مرحبا يا هابر! أقدم لكم ترجمة مقالة "Web2Text: إزالة هيكلية عميق" من قبل فريق من المؤلفين Thijs Vogels و Octavian-Eugen Ganea و Carsten Eickhof.
تعتبر صفحات الويب مصدرًا قيمًا للمعلومات للعديد من مهام معالجة اللغات واسترجاع المعلومات الطبيعية. يعد استخراج المحتوى الأساسي بشكل فعال من هذه المستندات أمرًا بالغ الأهمية لأداء التطبيقات المشتقة. لحل هذه المشكلة ، نقدم نموذجًا جديدًا يقوم بتصنيف كتل النص وتسميتها في الصفحة على HTMLأنها كتل قوالب ، أو كتل تحتوي على محتوى رئيسي. تستخدم طريقتنا نموذج Hidden Markov على رأس الإمكانات التي تم الحصول عليها من خصائص نموذج الكائن HTMLللوثيقة ( Document Object Model, DOM) باستخدام الشبكات العصبية التلافيفية ( Convolutional Neural Network, CNN). تعمل الطريقة المقترحة على تحسين الأداء لاستخراج البيانات النصية من صفحات الويب.
1 المقدمة
تعتمد الأساليب الحديثة لمعالجة اللغات الطبيعية واسترجاع المعلومات بشكل كبير على مجموعات كبيرة من النصوص. شبكة الويب العالمية هي مصدر لا ينضب من المحتوى لمثل هذه التطبيقات. ومع ذلك ، فإن المشكلة الشائعة هي أن صفحات الويب لا تتضمن المحتوى الرئيسي (النص) فحسب ، بل أيضًا الإعلانات وقوائم الارتباطات التشعبية والتنقل ومعاينات المقالات الأخرى واللافتات وما إلى ذلك. غالبًا ما يكون لمحتوى القالب هذا تأثير سلبي على أداء تطبيق مشتق [15،24]. تُعرف مهمة فصل النص الرئيسي في صفحة الويب عن باقي المحتوى (النموذج) في الأدبيات باسم "حذف قالب قياسي" أو "تقسيم صفحة الويب" أو "استخراج المحتوى". تستخدم الطرق الشائعة المعروفة لهذه المشكلة الخوارزميات المستندة إلى القواعد أو التعلم الآلي.تقسم أكثر الأساليب نجاحًا أولاً صفحة الويب المدخلة إلى كتل نصية ، ثم ثنائية{1, 0}تصنيف كل قالب على أنه المحتوى أو القالب الرئيسي. في هذه المقالة ، نقترح نموذج ماركوف المخفي على رأس الإمكانات العصبية لمهمة إزالة الأنماط. نحن نستخدم قدرة الشبكات العصبية التلافيفية على دراسة الاحتمالات المزدوجة والاقتران في كتل بناءً على مجموعات معقدة غير خطية من العلامات المستندة إلى DOM. أثناء التنبؤ ، نجد أكثر تسمية كتلة محتملة {1, 0}، مما يزيد من الاحتمال المشترك لتسلسل الملصقات باستخدام خوارزمية Viterbi [23]. يتم توضيح فعالية طريقتنا على مجموعات قياسية من البيانات المقارنة.
. 2 . 3 , . 4 -.
2.
HTML- [7] Body Text Extractor (BTE). BTE , , HTML- -. , BTE , . , : (1) HTML, , , (2) , -.
DOM, HTML [11,19,6]. , , <table>, .
DOM . . [24] [22]. , -, -, -. .
. [10] , . HTML , , , . , , (), , (). DOM [4,21]. . [3] DOM, , . . [21] / , DOM .
«», . FIASCO . [2] (SVM) HTML- , DOM , . . [17] SVM . . [20] , , . , . CleanEval [1].
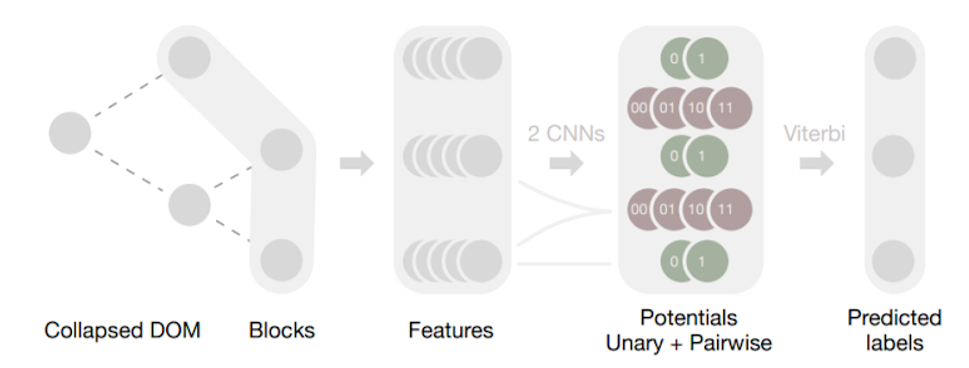
. 1. Web2Text. DOM (Collapsed DOM) - , . DOM. , , : . . , , , .
, DOM. , , . , - , .
3.
— - (- ) [1]. . 1.
3.1.
, - (X) HTML-. ( DOM) Jsoup [12].

. 2. DOM. : HTML, — DOM, — DOM.
DOM, i) , , ii) , , : , <br>, <checkbox>, <head>, <hr>, <iframe>, <img>, <input>. DOM. DOM- . 2 DOM, (<ul>), DOM. (, « »), . Collapsed () DOM (CDOM).
3.2.
. - , , . - , : i) HTML, ii) DOM, iii) DOM . DOM, . , , HTML. , DOM- ( #text) . , , . , Web2Text , , — .
3.3.
— , , , . , CDOM . .
. , CDOM, , CDOM. 128 , , « - <p>», « », « », « », « - » .. , , .
. 25 . . , , , 2, 3, 4 > 4. , HTML-, ..
3.4. (Convolutional Neural Network, CNN)
, , . , . pi (li = 1), pi (li = 0) , li i , . . pi, i + 1 (li = 1, li + 1 = 1), pi, i + 1 (li = 1, li + 1 = 0), pi, i + 1 (li = 0, li + 1 = 1) pi, i + 1 (li = 0, li + 1 = 0) — . .
CNN 5 , ReLU , (50, 50, 50, 10, 2) (50, 50, 50, 10, 4) . 1 (1, 1, 3, 3, 3) . CNN , , , . CNN , , , . , , . 2 , softmax. 4 , . , i . (dropout) 0,2 L2 10-4.
-:

l∗i — i, θunary — , n — .
-:

θpairwise — .
3.5.
- . (b0, b1, ..., bn) (l0, l1, ..., ln) ∈ {0, 1}n :

λ — . λ = 0,1 . [23], CNN.
4.
. Web2Text - . , . Web2Text .
4.1.
CleanEval 2007 [1] . 188 -. (60 ) (676 ). (55 ) (5 ). 10000 , , . CleanEval : (531 ), (58 ) (148 ).
. , ( CleanEval) . “- — ” ( ). , , . (, [20]) . (, ) (-, ). .
-, 10 . - ( ). , - , « ». -. , , , , 2/3 .
4.2.
[14] 10–3 5000 . - 128 - 9 . , . , .
4.3.
Web2Text , . BTE [7] Unfluff [8] . [17,16] — , , (. 1). CRF [20] CleanEval. (Conditional Random Field, CRF) , . , 4.1, CRF - . , , , , CleanEval. CleanEval, , .
. CRF [20] 9 705 . , CNN 17 960 , CNN 12 870 . 30 830. , .
4.4.
1 . , . , Web2Text (Accuracy), Recall F1 , CleanEval. , , , 3.2. , , Web2Text CNN, .

1. - CleanEval. : (55 — , 5 — , 676 — ) (531 — , 58 — , 148 — ). , .
. Web2Text 54 -; 35 DOM , 19 . Macbook Intel Core i5 2,8 .
4.5.
, , , . HTML, .
- ClueWeb12. . CW12-A 733M - (27,3 ) CW12-B 52M (1,95 ). Indri. 50 TREC Web Track 2013 [5].

2. . (*) HTML. (†) , .
2 , -. HTML . , , †. , , CW12-A, , , CW12-B. - . , (QL) , (RM). , . , (BTE, article-ext, large-ext, Unfluff) , . (CRF, Web2Text) . , Web2Text 0,05. , Web2Text CleanEval, 4.1.
5.
Web2Text -. , CRF [9], , DOM . CleanEval . , , , .
6.
, - .
, .
- Marco Baroni, Francis Chantree, Adam Kilgarriff, and Serge Sharoff. CleanEval: a competition for cleaning web pages. In LREC, 2008.
- Daniel Bauer, Judith Degen, Xiaoye Deng, Priska Herger, Jan Gasthaus, Eugenie Giesbrecht, Lina Jansen, Christin Kalina, Thorben Kräger, Robert Märtin, Martin Schmidt, Simon Scholler, Johannes Steger, Egon Stemle, and Stefan Evert. FIASCO: Filtering the internet by automatic subtree classification, osnabruck. In Building and Exploring Web Corpora: Proceedings of the 3rd Web as Corpus Workshop, incorporating CleanEval, volume 4, pages 111–121, 2007.
- Deepayan Chakrabarti, Ravi Kumar, and Kunal Punera. Page-level template detection via isotonic smoothing. In Proceedings of the 16th international conference on World Wide Web, pages 61–70. ACM, 2007.
- Deepayan Chakrabarti, Ravi Kumar, and Kunal Punera. A graph-theoretic approach to webpage segmentation. In Proceedings of the 17th international conference on World Wide Web, pages 377–386. ACM, 2008.
- Kevyn Collins-Thompson, Paul Bennett, Fernando Diaz, Charlie Clarke, and Ellen Voorhees. Overview of the TREC 2013 web track. In Proceedings of the 22nd Text Retrieval Conference (TREC’13), 2013.
- Sandip Debnath, Prasenjit Mitra, Nirmal Pal, and C Lee Giles. Automatic identification of informative sections of web pages. IEEE transactions on knowledge and data engineering, 17(9):1233–1246, 2005.
- Aidan Finn, Nicholas Kushmerick, and Barry Smyth. Fact or fiction: Content classification for digital libraries. Unrefereed, 2001.
- Adam Geitgey. Unfluff – an automatic web page content extractor for node.js!, 2014.
- John Gibson, Ben Wellner, and Susan Lubar. Adaptive web-page content identification. In Proceedings of the 9th annual ACM international workshop on Web information and data management, pages 105–112. ACM, 2007.
- Thomas Gottron. Content code blurring: A new approach to content extraction. In Database and Expert Systems Application, 2008. DEXA’08. 19th International Workshop on, pages 29–33. IEEE, 2008.
- Suhit Gupta, Gail Kaiser, David Neistadt, and Peter Grimm. DOM-based content extraction of HTML documents. In Proceedings of the 12th international conference on World Wide Web, pages 207–214. ACM, 2003.
- Jonathan Hedley. Jsoup HTML parser, 2009.
- Rong Jin, Alex G Hauptmann, and ChengXiang Zhai. Language model for information retrieval. In Proceedings of the 25th annual international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in information retrieval, pages 42–48. ACM, 2002.
- Diederik Kingma and Jimmy Ba. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980, 2014.
- Christian Kohlschütter. A densitometric analysis of web template content. In Proceedings of the 18th international conference on World wide web, pages 1165– 1166. ACM, 2009.
- Christian Kohlschütter et al. Boilerpipe – boilerplate removal and fulltext extraction from HTML pages. Google Code, 2010.
- Christian Kohlschütter, Peter Fankhauser, and Wolfgang Nejdl. Boilerplate detection using shallow text features. In Proceedings of the third ACM international conference on Web search and data mining, pages 441–450. ACM, 2010.
- Victor Lavrenko and W Bruce Croft. Relevance based language models. In Proceedings of the 24th annual international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in information retrieval, pages 120–127. ACM, 2001.
- Shian-Hua Lin and Jan-Ming Ho. Discovering informative content blocks from web documents. In Proceedings of the eighth ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, pages 588–593. ACM, 2002.
- Miroslav Spousta, Michal Marek, and Pavel Pecina. Victor: the web-page cleaning tool. In 4th Web as Corpus Workshop (WAC4)-Can we beat Google, pages 12–17, 2008.
- Fei Sun, Dandan Song, and Lejian Liao. Dom based content extraction via text density. In Proceedings of the 34th international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in Information Retrieval, pages 245–254. ACM, 2011.
- Karane Vieira, Altigran S Da Silva, Nick Pinto, Edleno S De Moura, Joao Cavalcanti, and Juliana Freire. A fast and robust method for web page template detection and removal. In Proceedings of the 15th ACM international conference on Information and knowledge management, pages 258–267. ACM, 2006.
- Andrew J Viterbi. Error bounds for convolutional codes and an asymptotically optimum decoding algorithm. In The Foundations Of The Digital Wireless World: Selected Works of AJ Viterbi, pages 41–50. World Scientific, 2010.
- Lan Yi, Bing Liu, and Xiaoli Li. Eliminating noisy information in web pages for data mining. In Proceedings of the ninth ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, pages 296–305. ACM, 2003.