};
size_t shift = DMA_GetCurrDataCounter(DMA1_Channel0);
for(int i = 0; i < ADC_BUFFER_SIZE; i++){ osc_data[i] = adc_data[i];}
shift = ADC_BUFFER_SIZE - shift;
for(size_t i = 0; i < ADC_BUFFER_SIZE; i++){
int shift_pos = (i + shift) % ADC_BUFFER_SIZE;
adc_data[i] = osc_data[shift_pos];
}
line.y = adc_data;
fig

. 8. — !
DMA STM8LDiscovery. 255 . , . 10.000 . , STM8LDiscovery — STM32F4Discovery. STM32F4 DMA 64 , . , sample rate , 255 .
, TIM1. - :
void TIM1_TimeBaseInit(uint16_t TIM1_Prescaler,
TIM1_CounterMode_TypeDef TIM1_CounterMode,
uint16_t TIM1_Period,
uint8_t TIM1_RepetitionCounter);
, . -, . . TIM1_Period, . TIM1_Period , .
, , :
SamplingTime = ADC_SamplingTime_4Cycles;
TIM1_Prescaler = 0x0;
TIM1_Period = 0x2;
TIM1_RepetitionCounter = 0;
, , 600-660 . .
, , notebook, ( DAC) STM8LDiscovery. , , DMA PF0 , , , , PC7( ) PF0( ) . notebook, :
DAC-DMA example
const uint16_t MEM_ADDRESS = ADC_BUFFER_SIZE*sizeof(adc_data.front()) + 1;
const uint8_t MEM_SIZE = 130;
uint8_t SINUS_TABLE[130] = {110,115,121,126,131,137,142,147,
152,157,161,166,171,175,179,183,187,191,195,198,201,204,207,209,
211,213,215,216,218,219,219,220,220,220,220,219,218,217,216,214,
212,210,208,205,202,199,196,193,189,185,181,177,173,168,164,159,
154,149,144,139,134,129,123,118,113,107,102,97,91,86,81,76,
71,66,61,56,52,47,43,39,35,31,27,24,21,18,15,12,
10,8,6,4,3,2,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,2,4,5,7,9,11,13,16,19,22,25,29,33,37,41,45,49,54,59,
63,68,73,78,83,89,94,99,105,110, };
CLK_PeripheralClockConfig(CLK_Peripheral_DAC, ENABLE);
CLK_PeripheralClockConfig(CLK_Peripheral_TIM4, ENABLE);
for(int i = 0 ; i < 130*sizeof(SINUS_TABLE[0]); i+=10){
remcu_store2mem(MEM_ADDRESS + i, (uint8_t*)SINUS_TABLE + i, 10);
}
/* DMA channel3 Config -----------------------------------------------------*/
#define DAC_CH1RDHRH_ADDRESS 0x5388
#define DAC_CH1RD8_ADDRESS 0x5390
#define DAC_CH1RDHLH_ADDRESS 0x538C
DMA_DeInit(DMA1_Channel3);
DMA_Init(DMA1_Channel3, MEM_ADDRESS,
DAC_CH1RD8_ADDRESS,
MEM_SIZE, DMA_DIR_MemoryToPeripheral, DMA_Mode_Circular,
DMA_MemoryIncMode_Inc, DMA_Priority_High,
DMA_MemoryDataSize_Byte
);
/* DMA1 Channel 3 enable */
DMA_Cmd(DMA1_Channel3, ENABLE);
DMA_GlobalCmd(ENABLE);
/* DAC Channel1 Config: 12bit right ----------------------------------------*/
/* DAC deinitialize */
DAC_DeInit();
/* Fill DAC Init param DAC_Trigger_T4_TRGO and DAC Channel1 Init */
DAC_Init(DAC_Channel_1, DAC_Trigger_T4_TRGO, DAC_OutputBuffer_Enable);
/* Enable DAC Channel1 */
DAC_Cmd(DAC_Channel_1, ENABLE);
/* Enable DMA for DAC Channel1 */
DAC_DMACmd(DAC_Channel_1, ENABLE);
TIM4_DeInit();
/* Time base configuration */
TIM4_TimeBaseInit(TIM4_Prescaler_1, 0x1);
/* TIM4 TRGO selection */
TIM4_SelectOutputTrigger(TIM4_TRGOSource_Update);
/* TIM4 enable counter */
TIM4_Cmd(ENABLE);
. big-endian, 8-bit.
, Standard Peripheral Library . , DAC_Noise&TriangleGenerator , -:
DAC_SetTriangleWaveAmplitude
- Standard Peripheral Library 1.4.0. , 1.4.0 REMCU.
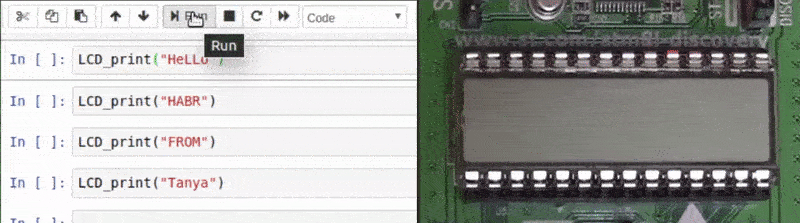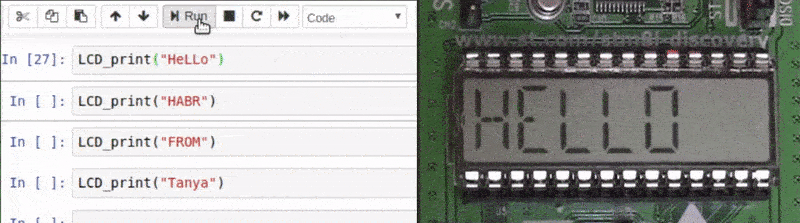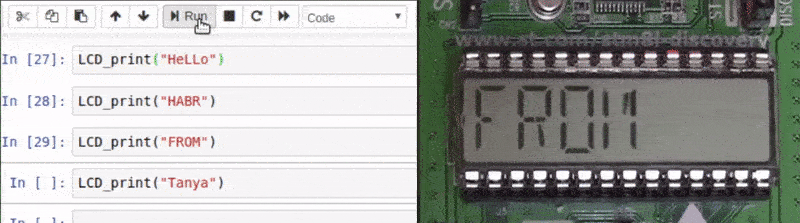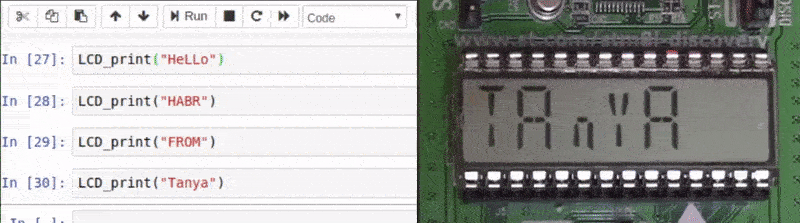
LCD , gif-. , . , 15 . STM8LDiscovery LCD . -:
void LCD_print(std::string str);
.
notebook' Github.
STM8L151 Jupyter Notebok. - , . , big-endian. , , , .
Ich halte die gesammelten Erfahrungen für erfolgreich und planen, STM8LDiscovery und das professionellere Modell STM32F4Discovery zur Automatisierung von Experimenten zu verwenden. Und jetzt sind sogar die REMCU-Bibliotheksordner für Python bereits erschienen. Daher können Sie unter Linux oder MacOS bereits auf eine virtuelle Maschine verzichten und Skripte in Ihr natives Fenstersystem schreiben.
Alle interessanten Experimente,
möge Jupyter mit dir kommen!