لذا ، في الجزء الثاني نبدأ التنفيذ. أولاً ، دعنا نقرر التكنولوجيا. أختار مكونات الويب. من السهل إعادة استخدام وتصحيح النهج المكون ، واجهة برمجة التطبيقات الأصلية.الخطوة 1 - وصف مواقف النهاية
سيتم تسمية علامة إطار العرض الافتراضي لدينا باسم منفذ العرض المخصص. لذا ، أولاً ، نصف الخصائص العامة لإطار العرض:custom-viewport {
min-height: 50vh;
max-height: 100vh;
width: 100%;
position: absolute;
bottom: 0;
overflow: hidden;
transform-origin: 50% 100% 0;
}
الموقع المحدد:custom-viewport[data-mode = "inited"] {
transform: translateY(calc(100% - 50vh));
transition: transform 1s;
}
تم فتح المركز:custom-viewport[data-mode = "opened"] {
transform: translateY(0);
transition: transform 1s;
overflow-y: scroll;
}
الموضع المحذوف:custom-viewport[data-mode = "deleted"] {
transform: translateY(100%);
transition: transform 1s;
}
الخطوة 2 - ابدأ كتابة مكون إطار العرض المخصص
class CustomViewport extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
super();
}
}
نقوم بتنفيذ أحداث السحب / السحبclass CustomViewport extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
super();
}
connectedCallback() {
this.addEventListener("touchstart", ev => {
this.firstTouch = ev.touches[0];
});
this.addEventListener("touchmove", ev => {
this.deltaY = ev.touches[0].clientY - this.firstTouch.clientY;
return this.deltaY > 0 ? this.dragDown(ev) : this.dragUp(ev);
});
}
dragUp(ev) {}
dragDown(ev) {}
}
من الناحية التخطيطية ، يمكن وصف الرمز أعلاه على النحو التالي.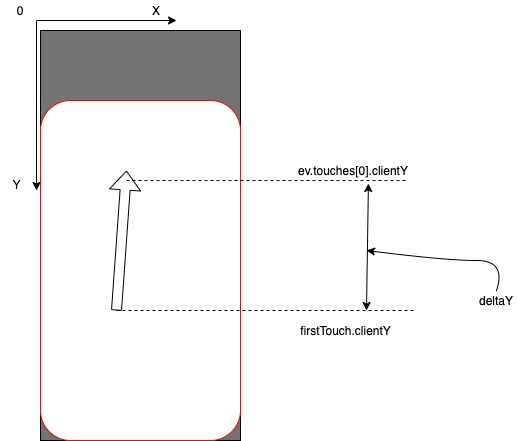 لذا ، يمكننا الآن التمييز بين أحداث السحب / السحب. الأداة المساعدة التالية هي حساب احتياطي الطاقة.
لذا ، يمكننا الآن التمييز بين أحداث السحب / السحب. الأداة المساعدة التالية هي حساب احتياطي الطاقة.class CustomViewport extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
super();
this.VIEWPORT_HEIGHT = window.innerHeight;
}
connectedCallback() {
this.addEventListener("touchstart", ev => {
this.firstTouch = ev.touches[0];
const rect = this.getBoundingClientRect();
const { height, top } = rect;
this.bottomOffsetBeforeDragging = (height + top) - this.VIEWPORT_HEIGHT;
});
this.addEventListener("touchmove", ev => {
this.deltaY = ev.touches[0].clientY - this.firstTouch.clientY;
return this.deltaY > 0 ? this.dragDown() : this.dragUp();
});
}
dragUp() {}
dragDown() {}
isBottomOffset() {
return (this.bottomOffsetBeforeDragging + this.deltaY) > 0;
}
}
هنا نتذكر أولاً مقدار احتياطي الطاقة الذي كان لدينا في اللحظة التي بدأت فيها الحركة ، ثم نضيف ببساطة دلتا إلى هذه القيمة ونرى ما إذا كان بإمكاننا التحرك لأعلى أم لا.سحب المنطق في الواقع:...
dragUp() {
if(this.isBottomOffset()) {
return;
}
this.style.transform = 'translateY(0)';
}
...
نكتب طريقة ستنقل إطار العرض:class CustomViewport extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
super();
this.VIEWPORT_HEIGHT = window.innerHeight;
}
connectedCallback() {
this.addEventListener("touchstart", ev => {
this.firstTouch = ev.touches[0];
const rect = this.getBoundingClientRect();
const { height, top } = rect;
this.bottomOffsetBeforeDragging = (height + top) - this.VIEWPORT_HEIGHT;
this.lastPosY = this.bottomOffsetBeforeDragging - this.scrollTop;
});
...
}
translateY() {
const pixels = this.deltaY + this.lastPosY;
this.style.transform = `translateY(${pixels}px)`;
this.style.transition = 'none';
}
...
}
دعونا نفحص بمزيد من التفصيل ماهية هذا الوضع. وآخر طريقة حسابه. إذا كتبنا في css convert: translateY (calc (100٪ - 50vh)) ؛ حيث 100٪ هو ارتفاع إطار العرض الافتراضي نفسه ، و 50 vh هو نصف ارتفاع إطار العرض الحقيقي ، وهذا يناسب تمامًا الوصف الثابت للموضع ، فمن الأنسب العمل بقيم مطلقة لحساب الحركة في الديناميكيات ، نحن نقوم بهذه التحولات هنا.لذا ، هذا POSY هو مقدار حركة إطار العرض الافتراضي بالبكسل في بداية الحركة ، وعلينا أن نضيف هذا deltaY ونحصل على موضع إطار عرض جديد.بما أننا حددنا الخصائص:bottom: 0;
transform-origin: 50% 100% 0;
ثم يأخذ نظام الإحداثيات الخاص بنا لحساب حركة إطار العرض الشكل الذي نصفه السحب:
نصفه السحب:...
dragDown() {
if(this.lastPosY < 0) {
return;
}
this.translateY();
}
...
حدث السحب في النهاية:class CustomViewport extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
super();
this.VIEWPORT_HEIGHT = window.innerHeight;
}
connectedCallback() {
this.addEventListener("touchend", ev => {
const { mode: currentMode } = this.dataset;
this.style = null;
if (Math.abs(deltaY) < 10) {
this.dataset.mode = currentMode;
return;
}
if (deltaY > 0) {
if (currentMode === "inited") {
this.dataset.mode = "deleted";
return;
}
this.dataset.mode = "inited";
return;
}
this.dataset.mode = "opened";
});
...
في السطر إذا (Math.abs (deltaY) <10) نشير إلى أنه إذا قمت بنقل أقل من 10 بكسل ، فاترك الموضع الحالي.نتيجة لذلك ، يجب أن نحصل على مكون مثل
class CustomViewport extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
super();
this.VIEWPORT_HEIGHT = window.innerHeight;
}
connectedCallback() {
this.addEventListener("touchstart", ev => {
this.firstTouch = ev.touches[0];
const rect = this.getBoundingClientRect();
const { height, top } = rect;
this.bottomOffsetBeforeDragging = (height + top) - this.VIEWPORT_HEIGHT;
this.lastPosY = this.bottomOffsetBeforeDragging - this.scrollTop;
});
this.addEventListener("touchmove", ev => {
this.deltaY = ev.touches[0].clientY - this.firstTouch.clientY;
return this.deltaY > 0 ? this.dragDown() : this.dragUp();
});
this.addEventListener("touchend", ev => {
const { mode: currentMode } = this.dataset;
this.style = null;
if (Math.abs(this.deltaY) < 10) {
this.dataset.mode = currentMode;
return;
}
if (this.deltaY > 0) {
if (currentMode === "inited") {
this.dataset.mode = "deleted";
return;
}
this.dataset.mode = "inited";
return;
}
this.dataset.mode = "opened";
});
}
dragUp() {
if(this.isBottomOffset()) {
this.translateY();
return;
}
this.style.transform = 'translateY(0)';
}
dragDown() {
if(this.lastPosY < 0) {
return;
}
this.translateY();
}
translateY() {
const pixels = this.deltaY + this.lastPosY;
this.style.transform = `translateY(${pixels}px)`;
this.style.transition = 'none';
}
isBottomOffset() {
return (this.bottomOffsetBeforeDragging + this.deltaY) > 0;
}
}
customElements.define('custom-viewport', CustomViewport);
هذا الرمز ليس تطبيقًا كاملاً ، ولكنه مجرد نموذج أولي. دراسة أكثر تفصيلاً عن التمرير ، والتنقيب ، وأي تحسينات أخرى ، لمس اللمس - تُرك للقارئ.